
(a)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
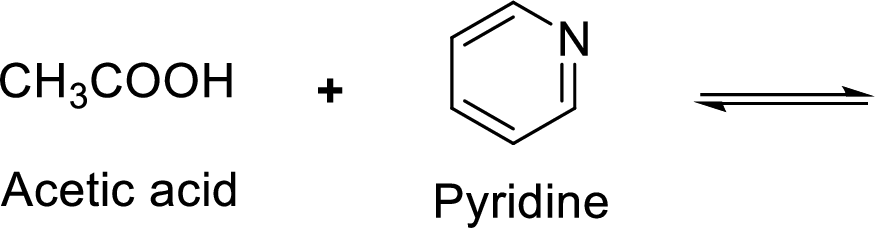
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
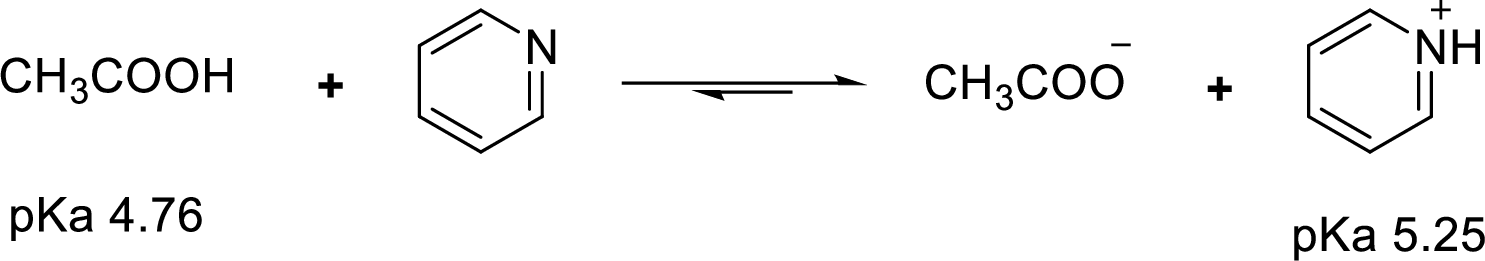
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, acetate anion is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the right.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
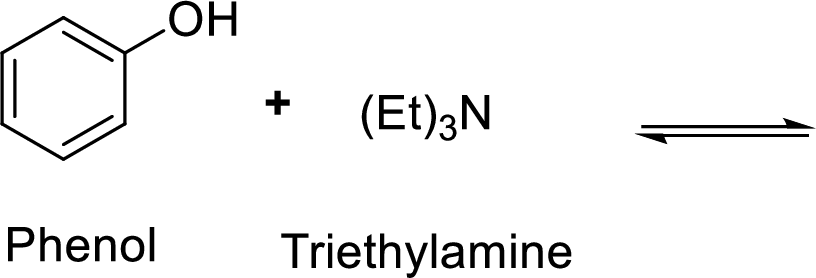
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
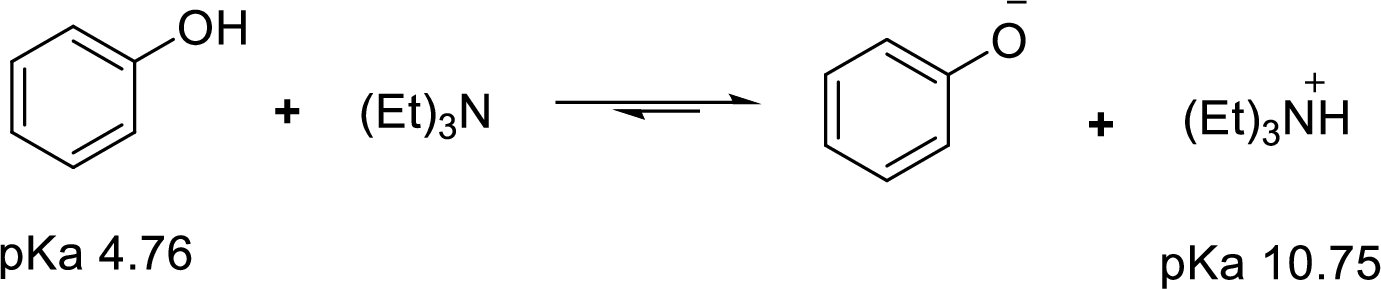
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, triethylammonium cation is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the right.
(c)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, phenyl acetylene is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the left.
(d)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here,
(e)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
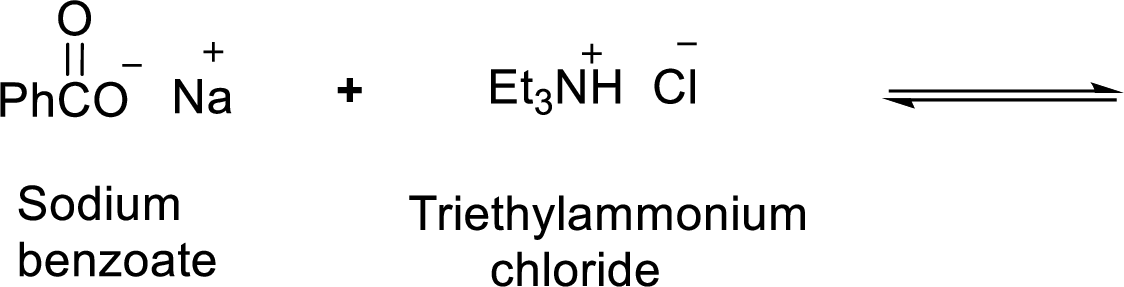
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
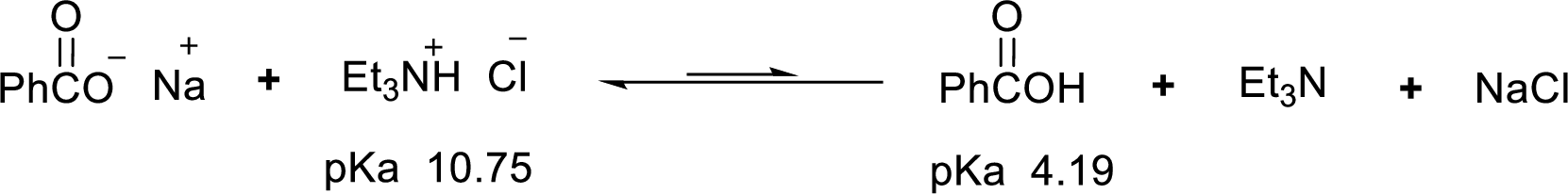
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, triethylammonium chloride is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the left.
(f)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
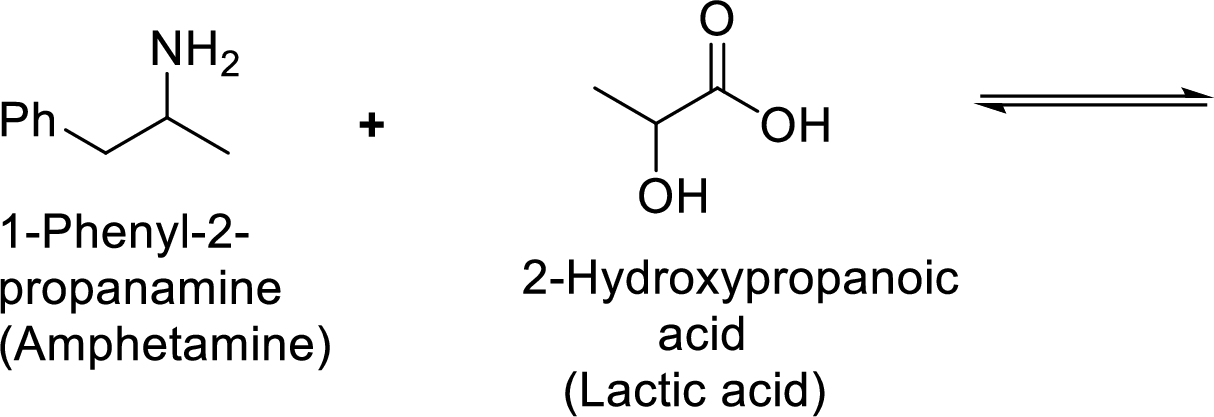
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
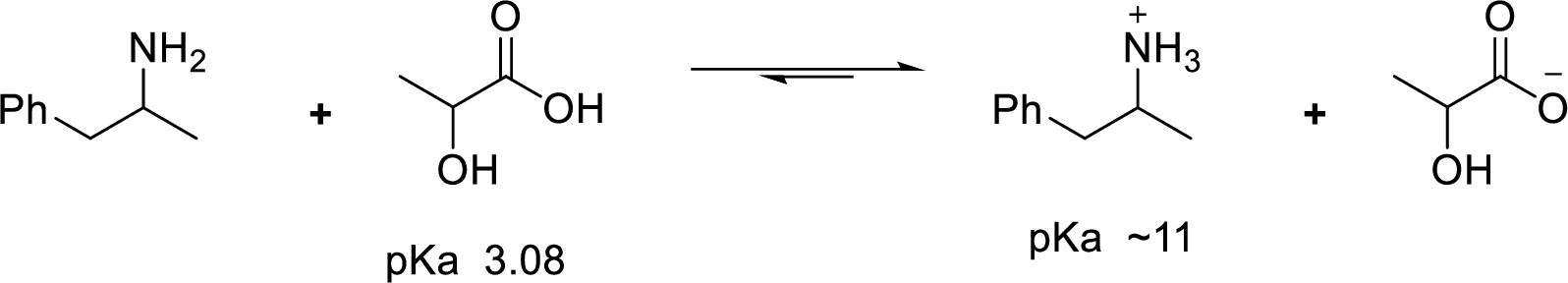
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, 1-phenyl-2-propanammonium ion is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the right.
(g)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
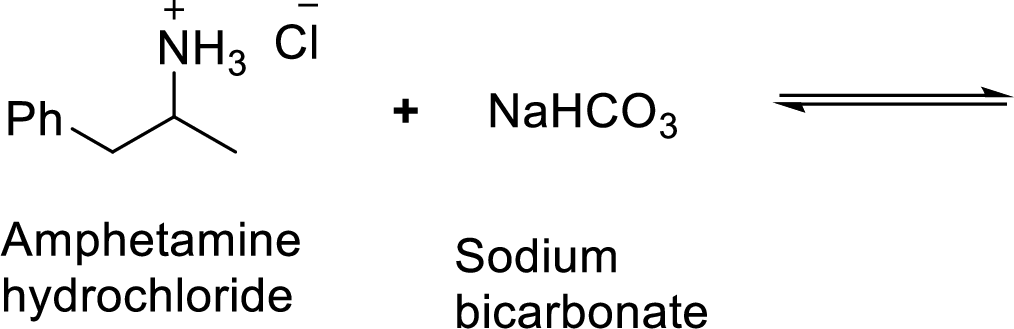
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
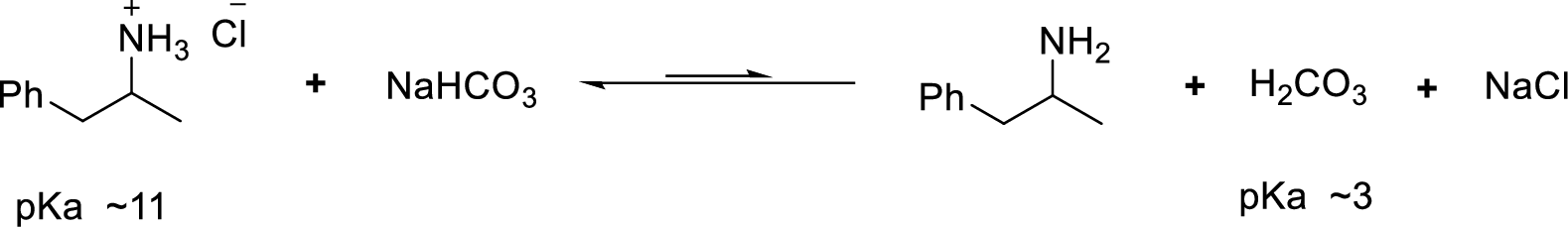
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, amphetamine hydrochloride is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the left.
(h)
Interpretation:
Given acid-base reaction has to be completed and the direction of equilibrium has to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base.
If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
Mixture of acid and base undergoes equilibrium reaction and it’s
Weak acids are more stable and less reactive, so equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction.
Lesser the
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is shown below,
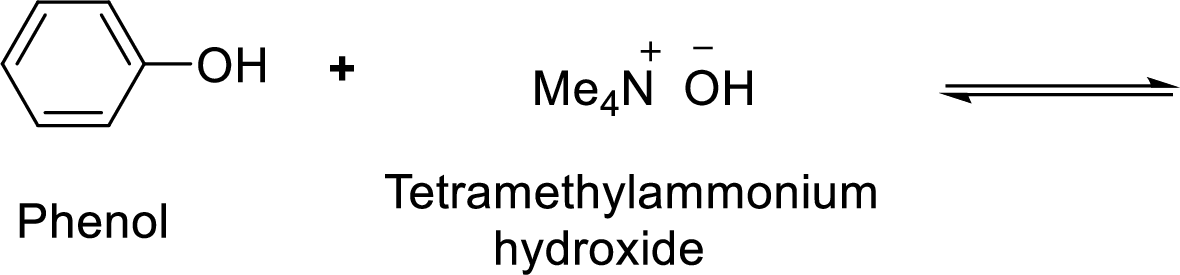
According to the explanations by Bronsted-Lowry, if a species loses a proton then it is an acid whereas if a species receives one proton, then it is base. If a base receives one proton, then the formed species is a conjugate acid whereas an acid lose one proton, then the formed species is a conjugated base.
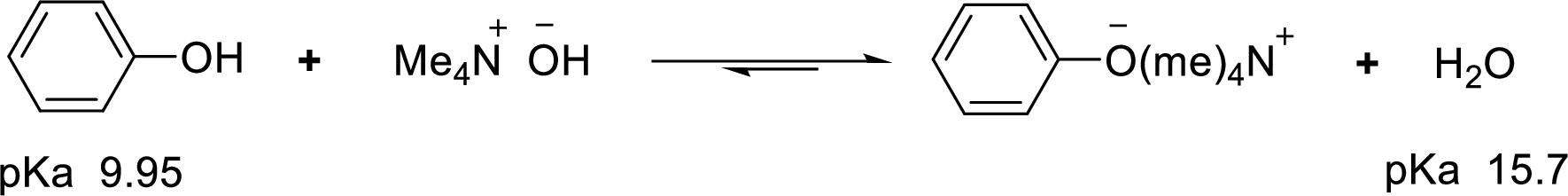
Weak acid is more stable, equilibrium follows the direction of formation weak acids in a reaction. Long arrow indicates the direction where equilibrium favors.
Here, water is the weaker acid and equilibrium lies towards the right.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM PKG W/OWL >IC< 2017
- Explain the observed difference in the pKa values of the conjugate acids of amines A and B.arrow_forwardexplain in great detail why the pKa values are what they are and compare them among the three compounds. The conjugate acids that are protonated are drawn in red for each compound. Which one based on the pKa is most acidic and what does that tell you about how basic their lone pairs are?arrow_forwardUsing pKa Values to Determine Relative Acidity and Basicity Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, and then rank their conjugate bases in order of increasing basicity.arrow_forward
- A dibasic organic acid has a neutralization equivalent of 45+1. Deduce the structure of this organic acidarrow_forwardThe hydrolysis of the ester shown here is catalyzed by morpholine. Explain how morpholine catalyzes the reaction. (Hint: The pKa of the conjugateacid of morpholine is 9.3, so morpholine is too weak a base to function as a base catalyst.)arrow_forwardThe pKa values of a few ortho-, meta-, and para-substituted benzoic acids are shown below: The relative pKa values depend on the substituent. For chloro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the para isomer is the least acidic; for nitro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the meta isomer is the least acidic; and for amino-substituted benzoic acids, the meta isomer is the most acidic and the ortho isomer is the least acidic. Explain these relative acidities. a. Cl: ortho > meta > para b. NO2: ortho > para > meta c. NH2: meta > para > orthoarrow_forward
- The pKa values of a few ortho-, meta-, and para-substituted benzoic acids are shown below: The relative pKa values depend on the substituent. For chloro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the para isomer is the least acidic; for nitro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the meta isomer is the least acidic; and for amino-substituted benzoic acids, the meta isomer is the most acidic and the ortho isomer is the least acidic. Explain these relative acidities.a. Cl: ortho 7 meta 7 para b. NO2: ortho 7 para 7 meta c. NH2: meta 7 para 7 orthoarrow_forwardArrange the compounds in each set in order of increasing base strength. consult Table 4.1 for pKa values of the conjugate acid of each base.arrow_forwardArrange the following amines in order of increasing basicity. For example, an answer of 1234 would indicate that you think 1 is least basic and 4 is most basicarrow_forward
- Show how acid derivatives hydrolyze to carboxylic acids under either acidic or basicconditions. Explain why some acid derivatives (amides, for example) require muchstronger conditions for hydrolysis than other derivatives.arrow_forwardThe side chain of cysteine is weakly acidic. Suppose in a protein, the side chain of a cysteine residue is surrounded by the side chains of several isoleucine residues. Would this make the side chain of the cysteine residue more acidic or less acidic? Please explain your answer.arrow_forwardRank each of the following sets of nitrogen bases in terms of basicity and explain your answerarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





