
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The rearrangement in which acyl azides
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
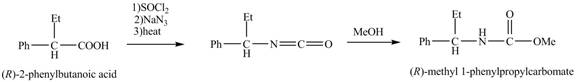
Explanation of Solution
The separation of enantiomers occurs in three steps.
In the first step, the two enantiomers,
The separation of the two enantiomers is shown below.
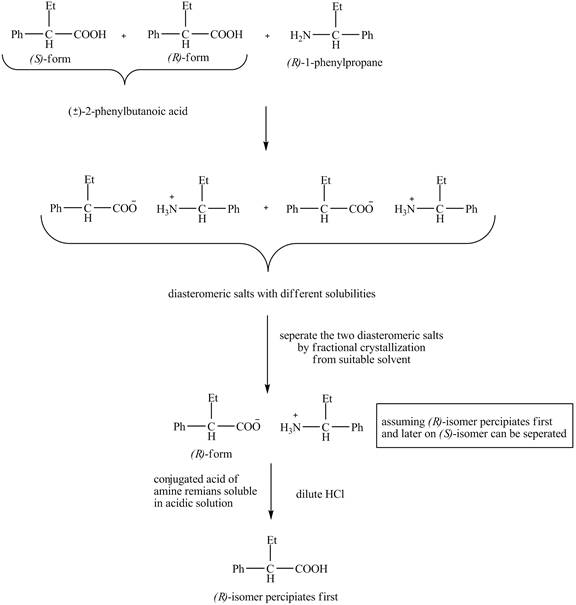
Figure 1
The formation of the given product follows the curtius rearrangement. The reaction follows a concerted mechanism, a reaction in which the bond formation and bond dissociation occurs in a single step.
The
The reaction for the formation of
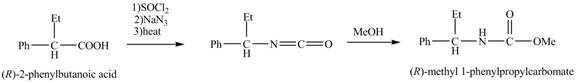
Figure 2
The desired product,
(b)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
An ester is formed by the reaction of carboxylic with alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction is known as Esterification.
Ester is the functional group which is formed from the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. Esters end with a suffix,
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
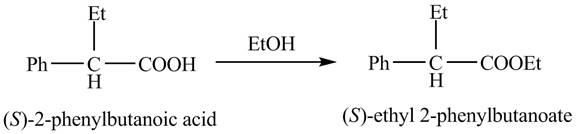
Explanation of Solution
The
The reaction of the formation of
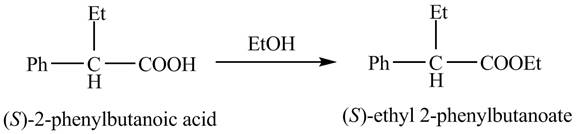
Figure 3
The formation of
(c)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann rearrangement reaction is the conversion reaction of the primary amide to a primary amine with the loss of one carbon chain. The reaction requires basic conditions. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with bromine forms sodium hypobromite as an intermediate in situ.
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
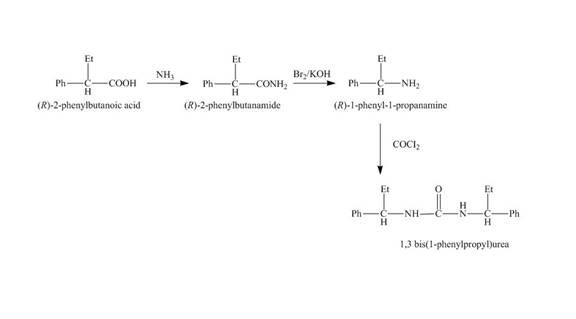
Explanation of Solution
The isomer,
The reaction of the formation of
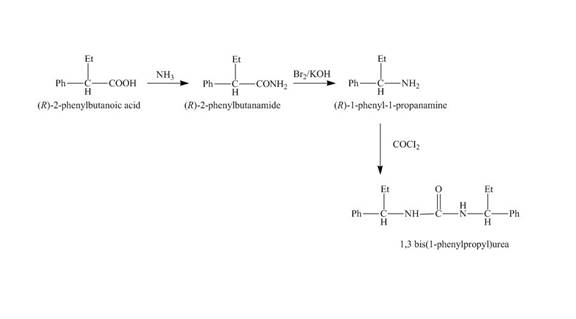
Figure 4
The formation of
(d)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann rearrangement reaction is the conversion reaction of the primary amide to a primary amine with the loss of one carbon chain. The reaction requires basic conditions. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with bromine forms sodium hypobromite as an intermediate in situ.
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The isomer,
The reaction of the formation of

Figure 5
The formation of
(e)
Interpretation:
The steps required to obtain the pure samples of the given compound from the starting material are to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann rearrangement reaction is the conversion reaction of the primary amide to a primary amine with the loss of one carbon chain. The reaction requires basic conditions. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with bromine forms sodium hypobromite as an intermediate in situ.
Answer to Problem 23.60AP
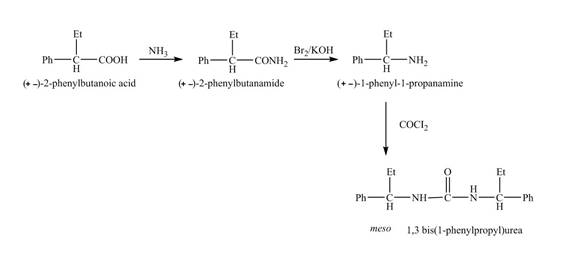
The reaction route for the synthesis of the given product is shown below.
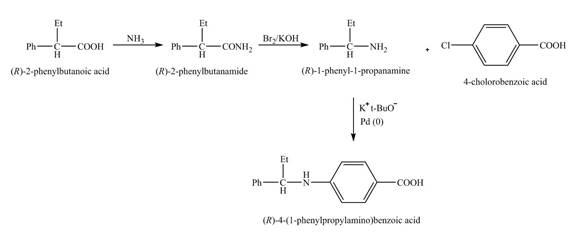
Explanation of Solution
The isomer,
The reaction of the formation of
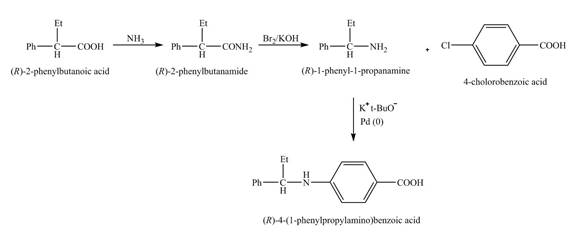
Figure 6
The formation of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- We are currently working with diastereomeric products of acid-base reactions in my organic chemistry class and while I understand the basics of the creation of selectively soluble salt products, drawing the reactions has always been difficult. Our prelab asks us to "draw the expected diasteromeric products from the reaction of racemic phenylsuccinic acid with excess (s)-methylbenzylamine and label the chiral centers" I would really appreciate some help with this!arrow_forwardBriefly explain why, under aqueous acidic conditions, furan readily undergoes a reversible ring opening reaction to give succinaldehyde.arrow_forwardBringing together your knowledge of the reaction chemistry of substituted benzenes, suggest a preparative route for conversion of compound A to compound B shown belowarrow_forward
- Provide a mechanism which explains the following conversions. Include all intermediates (where appropriate) and watch your arrows and chargesarrow_forwardOutline a synthesis of the following compounds (A-C) from acetoacetic ester OR malonic ester. Show the starting material and reagents. If the synthesis is not possible, indicate why. A) hept-6-en-2-one B) 2-benzylheptanoic acid C) 3-isobutyl-2-heptanonearrow_forwardDraw the products formed by the following acid-base reaction without consideration of the equilibrium position: You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You should include all products. Include counter-ions, e.g., Na+, I-, in your submission, but draw them in their own separate sketcher. Separate structures with + signs from the drop-down menu.arrow_forward
- The reactions given in the synthesis scheme showing the synthesis of D, a phremone of the moth .write the explicit structures of programs A,B,C and D.arrow_forwardCompound A produce compound D while undergo Friedel Crafts Alkylation. Compound D is then oxidized and produce compound E (C11H12O3) as a major product.What are the possible structural formula of compound D and E?arrow_forwardSuggest reactivity of compound A, B and C in increasing order of E2 reactionarrow_forward
- Using 1-bromobutane and any organometallic reagent among those seen in class, suggest the synthesis for each of the following compounds: A. 1-phenyl-1-hexanol b. 1-butylciclobutanolarrow_forwardThe sex attractant of the female housefly (Musca domestica) is called muscalure, and its structure follows. Outline a synthesis of muscalure, using the Wittig reaction. Will your synthesis lead to the required cis isomer?arrow_forward(a) How many Stereoisomers are possible for 9,10- dibromoexadecanoic acid?(b) Addition of bromine to palmitoleic acid primarily yields a set of enantiomers, (±) -three-9,10-dibromohexadecanoic acid. The addition of bromine is an anti-addition to the double bond (ie, it appears to occur through the intermediary of the bromonium ion). Taking into account the stereochemistry of the cis double bond of palmitoleic acid and the stereochemistry of adding bromine,Write a three-dimensional structure for (±) -three-9,10-dibromohexadecanoic acid!arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
