
(a)
Interpretation:
When the given compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with the formula
Concept introduction:
The Diels-Alder reaction is reversible at high temperature, and this process is called a retro Diels-Alder reaction. The mechanism for this reaction is as the reverse of a Diels-Alder mechanism i.e. the entire six-membered ring is break-down into the corresponding diene and the dienophile. The aromatic proton given signal range from
Answer to Problem 24.82P
The structure of
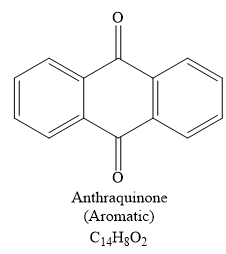
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is
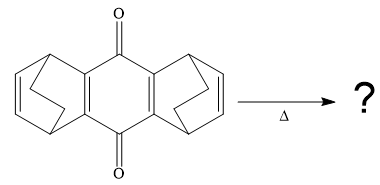
So when this compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with formula
The signal in
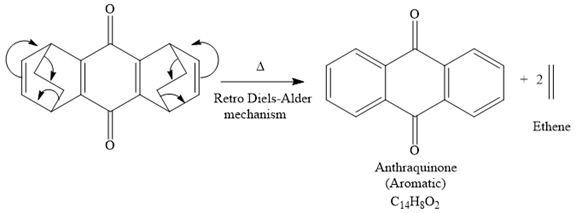
The product of the retro Diels-Alder reaction is also aromatic and matched with the given spectra and also ethene gas is evolved. so the above product is the correct one.
When the given compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with the formula
(b)
Interpretation:
When the given compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with the formula
Concept introduction:
The Diels-Alder reaction is reversible at high temperature and this process is called a retro Diels-Alder reaction. The mechanism for this reaction is as the reverse of a Diels-Alder mechanism i.e. the entire six-membered ring is broken down into the corresponding diene and the dienophile. The aromatic proton given signal range from
Answer to Problem 24.82P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
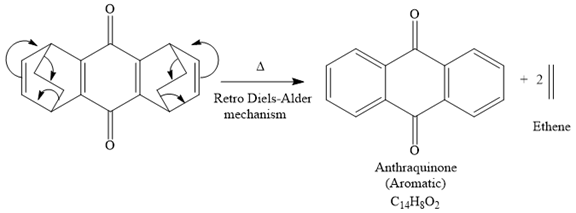
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is

So when this compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and product with formula
The signal in
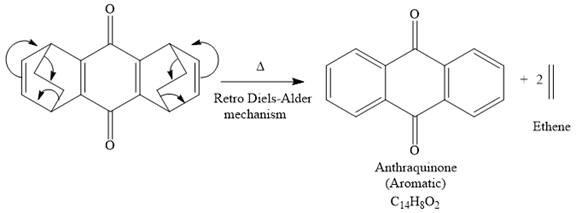
The product of the retro Diels-Alder reaction is also aromatic and matched with the given spectra and also ethene gas is evolved. So the above product and the mechanism (retro Diels-Alder mechanism) is the correct one.
When the given compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with the formula
(c)
Interpretation:
When the given compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with the formula
Concept introduction:
The Diels-Alder reaction is reversible at high temperature and this process is called a retro Diels-Alder reaction. The mechanism for this reaction is as the reverse of a Diels-Alder mechanism i.e. the entire six-membered ring is break-down into the corresponding diene and the dienophile. The aromatic proton given signal range from
Answer to Problem 24.82P
The main driving force that favours the product in the given reaction is the formation of a more stable aromatic compound.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
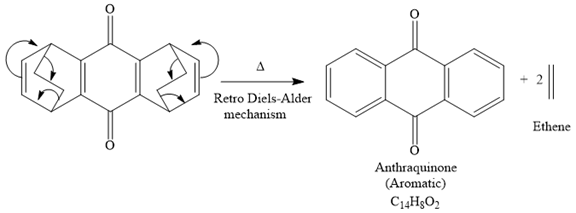
It is noticed that the starting material in the given reaction is overall non-aromatic and also possesses strain due to middle ethylene groups on both sides, but the product is aromatic and strain-free one. Since aromatic compounds are more stable than the non-aromatic compounds this is a key state and the main driving force for the given reaction.
When the given compound is heated, ethene gas is evolved and a product with the formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 24 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





