
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The sequence of steps for the given reaction involving the adenylation of aspartic acid, is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
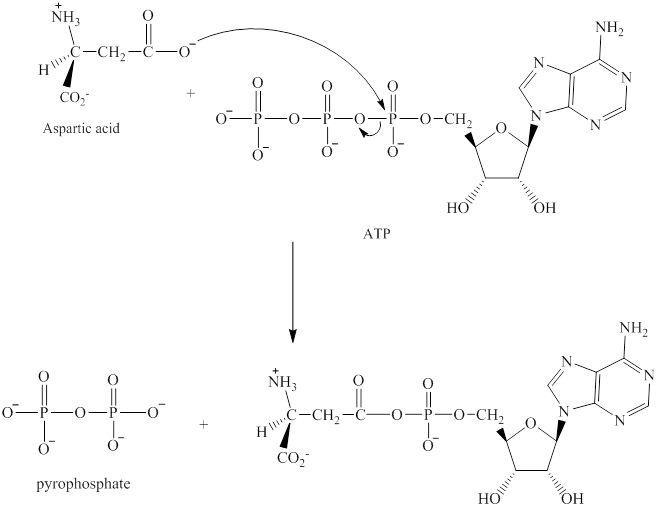
The adenylation of aspartic acid takes place in three steps. In the first step, aspartic acid reacts with ATP. The pyrophosphate is the leaving group in this
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
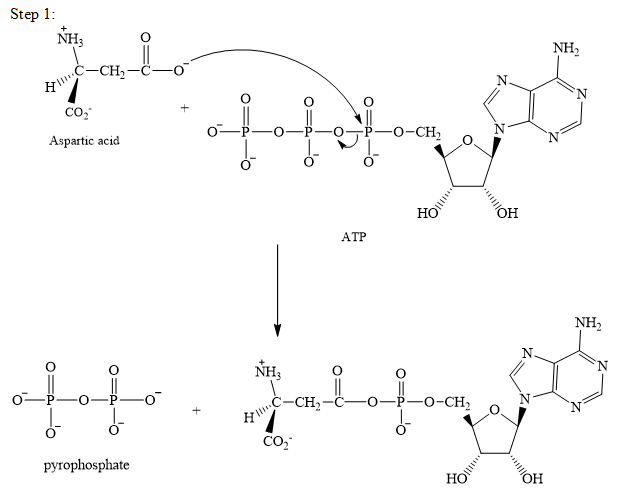
Step 2:
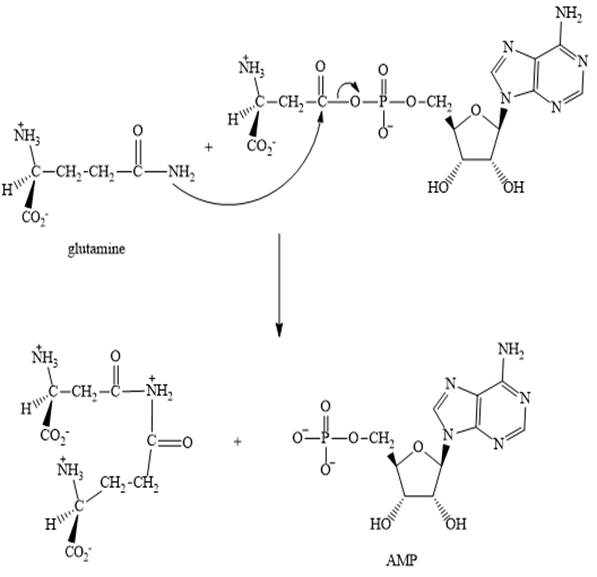
Step 3:
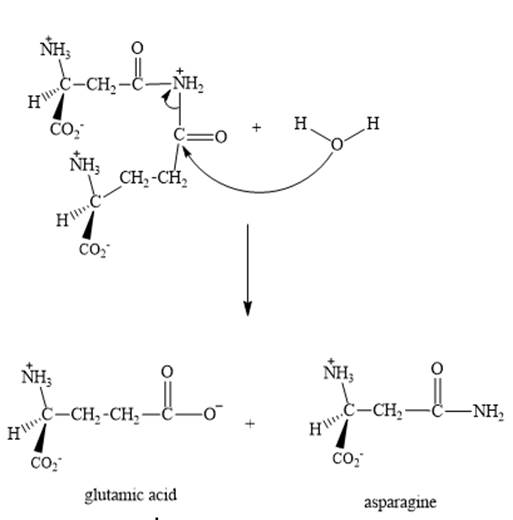
Explanation of Solution
The adenylation of aspartic acid takes place in three steps.
Step 1: In the first step, aspartic acid reacts with ATP. The pyrophosphate is the leaving group in this
Step 2: In the second step, glutamine displaces AMP by a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
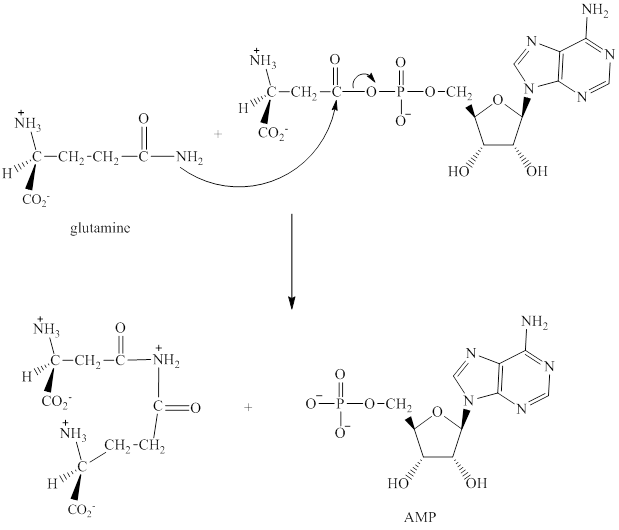
Step 3: The intermediate produced in the step 2 undergoes hydrolysis to the form of glutamic acid and asparagine.
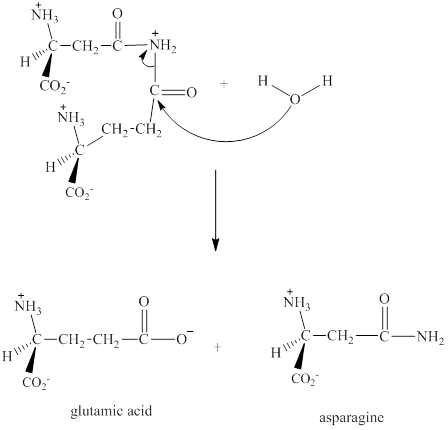
The sequence of steps for the given reaction involving the adenylation of aspartic acid is as shown above.
(b)
Interpretation:
The utilization of ATP in the equilibrium between glutamine and asparagine, is to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
ATP hydrolysis reactions are highly favorable. The reaction is used to help less favorable reactions which occur in high yield. In the adenylation of aspartic acid, the AMP group is a better leaving group than the hydroxyl group.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
ATP is highly energetically favorable and produces AMP, which is a better leaving group than
Explanation of Solution
To make the less favorable reactions occur in high yield, the high energetic favorability of ATP is utilized. AMP is a better leaving group than
ATP is highly energetically favorable and produces AMP, which is a better leaving group than
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept Introduction:
The free energy change of two or more reactions can be used to determine the free energy change of a third reaction. The reactions are treated just like algebraic equations.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
Explanation of Solution
_____________________________________________________________________
The
(d)
Interpretation:
The meaning of ATP hydrolysis in biosynthesis of asparagine is to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
ATP hydrolysis is a high energy reaction. It drives other reactions coupled to it, to completion.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
If ATP is removed from the process, then the reaction is unfavorable. ATP drives the reaction to completion.
Explanation of Solution
If ATP is removed from the process, then the reaction is unfavorable. ATP does not actually undergo hydrolysis, but when coupled to the adenylation of aspartic acid, it becomes favorable and drives the reactions towards completion.
If ATP is removed from the process, then the reaction is unfavorable. ATP drives the reaction to completion.
(e)
Interpretation:
The reaction that ensures the completion of asparagine biosynthesis, is to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Pyrophosphatase catalyzes the irreversible conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate. This reaction ensures the completion of asparagine biosynthesis.
Answer to Problem 25.40AP
The other reaction which drives asparagine synthesis towards completion is the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate.
Explanation of Solution
The other reaction which drives asparagine synthesis towards completion is the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate, which is irreversible. Pyrophosphate is generated as a by-product during the adenylation of aspartic acid.
The other reaction which drives asparagine synthesis towards completion is the conversion of pyrophosphate to phosphate, which is irreversible.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Fats belong to the class of organic compounds represented by the general formula, RCOOR', where R and R' represent hydrocarbon groups; therefore, fats are: a. ethers. b. soaps. c. esters. d. lipases.arrow_forwardConsider the tripeptide leucylvalyltryptophan. a. Specify its structure using three-letter symbols for the amino acids. b. How many peptide bonds are present within the peptide? c. Which of the amino acid residues has the largest R group? d. Which of the amino acid residues, if any, has a basic side chain?arrow_forwardOn complete hydrolysis, a polypeptide gives two alanine, one leucine, one methionine, one phenylalanine, and one valine residue. Partial hydrolysis gives the following fragments: Ala-Phe, Leu-Met, Val-Ala, Phe-Leu. It is known that the first amino acid in the sequence is valine and the last one is methionine. What is the complete sequence of amino acids?arrow_forward
- Consider the tripeptide tyrosylleucylisoleucine. a. Specify its structure using three-letter symbols for the amino acids. b. How many peptide bonds are present within the peptide? c. Which of the amino acid residues has the largest R group? d. Which of the amino acid residues, if any, has an acidic side chain?arrow_forwardAs we’ve discussed, a peptide bond is made when amino group of one amino acid combines with the carboxylic acid group of another amino acid (releasing a water molecule in the process). The C-N bond formed in this process is called a peptide bond. Peptide bonds have a few properties that might be unexpected. b) Another observation is that although the N-H of the peptide bond is able to serve as a H-bond donor the N atom of the peptide bond does not serve as an effective H-bond acceptor. Provide an explanation for this observation, using Lewis structures, VSEPR theory and/or valence bond theory as appropriate.c) It is also fairly accepted that while proteins undergo dynamic motions and conformational changes, and while R groups can freely rotate about Cα, it is generally not possible to freely rotate around a peptide bond. Please explain this observation, using a picture showing relevant orbitals on relevant atoms (your answer for part (a) might provide a useful basis for your reasoning…arrow_forwardLanthionine is a nonstandard amino acid consisting of two alanine residues linked via their β carbon atoms by a thioether (—S—) linkage. Draw the structure of lanthionine.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





