
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To determine whether glutamate can be converted to
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
Yes, glutamate can be converted to
Explanation of Solution
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
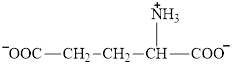
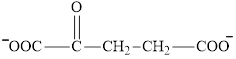
Both glutamate and
(b)
Interpretation: To determine whether
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(b)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
Yes,
Explanation of Solution
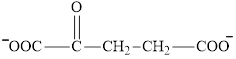
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
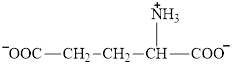
Both glutamate and
(c)
Interpretation: To determine whether glutamate can be converted to aspartate via a transamination reaction or not.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
No, glutamate cannot be converted to aspartate by transamination.
Explanation of Solution
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
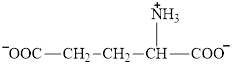
Aspartate is an amino acid and its structure is:
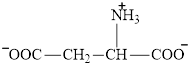
Transamination reaction involves the exchange of an amino group from an
(d)
Interpretation: To determine whether
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
During transamination reaction the new keto acid formed has carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting amino acid and the new amino acid formed has the carbon skeleton similar to the carbon skeleton of the reacting keto acid.
(d)
Answer to Problem 26.32EP
No,
Explanation of Solution
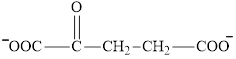
Oxaloacetate is a keto acid and its structure is:
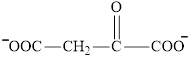
Transamination reaction involves the exchange of an amino group from an
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- What is a likely source of oxaloacetate?arrow_forwardWill an amino acid be glucogenic or ketogenic if it is catabolized to the following molecules?(a) Phosphoenolpyruvate(b) -Ketoglutarate (c) Succinyl-CoA(d) Acetyl-CoA(e) Oxaloacetate(f) Acetoacetatearrow_forwardGiven the following choices,a. what is the structure of the product of the reaction catalysed by ACAT?b. structure of the product produced from the reaction catalysed by phospolipase A2?c. general structure of TAGd. structure of glycerolarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





