
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To determine whether glutamate and aspartate could function as the two reactants in a transamination reaction or not.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
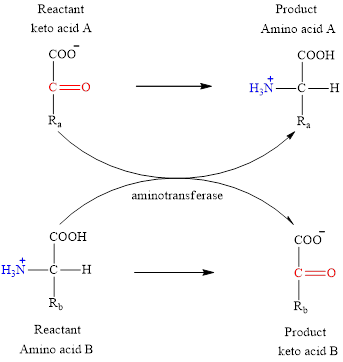
The general structure of an amino acid is:
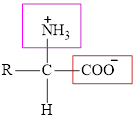
Here,
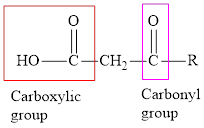
An acid containing both carbonyl and carboxyl functional group is known as a keto acid. A general representation of a keto acid is:
(a)
Answer to Problem 26.34EP
No, glutamate and aspartate cannot function as the reactants in a transamination reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Glutamate is an amino acid and its structure is:
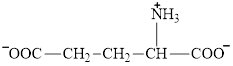
Aspartate is an amino acid and its structure is:
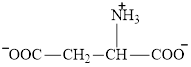
The two reactants in transamination reaction are a keto acid and an amino acid. Both glutamate and aspartate are amino acids thus they cannot function as reactants in a transamination reaction. For a transamination reaction to take place there must be one amino acid present along with a keto acid.
(b)
Interpretation: To determine whether aspartate and
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an

The general structure of an amino acid is:

Here,
An acid containing both carbonyl and carboxyl functional group is known as a keto acid. A general representation of a keto acid is:

(b)
Answer to Problem 26.34EP
Yes, aspartate and
Explanation of Solution
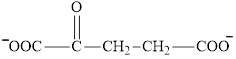
Aspartate is an amino acid and its structure is:
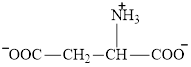
Transamination reaction involves the exchange of an amino group from an
(c)
Interpretation: To determine whether succinate and
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an

The general structure of an amino acid is:

Here,
An acid containing both carbonyl and carboxyl functional group is known as a keto acid. A general representation of a keto acid is:

(c)
Answer to Problem 26.34EP
No, succinate and
Explanation of Solution
Succinate is a diacid acid and its structure is:
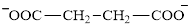
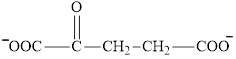
The two reactants in transamination reaction are a keto acid and an amino acid.
(d)
Interpretation: To determine whether glutarate and aspartate could function as the two reactants in a transamination reaction or not.
Concept introduction: Transamination reaction is a biochemical reaction that involves the transfer of an amino group. In transamination reaction exchange of an amino group from an
The general reaction to illustrate transamination is as follows:

The general structure of an amino acid is:

Here,
An acid containing both carbonyl and carboxyl functional group is known as a keto acid. A general representation of a keto acid is:

(d)
Answer to Problem 26.34EP
No, glutarate and aspartate cannot function as the reactants in a transamination reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Aspartate is an amino acid and its structure is:
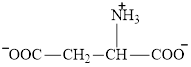
Glutarate is a diacid and its structure is:
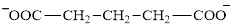
The two reactants in transamination reaction are a keto acid and an amino acid. Aspartate is an amino acid but glutarate is not a keto acid. For a transamination reaction to take place there must be one keto acid present along with an amino acid. Thus, glutarate and aspartate cannot function as the reactants in a transamination reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
EBK GENERAL, ORGANIC, AND BIOLOGICAL CH
- What kind of inhibitor is threo-sphingosine? Explain this type of inhibition.arrow_forwardwhat will be the effect of hot dry conditions in the carboxylase activity of RuBisCO?arrow_forwardIn transamination reactions, which of the following is not a donor amino acid–acceptor α-keto acid pair? a. aspartate and pyruvate b. alanine and pyruvate c. glutamate and α-ketoglutarate d. aspartate and oxaloacetatearrow_forward
- Given the following choices,a. what is the structure of the product of the reaction catalysed by ACAT?b. structure of the product produced from the reaction catalysed by phospolipase A2?c. general structure of TAGd. structure of glycerolarrow_forward"which of the following can be used to replenish oxaloacetate in the krebs cycle"a. aspartic acid b.glutamine c.asparagine d. glutamic acidarrow_forwardWhat would be the fate of oxaloacetate if there were sufficient fluoroacetate present?arrow_forward
- Pyridoxal phosphate acts as an intermediate carrier of amino groups during transamination reactions. Write a series of reactions to show the role of pyridoxal phosphate in the transamination reaction involving alanine and α-ketoglutarate.arrow_forwardWhat are the nonoxidative reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway, and why are they important?arrow_forwardWhich folate structure (from the list below)(a) is the substrate for the enzyme that is inhibited by methotrexate andtrimethoprim?(b) has the most highly oxidized one-carbon substituent?(c) is used in the conversion of serine to glycine?(d) transfers its one-carbon substituent to a B12 coenzyme? What amino acid is synthesized as the end result of this reaction?(e) is the coenzyme for the thymidylate synthase reaction?(f) is not known to exist in nature?(g) is used in purine nucleotide synthesis?arrow_forward
- What is the catalytic triad on chymotrypsin? Detail its importance.arrow_forwardRadiation exerts part of its damaging effect by causing the formation of hydroxyl radicals. Write a reaction equation to explain how glutathione acts to protect against this form of radiation damage.arrow_forwardThe immediate donors of the nitrogen atoms of urea are: a. Aspartate and glutamate b. Glutamate and carbamoyl phosphate c. Aspartate and carbamoyl phosphate d. Glutamine and aspartatearrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





