
The following nonlinear, parasitic ODE was suggested by Hornbeck (1975):
If the initial condition is
(a) Analytically
(b) Using the fourth-order RK method with a constant step size of 0.03125.
(c) Using the MATLAB function ode45.
(d) Using the MATLAB function ode23s.
(e) Using the MATLAB function ode23tb.
Present your results in graphical form.
(a)
To calculate: The analytical solution of the nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
The analytical solution of the differential equation is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Formula used:
The general linear differential equation is,
Calculation:
Consider the nonlinear ordinary differential equation,
Rearrange the above differential equationto get,
Now, compare the above differential equation with the general linear differential equation
Thus,
Now, find the integrating factor (I. F.) as shown below,
Therefore, the solution of the linear differential equation is given as,
Substitute the value of integrating factor (I. F.) in above equation,
Now, integrate the right-hand-side of the above equation,
Solve further, to get
Thus, the solution is
Now, to determine the constant c, use the initial condition
Substitute
Therefore,
Hence, the solution of the differential equation is
(b)
To calculate: Thesolution of the nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
The graph of the solution of the differential equation is,
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Calculation:
Consider the nonlinear ordinary differential equation,
The VBA code to solve the above differential equation with fourth-order RK method with a constant step size of 0.03125 is given below,
The output given below is obtained in the Excel after the execution of the above code:
| 4th order RK | ||
| t | y1 | |
| 0 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| 0.03125 | 0.093476 | 0.093477 |
| 0.0625 | 0.108906 | 0.108906 |
| 0.09375 | 0.126289 | 0.126289 |
| 0.125 | 0.145625 | 0.145625 |
| 0.15625 | 0.166914 | 0.166914 |
| 0.1875 | 0.190156 | 0.190156 |
| 0.21875 | 0.215351 | 0.215352 |
| 0.25 | 0.242499 | 0.2425 |
| 0.28125 | 0.2716 | 0.271602 |
| 0.3125 | 0.302655 | 0.302656 |
| 0.34375 | 0.335662 | 0.335664 |
| 0.375 | 0.370622 | 0.370625 |
| 0.40625 | 0.407536 | 0.407539 |
| 0.4375 | 0.446403 | 0.446406 |
| 0.46875 | 0.487222 | 0.487227 |
| 0.5 | 0.529995 | 0.53 |
| 0.53125 | 0.57472 | 0.574727 |
| 0.5625 | 0.621399 | 0.621406 |
| 0.59375 | 0.670031 | 0.670039 |
| 0.625 | 0.720615 | 0.720625 |
| 0.65625 | 0.773152 | 0.773164 |
| 0.6875 | 0.827642 | 0.827656 |
| 0.71875 | 0.884085 | 0.884102 |
| 0.75 | 0.942481 | 0.9425 |
| 0.78125 | 1.002829 | 1.002852 |
| 0.8125 | 1.06513 | 1.065156 |
| 0.84375 | 1.129383 | 1.129414 |
| 0.875 | 1.195589 | 1.195625 |
| 0.90625 | 1.263747 | 1.263789 |
| 0.9375 | 1.333857 | 1.333906 |
| 0.96875 | 1.405919 | 1.405977 |
| 1 | 1.479932 | 1.48 |
| 1.03125 | 1.555897 | 1.555977 |
| 1.0625 | 1.633814 | 1.633906 |
| 1.09375 | 1.713681 | 1.713789 |
| 1.125 | 1.795498 | 1.795625 |
| 1.15625 | 1.879266 | 1.879414 |
| 1.1875 | 1.964983 | 1.965156 |
| 1.21875 | 2.052649 | 2.052852 |
| 1.25 | 2.142263 | 2.1425 |
| 1.28125 | 2.233824 | 2.234102 |
| 1.3125 | 2.327332 | 2.327656 |
| 1.34375 | 2.422785 | 2.423164 |
| 1.375 | 2.520181 | 2.520625 |
| 1.40625 | 2.61952 | 2.620039 |
| 1.4375 | 2.7208 | 2.721406 |
| 1.46875 | 2.824017 | 2.824727 |
| 1.5 | 2.929171 | 2.93 |
| 1.53125 | 3.036257 | 3.037227 |
| 1.5625 | 3.145273 | 3.146406 |
| 1.59375 | 3.256214 | 3.257539 |
| 1.625 | 3.369075 | 3.370625 |
| 1.65625 | 3.483852 | 3.485664 |
| 1.6875 | 3.600538 | 3.602656 |
| 1.71875 | 3.719125 | 3.721602 |
| 1.75 | 3.839605 | 3.8425 |
| 1.78125 | 3.961966 | 3.965352 |
| 1.8125 | 4.086198 | 4.090156 |
| 1.84375 | 4.212287 | 4.216914 |
| 1.875 | 4.340215 | 4.345625 |
| 1.90625 | 4.469964 | 4.476289 |
| 1.9375 | 4.601512 | 4.608906 |
| 1.96875 | 4.734831 | 4.743477 |
| 2 | 4.869893 | 4.88 |
| 2.03125 | 5.00666 | 5.018477 |
| 2.0625 | 5.145091 | 5.158906 |
| 2.09375 | 5.285137 | 5.301289 |
| 2.125 | 5.426742 | 5.445625 |
| 2.15625 | 5.569837 | 5.591914 |
| 2.1875 | 5.714346 | 5.740156 |
| 2.21875 | 5.860176 | 5.890352 |
| 2.25 | 6.007221 | 6.0425 |
| 2.28125 | 6.155356 | 6.196602 |
| 2.3125 | 6.304436 | 6.352656 |
| 2.34375 | 6.454288 | 6.510664 |
| 2.375 | 6.604715 | 6.670625 |
| 2.40625 | 6.755482 | 6.832539 |
| 2.4375 | 6.906318 | 6.996406 |
| 2.46875 | 7.056903 | 7.162227 |
| 2.5 | 7.206864 | 7.33 |
| 2.53125 | 7.355766 | 7.499727 |
| 2.5625 | 7.503099 | 7.671406 |
| 2.59375 | 7.648268 | 7.845039 |
| 2.625 | 7.790577 | 8.020625 |
| 2.65625 | 7.92921 | 8.198164 |
| 2.6875 | 8.063218 | 8.377656 |
| 2.71875 | 8.191486 | 8.559102 |
| 2.75 | 8.312714 | 8.7425 |
| 2.78125 | 8.425381 | 8.927852 |
| 2.8125 | 8.527709 | 9.115156 |
| 2.84375 | 8.617619 | 9.304414 |
| 2.875 | 8.69268 | 9.495625 |
| 2.90625 | 8.750052 | 9.688789 |
| 2.9375 | 8.786412 | 9.883906 |
| 2.96875 | 8.797877 | 10.08098 |
| 3 | 8.779905 | 10.28 |
| 3.03125 | 8.727189 | 10.48098 |
| 3.0625 | 8.633523 | 10.68391 |
| 3.09375 | 8.491649 | 10.88879 |
| 3.125 | 8.293087 | 11.09563 |
| 3.15625 | 8.027917 | 11.30441 |
| 3.1875 | 7.684546 | 11.51516 |
| 3.21875 | 7.249417 | 11.72785 |
| 3.25 | 6.706683 | 11.9425 |
| 3.28125 | 6.037815 | 12.1591 |
| 3.3125 | 5.221152 | 12.37766 |
| 3.34375 | 4.231369 | 12.59816 |
| 3.375 | 3.038857 | 12.82063 |
| 3.40625 | 1.609002 | 13.04504 |
| 3.4375 | -0.09867 | 13.27141 |
| 3.46875 | -2.13146 | 13.49973 |
| 3.5 | -4.5447 | 13.73 |
| 3.53125 | -7.40305 | 13.96223 |
| 3.5625 | -10.7821 | 14.19641 |
| 3.59375 | -14.7703 | 14.43254 |
| 3.625 | -19.4709 | 14.67063 |
| 3.65625 | -25.0048 | 14.91066 |
| 3.6875 | -31.5132 | 15.15266 |
| 3.71875 | -39.1613 | 15.3966 |
| 3.75 | -48.1421 | 15.6425 |
| 3.78125 | -58.6814 | 15.89035 |
| 3.8125 | -71.043 | 16.14016 |
| 3.84375 | -85.5354 | 16.39191 |
| 3.875 | -102.519 | 16.64563 |
| 3.90625 | -122.417 | 16.90129 |
| 3.9375 | -145.72 | 17.15891 |
| 3.96875 | -173.006 | 17.41848 |
| 4 | -204.949 | 17.68 |
| 4.03125 | -242.336 | 17.94348 |
| 4.0625 | -286.088 | 18.20891 |
| 4.09375 | -337.283 | 18.47629 |
| 4.125 | -397.179 | 18.74563 |
| 4.15625 | -467.248 | 19.01691 |
| 4.1875 | -549.211 | 19.29016 |
| 4.21875 | -645.079 | 19.56535 |
| 4.25 | -757.205 | 19.8425 |
| 4.28125 | -888.338 | 20.1216 |
| 4.3125 | -1041.69 | 20.40266 |
| 4.34375 | -1221.03 | 20.68566 |
| 4.375 | -1430.74 | 20.97063 |
| 4.40625 | -1675.96 | 21.25754 |
| 4.4375 | -1962.71 | 21.54641 |
| 4.46875 | -2297.99 | 21.83723 |
| 4.5 | -2690.02 | 22.13 |
| 4.53125 | -3148.39 | 22.42473 |
| 4.5625 | -3684.34 | 22.72141 |
| 4.59375 | -4310.97 | 23.02004 |
| 4.625 | -5043.62 | 23.32063 |
| 4.65625 | -5900.23 | 23.62316 |
| 4.6875 | -6901.75 | 23.92766 |
| 4.71875 | -8072.7 | 24.2341 |
| 4.75 | -9441.73 | 24.5425 |
| 4.78125 | -11042.3 | 24.85285 |
| 4.8125 | -12913.7 | 25.16516 |
| 4.84375 | -15101.5 | 25.47941 |
| 4.875 | -17659.5 | 25.79563 |
| 4.90625 | -20650.1 | 26.11379 |
| 4.9375 | -24146.4 | 26.43391 |
| 4.96875 | -28234.2 | 26.75598 |
Now, plot the following chart using the data obtained in Excel.
In the above plot, the series1 represent the numerical solution whereas the series2 represent the exact solution.
(c)
The solution of the nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
The graph of the solution of the differential equation is,
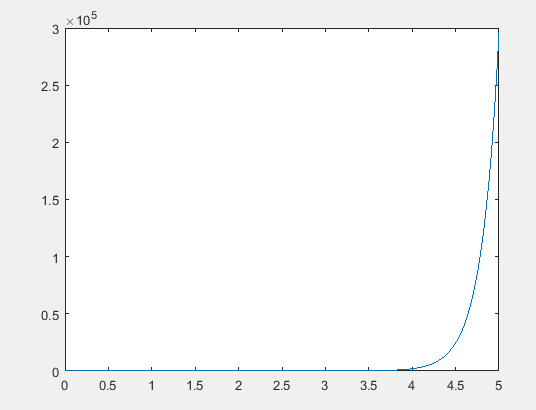
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Consider the nonlinear ordinary differential equation,
Use the MATLAB function
Write the code given below in MATLAB editor window and save it.
function
Now, write the following code in MATLAB command window

Following graph is obtained after the execution of the above MATLAB code.

(d)
The solution of the nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
The graph of the solution of the differential equation is,
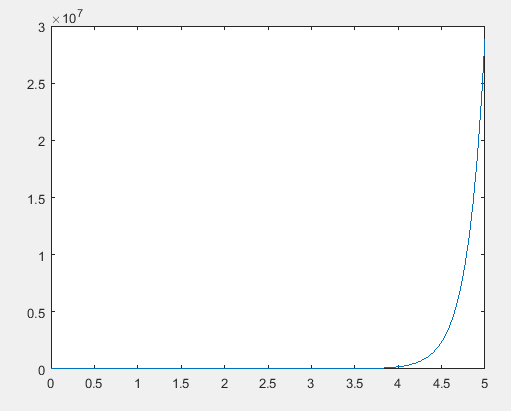
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Consider the nonlinear ordinary differential equation,
Use the MATLAB function
Write the code given below in MATLAB editor window and save it.
function
Now, write the following code in MATLAB command window

Following graph is obtained after the execution of the above MATLAB code.

(e)
The solution of the nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
The graph of the solution of the differential equation is,
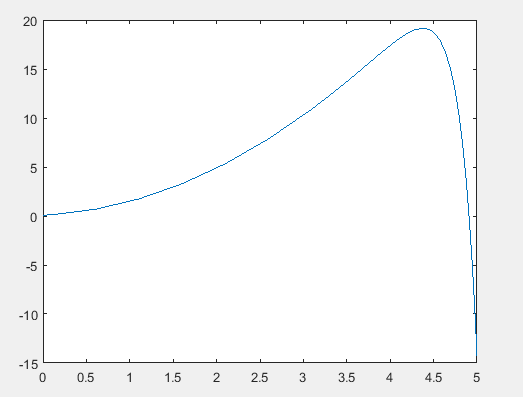
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A nonlinear, parasitic ordinary differential equation,
Consider the nonlinear ordinary differential equation,
Use the MATLAB function
Write the code given below in MATLAB editor window and save it.
function
Now, write the following code in MATLAB command window

Following graph is obtained after the execution of the above MATLAB code.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Technical Mathematics
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Fundamentals of Differential Equations (9th Edition)
Calculus: Single And Multivariable
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,






