
Concept explainers
(a)
To infer:
About the relative costs and benefits of large brains documented in the fossil records of certain lineages of humans and other animals.
Concept introduction:
Animals with larger brain size are considered as more intelligent and hence they are more successful than animals with smaller brain size. The larger brain size can also help an animal in obtaining mates and therefore can increase their survival.
The larger brain size involves a higher cost, but it is outweighed by the survival benefits that an animal gets.
(b)
To hypothesize:
In what way the natural selection might have favored the evolution of large brains despite their high maintenance costs.
Concept introduction:
Animals with larger brain size are considered as more intelligent and hence they are more successful than animals with smaller brain size. The larger brain size can also help an animal in obtaining mates and therefore can increase their survival.
The larger brain size involves a higher cost, but it is outweighed by the survival benefits that an animal gets.
(c)
To graph:
The data for 14 bird species and conclude about the relationship between brain size and mortality.
Concept introduction:
Animals with larger brain size are considered as more intelligent and hence they are more successful than animals with smaller brain size. The larger brain size can also help an animal in obtaining mates and therefore can increase their survival.
The larger brain size involves a higher cost, but it is outweighed by the survival benefits that an animal gets.
Graphical representation:
The graph between the mortality rate and deviation of brain size from expected is shown below:
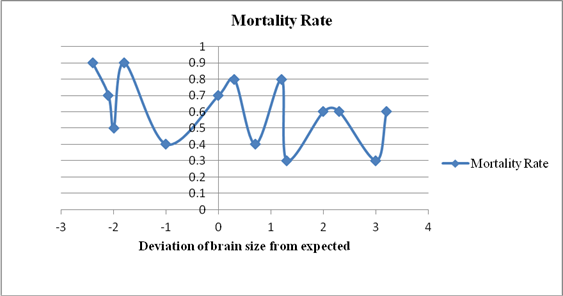
Graph 1: Relationship between the mortality rate and deviation of brain size from the expected value. The x-axis represents the deviation of brain size from expected and the y-axis represents the mortality rate.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
Campbell Biology In Focus, Loose-leaf Edition (3rd Edition)
- There are two main groups of bats: Smaller “microbats” navigate by using sonar, and larger “megabats” rely on vision. Mammalogists once though that both kinds of bats evolve from insectivorous mammals. But similarities between the visual systems of megabats and primates have led some researchers to think that megabats may have evolve from primates, perhaps lemurs. What results would support the hypothesis that the two groups of bats have a common origin? Separate origins?arrow_forwardA. The earliest evolutionary change in the hominins was a. increased brain size. b. habitual bipedalism. c. changes in dentition. d. all of the above (they happened at the same time). B. Which of the following statements about endurance running is correct? a. Endurance running is found among all primates, but humans are most adapted for it. b. The ability to control body temperature is likely the most important running adaptation. c. Humans can outrun almost all other mammals, including horses, at short distances. d. Endurance running probably emerged with the appearance of Homo sapiens. Clear my choicearrow_forwardPakicetus is an ancient wolf-like organism that lived 50 million year ago. It had wolf-like ears and nostrils on the front of its skull. Modern whales have a similar ear structure, but their nostrils are on the back of their skull. Aetiocetus lived 25 million years ago, had the same ear structure as both Pakicetus and modern whales, but nostrils in the middle of its skull. According to this information, the most likely conclusion that biologists could draw about the relationship of Aetiocetus to the other organisms is that Aetiocetus...arrow_forward
- Explain the difference between generalized and specialized characteristics. What are examples of each in terms of the adaptive potential? Define the term “adaptive radiation” and explain why it is important to the principle of evolution. Why was adaptive radiation especially important to mammals’ eventual rapid evolutionary success and diversification? What are some of the different groups of mammals?arrow_forwardThe biological variation in living primates provides models for understanding A. Morphology, behavior, adaptation in the evolutionary past, and alternative forms of classification B. Alternative forms of classification C. The uses of anatomical and genetic evidence D. Morphology, behavior, and adaptation in the evolutionary pastarrow_forwardConsider the figure attached. A student in a course on intelligent design theory claims that the graph in part (a) shows that losing the ability to respire actually is adaptive for yeast cells living in small populations. Please read the incomplete sentence that appears immediately below, assess as possible completions the lowercase-Roman-numeral-labelled statements that follow, and click each uppercase-letter-labelled response that is presented below and completes accurately the sentence. An astute student in an evolution course would respond that i. the graph in part (a) shows that selection among mitochondria within yeast cells can lead to fixation for traits that decrease mean fitness for that yeast population. ii. the student in the course on intelligent design is wrong; the yeast cells in the small population group retained completely the ability to respire, as they otherwise would have been unable to harvest energy. iii. a property (e.g., inability to respire) that is…arrow_forward
- A group of scientists examine the skeletal evidence below. Gibbon Orangutan Chimpanzee Gorilla Human What conclusion can be drawn from the diagram to support the theory of evolution? Man evolved from gorillas which evolved from chimpanzees. O Gibbons are most closely related to man because of similarities in their skeletal structure. O Orangutans have a larger jaw size than chimpanzees, allowing them to have a more carnivorous diet. Gorillas continued to walk on all four limbs to move around on the floor of forests, while man became bipedal to live in grasslands in order to hunt and carry food. O O O Oarrow_forwardDEVELOPMENT OF EVOLUTIONARY THOUGHT ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. 1. Lamarck's idea of evolution was considered significant though today it is no longer acceptable due to lack of evidence at that time. What do you think it was? Why do you think this evidence is missing? 2. One of the criticisms of Lamarck's idea was a wrestler with very well-developed muscles. Consider this hypothetical situation: YOU decided NOW that when you have children, you want them to be big and strong. You decided to go to the gym every day for a year. You did all your exercise routines diligently and you were able to develop really bulky and toned muscles. Do you think this will work? Write down in one sentence the main reason why this would or would not work. 3. How did Darwin disproved Lamarck? Why did Darwin still thought that Lamarck's work was very important?arrow_forwardAccording to Lamarck’s theory of evolution, organisms change during their lifetime to survive then pass these changes to their offspring. What supports the hypothesis of Lamarck? a. Webbed toes of ducks to quickly move through the water, retractile claws of carnivorous mammals to catch the prey, millipede producing awful smell for self-defense and evolution of short-necked to long-necked giraffe b. Evolution of short-necked to long-necked giraffe, webbed toes of ducks to quickly move through the water, disappearance of limbs in snakes and retractile claws of carnivorous mammals to catch the prey c. Rattlesnake producing venom against predators, jellyfish bioluminescence for intraspecific communication chameleons camouflage to hide from predators and millipede producing awful smell for self-defense d. Disappearance of limbs in snakes, chameleons camouflage to hide from predators, evolution of short-necked to long-necked giraffe and rattlesnake…arrow_forward
- A. According to Gould and Vrba (1982), when the original cooling function of insect appendages was changed to flying, this is an example of a. inheritance. b. exaptation. c. apatation. d. adaptation. B. When primates first evolved away from their mammalian ancestors, they a. developed a larger and more complex brain. b. increased their reliance on the sense of smell. c. increased the number of canines (for meat-eating). d. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is BEST supported by the phylogenetic tree? A The development of a bony skeleton was a significant evolutionary step for ocean-dwelling animals. B Most warm-blooded animals evolved to have hair, while cold-blooded animals did not. C Most land animals require a vertebral column, while ocean animals do not. D The evolution of the amniotic egg was specific to ocean-dwelling animals.arrow_forwardMatch the descriptions/examples types of evidence that support evolution. 1.Biogeography 2.Comparative Embryology 3.Comparative Anatomy 4.Molecular Biology A.Organisms in New Zealand are more similar to organisms in Australia than they are to organisms in North America . B.The embryos of many species have gill pouches even though the gill pouches are not used in these species . C.The forelimbs of the human ,cat ,whale and bat have many similar bones despite the fact that the forelimbs have different functions . D.The Human genome is 98% identical to the Chimpanzee genome .arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





