
Concept explainers
Draw the Lewis structure and name the molecular geometry for each molecule.
- a. H2S
- b. OCl2 (oxygen is the central atom)
- c. N2O (nitrogen is the central atom)
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure and name of molecular geometry should be provided for the given molecule
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
The chemical bonding present in covalently bonded molecules and in coordination compounds are represented using Lewis structures.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Molecular geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering only bond pair of electrons.
Geometry of different type of molecules with respect to the number of electron pairs are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The given moleucle is
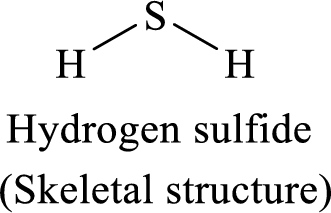
Thus, the Lewis structure of given compound is,
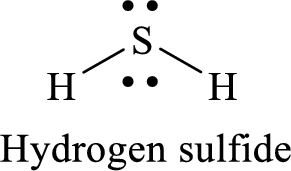
There are two sets of lone pair electrons on the central atom sulfur along with two bond pair of electrons and so its molecular geometry is bent.
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure and name of molecular geometry should be provided for the given molecule
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
The chemical bonding present in covalently bonded molecules and in coordination compounds are represented using Lewis structures.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Molecular geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering only bond pair of electrons.
Geometry of different type of molecules with respect to the number of electron pairs are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The given moleucle is
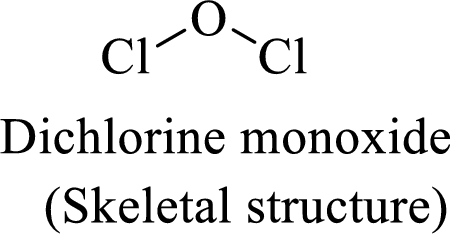
Thus, the Lewis structure of given compound is,
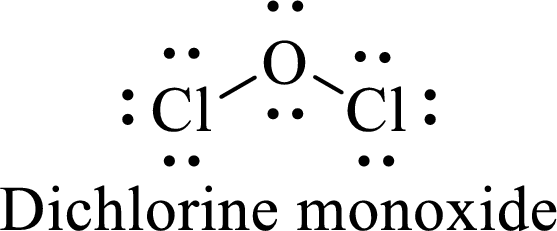
There are two lone pair of electron on the central atom oxygen along with two bond pair of electrons and so its molecular geometry is bent.
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure and name of molecular geometry should be provided for the given molecule
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
The chemical bonding present in covalently bonded molecules and in coordination compounds are represented using Lewis structures.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
Molecular geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering only bond pair of electrons.
Geometry of different type of molecules with respect to the number of electron pairs are mentioned below,
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The given moleucle is

Thus, the Lewis structure of given compound is,
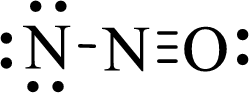
Since the molecule has two bond pair of electrons, (multiple bond is consider as a single bond) its molecular geometry is linear.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Laboratory Manual Chemistry in Context
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Chemistry: Atoms First
Chemistry: Atoms First
Principles of General, Organic, Biological Chemistry
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
- Why is the geometric structure of a molecule important, especially for biological molecules?arrow_forwardWhat is the geometric structure of the water molecule? How many pairs of valence electrons are there on the oxygen atom in the water molecule? What is the approximate HOHbond angle in water?arrow_forwardConsider the compound xenon dichloride, XeCl2 a.What is the polarity of the molecule? b. What type of bond is the Xe-Cl bond? c. How many bonding pairs of electrons are there?arrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis structure for NO2- what is the electron-pair geometry for NO2- what is the shape (molecular geometry of NO2-arrow_forwardPart 1) If 3.36 moles of N2 and 3.90 moles of H2 are combined under, which would be considered the limiting reactant? Part 2) How many grams of NH will be formed during the reaction? Part 3) In sufficient detail, describe the most valid Lewis structure of NH3 (types of bonds, presence of unbonded electrons, existence of any formal charges etc.), then specify its molecular geometry. Based on the reaction to form ammonia (NH3arrow_forwardPropylene, C3H6,C3H6, is a gas that is used to form the important polymer called polypropylene. Its Lewis structure is (a) What is the total number of valence electrons in the propylene molecule? (b) How many valence electrons are used to make σσ bonds in the molecule? (c) How many valence electrons are used to make ππ bonds in the molecule? (d) How many valence electrons remain in nonbonding pairs in the molecule? (e) What is the hybridization at each carbon atom in the molecule?arrow_forward
- a) how many total pairs of electrons does CF4 have? b) How many bonded pairs and how many lone pairs does CF4 have? c) What is the molecular shape and angle of CF4? d) what is the lewis structure for CF4?arrow_forwardE is a made up element and contains 6 valence electrons Y is a made up element and contains 7 valence electrons Calculate the number of valence electrons in EY2 Using your knowledge of Lewis structures, draw the Lewis structure of EY2 What is the electron geometry of EY2 What is the molecular shape of EY2arrow_forwardExplain why the HOH molecule is bent, whereas the HBeH molecule is linear.arrow_forward
- Consider the following Lewis structure where E is an unknown element: What are some possible identities for element E? Predict the molecular structure (including bond angles) for this ion.arrow_forwardDescribe the VSEPR model. How is the model used to predict molecular structure?arrow_forwardConsider the following Lewis structure where E is an unknown element: What are some possible identities for element E? Predict the molecular structure (including bond angles) for this ion. (See Exercises 115 and 116.)arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





