
Principles of Human Physiology - Mastering A&P
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134298900
Author: STANFIELD
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 28E
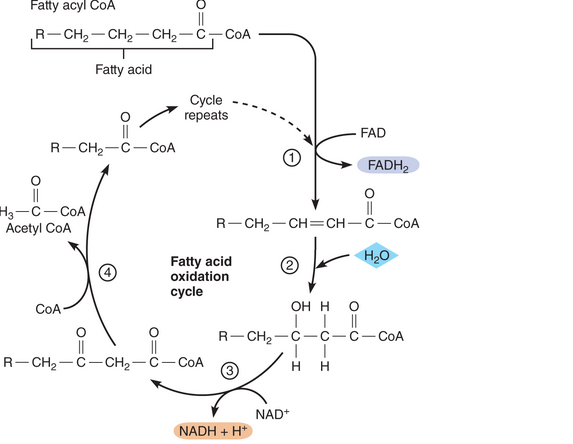
As you know, fatty acids can be oxidized to provide energy for making ATP. This process begins with a set of reactions known as the fatty acid oxidation cycle, or beta oxidation. Before entering the cycle, a fatty acid reacts with coenzyme A to form a molecule called fatty acyl CoA. This molecule then enters the cycle and continues to go through it until all its carbons have been eliminated, as shown on the following page. From your examination of this diagram, answer the following questions for a 1 2-carbon fatty acid.
- How many acetyl CoA molecules will be produced by beta oxidation of this fatty acid? How many ATP molecules can be produced from each acetyl CoA molecule that goes through the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation?
- How many NAD+ and FAD molecules will be reduced? (Hint: How many bonds must be broken to split a 12-carbon fatty acid into acetyl CoA molecules?)
- How many ATP molecules will be produced per each NADH + H+ and each FADH2 molecule that provides electrons to the electron transport system?
- It takes two ATP molecules to get the cycle started. Based on this information and your answers to the previous questions, how many ATP molecules can be generated from a 1 2-carbon fatty acid?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Place the following list of reactions or relevant locations in the β oxidation of fatty acids in the proper order. (a) Reaction with carnitine (b) Fatty acid in the cytoplasm (c) Activation of fatty acid by joining to CoA (d) Hydration (e) NAD+ -linked oxidation (f) Thiolysis (g) Acyl CoA in mitochondrion (h) FAD-linked oxidation.
Which of the following is the chemical end product of fatty-acids metabolized in the beta-oxidation pathway?
Select one:
a.
Beta-carotine
b.
Free-radicals
c.
Lactic acid
d.
Acetyl-CoA
e.
Pyruvate
The citric acid cycle is a critical sequence of reactions for energy production, which take place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The reaction cycle requires materials from the cytosol to be converted into acetyl CoA, which represents the starting point of a new cycle. Which of the following statements about acetyl CoA is true?
(a) Acetyl CoA is recycled at the end of every cycle.
(b) Oxaloacetate is attached to acetyl CoA to feed the citric acid cycle.
(c) Triacylglycerol molecules are transported into the mitochondrial matrix and cleaved by lipases to produce acetyl CoA.
(d) Oxaloacetate is converted directly into acetyl CoA to feed the citric acid cycle
Chapter 3 Solutions
Principles of Human Physiology - Mastering A&P
Ch. 3.1 - What is the primary distinction between an...Ch. 3.1 - Describe in general terms what occurs in...Ch. 3.2 - In an exergonic reaction, which has more...Ch. 3.2 - Which factor determines the direction of a...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 3.2.3QCCh. 3.2 - What is activation energy? How does it affect a...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 3.3.1QCCh. 3.3 - How is the rate of an enzymatic reaction affected...Ch. 3.3 - What is the primary distinction between allosteric...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 3.4.1QC
Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 3.4.2QCCh. 3.5 - Prob. 3.4.3QCCh. 3.6 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 2CTQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3.5.1QCCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3.5.2QCCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3.5.3QCCh. 3.6 - Prob. 3.5.4QCCh. 3.7 - Prob. 3.6.1QCCh. 3.7 - Prob. 3.6.2QCCh. 3.7 - Prob. 3.6.3QCCh. 3 - Prob. 1ECh. 3 - Prob. 2ECh. 3 - Prob. 3ECh. 3 - Prob. 4ECh. 3 - Prob. 5ECh. 3 - Prob. 6ECh. 3 - Prob. 7ECh. 3 - Prob. 8ECh. 3 - Prob. 9ECh. 3 - Prob. 10ECh. 3 - The removal of hydrogen atoms from a molecule is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 12ECh. 3 - Prob. 13ECh. 3 - Prob. 14ECh. 3 - Prob. 15ECh. 3 - Prob. 16ECh. 3 - Prob. 17ECh. 3 - Prob. 18ECh. 3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3 - Prob. 20ECh. 3 - Prob. 21ECh. 3 - Prob. 22ECh. 3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3 - Compare and contrast the mechanisms of...Ch. 3 - Explain how the conversion of pyruvate to lactate...Ch. 3 - Prob. 26ECh. 3 - Prob. 27ECh. 3 - As you know, fatty acids can be oxidized to...Ch. 3 - Prob. 29E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cholesterol synthesized by cells uses which component of the glycolytic pathway as a starting point? a. glucose b. acetyl CoA c. pyruvate d. carbon dioxidearrow_forwardWhen one acetyl CoA is processed through the citric acid cycle, how many times does each of the following events occur? a. A FAD molecule is a reactant. b. A CoA-SH molecule is produced. c. A dehydrogenase enzyme is needed for the reaction to occur. d. A C5 molecule is produced.arrow_forwardTwo carbon atoms are fed into the citric acid cycle as acetyl-CoA. In what form are two carbon atoms removed from the cycle?arrow_forward
- In fatty acid oxidation, each cycle shortens the fatty acid being catabolised by 2 carbons, producing acetyl CoA and 2 reduced carrier molecules. Complete oxidation of a saturated fatty acid with 18 carbons would produce how many acetyl CoA and reduced carrier molecules? a. 8 acetyl CoA, 8 NADH and 8 FADH2 b. 9 acetyl CoA, 8 NADH and 8 FADH2 c. 8 acetyl CoA, 9 NADH and 9 FADH2 d. 9 acetyl CoA, 9 NADH and 9 FADH2arrow_forwardWhich citric acid cycle intermediate can move from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm to become the activator of fatty acid synthesis? Select one: a. Succinyl-CoA b. Fumarate c. Citrate d. Malatearrow_forwardStarting with acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria, how many ATP molecules are needed to synthesize a 14 C fatty acid? A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12arrow_forward
- One consequence of ethanol addiction is fatty liver disease, an illness in which liver cells accumulate large amounts of triacylglycerols, the esters derived from glycerol and fatty acids. Ethanol is oxidized in the cytoplasm of liver cells by alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase to yield acetate and 2 NADH. Acetate is then transported into the mitochondrion, where it is converted to acetyl-CoA and metabolized in the citric acid cycle. When alcohol is consumed in excessive quantities, the resulting high levels of NADH cause metabolic abnormalities, one of which is high levels of fatty acid synthesis. Fatty acid synthesis, also a cytoplasmic process, uses acetyl-CoA as a substrate and NADPH as a reducing agent. Speculate about how a high level of cytoplasmic NADH provides a source of NADPH for fatty acid synthesis.arrow_forwardBefore a fatty acid can undergo β-oxidation, it must be activated and then shuttled across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The activating agent and shuttle molecule are, respectively: A. CoA and carnitine B. CoA and citrate C. acetyl CoA and carnitine D. acetyl CoA and citratearrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are TRUE?Multiple answers are accepted for this question a .Two molecules of CO2 are produced each time a molecule of Acetyl-CoA is oxidized. b. During the first turn of the TCA Cycle the carbon atoms of Acetyl-CoA become CO2. c. The number of molecules of ATP that can be produced in the Citric Acid Cycle by substrate level phosphorylation of ADP from two molecules of Acetyl-CoA is 30. d. Fumarate contains a trans double bond. The cis isomer of Fumarate is Maleate which cannot serve as carbon source for a cell. e. Lack of O2 would decrease the rate of the Citric Acid Cycle in red blood cells. f. If a potent inhibitor of Succinyl-CoA Synthetaseis is applied to liver cells both energy production and synthesis of carbohydrate would be affected. g. The overall chemical changes that occur during one complete turn of the Citric Acid Cycle is the complete oxidation of one molecule of Acetyl-CoA plus the production of two molecules of CO2 plus the…arrow_forward
- What are the three names for the metabolic cycle that occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria? This pathway receives acetyl-CoA, combines it to other metabolites, steals its available electrons, and releases carbon in its most oxidized form.arrow_forward___ molecules of ATP are ultimately formed per every acetyl-CoA that enters the citric acid cycle and the remaining ATP molecules are generated via the ___ of NADH and FADH2. A) Nine; oxidation B) Ten; reduction C) Ten; oxidation D)Nine; reductionarrow_forwardThe completion of one cycle of the citric acid cycle oxidizing one acetyl CoA results in net... Group of answer choices 2 ATP produced consumption of 1 molecule of citrate consumption of 1 molecule of oxaloacetate production of 2 CO2 Which of the following is not a component of the citric acid cycle? Group of answer choices Oxaloacetate Succinyl CoA Malate Pyruvate Which of the following enzymes catalyzes an anaplerotic reaction? Group of answer choices citrate synthase pyruvate dehydrogenase complex malate dehydrogenase pyruvate carboxylasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College
Anaerobic Respiration; Author: Bozeman Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cDC29iBxb3w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY