
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.29P
The arrangement of the given compounds in decreasing order of their
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
Figure 1
The acidity of an atom is directly proportional to the electronegativity of an atom. The
Compound C contains
Compound A contains sulfur atom which is less electronegative than oxygen atom but it contains a chlorine atom. Chlorine atom is electronegative in nature due to which acidity of compound A increases.
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
Figure 2
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
Figure 3
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the given compounds in decreasing order of their
(b)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.29P
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
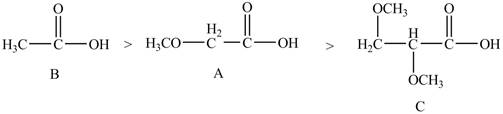
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
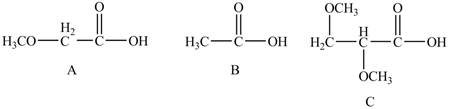
Figure 4
The acidity of an atom is directly proportional to the electronegativity of an atom. Compound C contains two
Compound A contains only one
Compound B contains
Therefore, the order of acidity of the compounds is shown below.
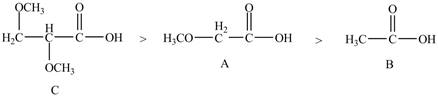
Figure 5
The
Therefore, the order of decreasing
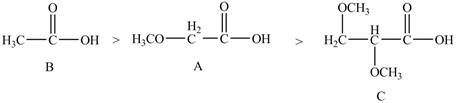
Figure 6
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
(c)
Interpretation:
An explanation regarding the arrangement of the compounds in order of their decreasing
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 3.29P
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
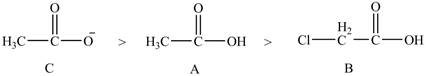
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are shown below.
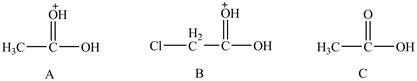
Figure 7
The conjugate bases of the compounds are shown below.
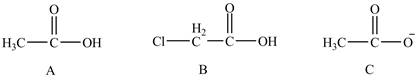
Figure 8
Compound C shown in Figure 8 is more basic than compound A and B due he presence of carboxylate ion. Compound B contains one chlorine atom which is an electron-withdrawing group. Thus, due to
The order of basicity of the compounds is shown below.
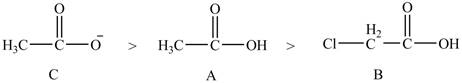
Figure 9
The order of basicity is directly proportional to the
Therefore, the order of decreasing
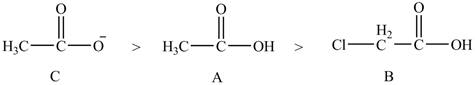
Figure 9
The order of decreasing
The arrangement of the order of decreasing
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- If the G for a reaction is 4.5 kcal/mol at 298 K, what is the Keq for this reaction? What is the change in entropy of this reaction if H = 3.2 kcal/mol?arrow_forwardS.2. List the following compounds by discussing their basicity.arrow_forwardPart 1. Choose the stronger acid in each pair of compounds. Part 2. Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing basicity. Part 3. Determine if the oxide is acidic or basearrow_forward
- (i) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of basic strength :C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C2H5)2NH and CH3NH2(ii) Arrange the following compounds in a decreasing order of pKb values :C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2NH and C6H5NHarrow_forwardArrange the compounds in increasing order according to its basicityarrow_forwardThe acids are: isopropanol, ethyne, and phenol. Which acid will NOT be deprotanated by NaOH and which acid will deprotonate in the presence of NaHCO3. After an acid base reaction, which compound above has the weakest conjugate base?arrow_forward
- Arrange the following molecules in increasing order of acidity. Base it only on their structural differences and explain how it is so. 1. HF, CH3CH2CH2OH, CH3CH2COOH 2. Ethyl amine, Ethanol, Propanearrow_forwardWhich species is the stronger Lewis Acid? Why? (Use resonance structures to explain your answer.) BH3 or trimethoxyboratearrow_forwardWill acetylene react with sodium hydride according to the following equation to form a salt and hydrogen, H2? Using pKa values given in Table 4.1, calculate Keq for this equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Arrange the following organic molecules in order of increasing acidity, starting with the least acidic and explain your answer CH3CH3, HC≡CH and CH2=CH2arrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity, and explain in detail your choice of order.arrow_forwardWhich is true regarding the direction of the following reaction? CH3COOH (aq) + H2PO-4 <<>>> CH3COO- + H3PO4 a) the reaction favors the reactant side b) the reaction favors the product side c) the reaction favors both reactants and products equally d) the table of acidity does not proviede enough information to answer this questionarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

