
Concept explainers
The code that follows shows an example of branching on an enumerated type value in a switch statement. Recall that enumerated types in C are simply a way to introduce a set of names having associated integer values. By default, the values assigned to the names count from zero upward. In our code, the actions associated with the different case labels have been omitted.
The part of the generated assembly code implementing the differents actions is shown in Figure 3.52. The annotations indicate the argument locations, the register values, and the ease labels for the different jump destinations.
Fill in the missing parts of the C code. It contained one case that fell through to another—try to reconstruct this.
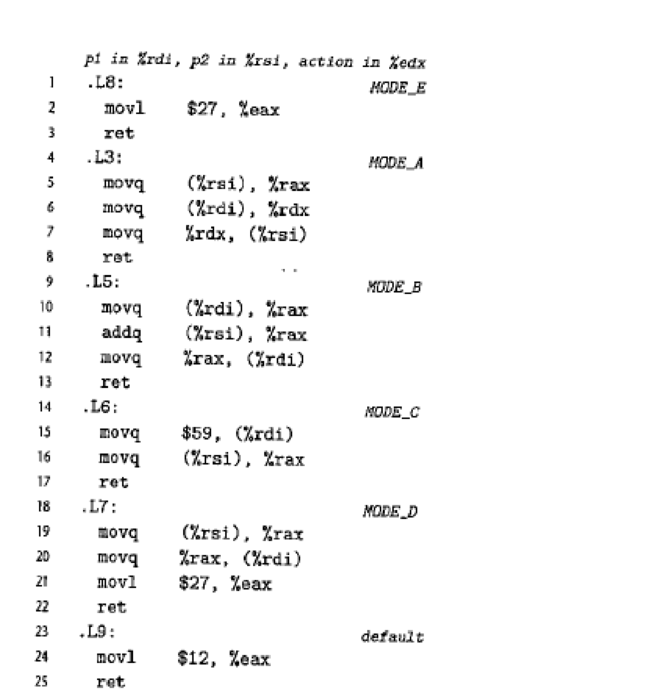
Figure 3.52 Assembly code for Problem 3.62. This code implements the different branches of a switch statement.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
C++ How to Program (10th Edition)
Starting out with Visual C# (4th Edition)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (9th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (8th Edition)
Problem Solving with C++ (9th Edition)
Concepts Of Programming Languages
- First, make the code in the previous question an actual C program so that it can be compiled and it runs. Play with it so that you feel comfortable with the logic of the code.Then implement the code in TTPASM. Note that you need to preserve the actual C code structure, this means you cannot it into a non-recursive subroutine. Furthermoreall conventions discussed in class regarding subroutines must be followed. The idea is that I should be able to substitute f with my own code, and main should work. Or, I can substitute main with my own, and f should work.Attach the source code of your assembly language program as answer to this question. It should be a text file that the assembler be able to assemble.UploadChoose a Filearrow_forwardWhen referring to coded components like subprograms, variables, and objects, is it better to use fully qualified references or unqualified references? Issues with C's primitive encapsulation and how they influenced C++ are discussed.arrow_forwardWhat are the differences between an assembly and a namespace in C#? A namespace defines a logically separate unit of compilation whereas an assembly is a packaging tool for separating name scopes. An assembly is designed only to allow for deploying code and as such is not an encapsulation construct whereas namespaces are. An assembly defines a syntactical unit that allows for separate compilation/deployment whereas a namespace is a naming encapsulation as it is by design used to define name scopes. While they both are encapsulation constructs, the assembly is like a package as it relates to name scopes and the namespace is used to connect friends like in C++arrow_forward
- Which of these two types of references to subprograms, variables, and objects in code is superior: fully qualified references or unqualified references? An explanation of the issues that arise with C's basic encapsulation and the influence that this has on C++.arrow_forwardWhat is meant by memory leak and dangling pointer? Explain the concept with the help of example.(in c language)arrow_forwardThe following question is related to C programming system call Task-3: Consider the following code snippet in your main function - a = fork(); b = fork(); c = fork(); Now, write the full program, that will check the children’s PID and if it is odd then the process will create another child process. Lastly, print how many processes have been created considering the first parent process.arrow_forward
- Please write a Program in C that gives the output as shown. Problem: Write a program in c that the parent process will create one child process and 3 grandchildprocesses and print their IDs Output: 1. Parent process ID : ....2. Child process ID: ....3. Grand Child process ID: ...4. Grand Child process ID: ...arrow_forwardWhat is meant by memory leak and dangling pointer?.explain the concept with suitable example.(in C language )arrow_forwardIn Subprograms concept, Compare each of the following data types with that for the C based languages with an example for each type. (a) Types of Subprograms, (b) Subprogram definitions and subprogram calls, (c) Types of Parameter Passing, (d) Subprogram Overloading, (e) Generic Subprograms, (f) Recursive Subprograms.arrow_forward
- Write a C++ program to create a Class of magi with data members of type double x and y and one constructor to initialize the values of x and y. Perform addition operations on complex data using class and object. The program should ask for the real and imaginary parts of two complex numbers, and display the real and imaginary parts of their sum.arrow_forwardThe concept of memory types in c# is implemented using either of the following two ways1. Heap and Stack2. BoxIng and Unboxing Explain and demonstrate the above using appropriate C# examples.arrow_forwardWhen you speak about execution flow, could you maybe explain precisely what you mean by that?arrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
