
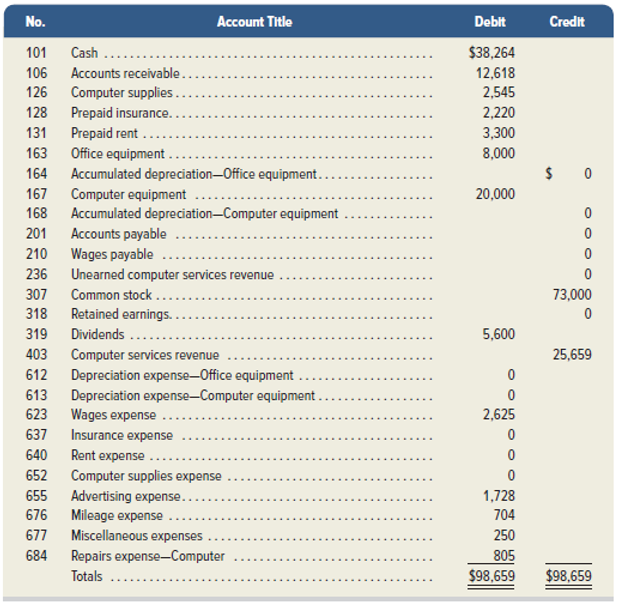
After the success of the company’s first two months, Santana Rey continues to operate Business Solutions. (Transactions for the first two months are described in the Chapter 2 serial problem.) The November 30,2019, unadjusted
Dec. Paid $1,025 cash to Hillside Mall for Business Solutions's share of mall advertising costs.
2
3 Paid $500 cash for minor repairs to the company's computer.
4 Received $3,950 cash from Alex's Engineering Co. for the receivable from November.
10 Paid cash to Lyn Addie for six days of work at the rate of $125 per day.
14 Notified by Alex's Engineering Co. that Business Solutions's bid of $7,000 on a proposed project has been accepted. Alex's paid a $1,500 cash advance to Business Solutions.
15Purchased $1,100 of computer supplies on credit from Harris Office Products.
16 Sent a reminder to Gomez Co. to pay the fee for services recorded on November 8.
20 Completed a project for Liu Corporation and received $5,625 cash.
22-26 Took the week off for the holidays.
28 Received $3,000 cash from Gomez Co. on its receivable.
29 Reimbursed S. Rey for business automobile mileage
31 The company paid $1,500 cash in dividends.
The following additional facts are collected for use in making
- The December 31 inventory count of computer supplies shows $580 still available.
- Three months have expired since the 12-month insurance premium was paid in advance.
- As of December 31, Lyn Addie has not been paid for four days of work at $125 per day.
- The computer system, acquired on October 1, is expected to have a four-year life with no salvage value.
- The office equipment, acquired on October 1, is expected to have a five-year life with no salvage value.
- Three of the four months' prepaid rent have expired.
- Prepare
journal entries to record each of the December transactions and events for Business Solutions.Post those entries to the accounts in the ledger. - Prepare adjusting entries to reflect a through f. Post those entries to the accounts in the ledger.
- Prepare an adjusted trial balance as of December 31, 2019.
- Prepare an income statement for the three months ended December 31,2019.
- Prepare a statement of
retained earnings for the three months ended December 31, 2019. - Prepare a balance sheet as of December 31,2019.
- Record and post the necessary closing entries as of December 31, 2019.
- Prepare a post-closing trial balance as of December 31,2019.
Check (3) Adjusted trial balance totals, $109,034
(6) Total assets, $83,460
(8) Post-closing trial balance totals, $85,110
Adjusting Entries: Adjusting entries are made at the end of the year to adjust the financial position of the enterprise according to accrual basis of accounting.
Accounting rules regarding journal entries:
- Balance increase when: Assets, losses and expenses get debited and liabilities, gains, and revenue get credited.
- Balance decrease when: Assets, losses and expenses get credited and liabilities, gains, and revenue get debited.
Journal Entries: It is a book of original entry. It records and summarizes financial transaction of an entity in chronological manner, generally according to dual aspect of accounting.
Adjusted Trial Balance: It is a statement which contain balances of all account after all the adjusting entries has been made.
Income Statement: It is a financial statement which show the profit and loss made by the firm in a particular accounting period.
Retained Earnings: It is a financial statement which show the amount of profit retained by the company for their future unforeseen events.
Closing entries: These entries is made for those item whose balance need to be zero for next accounting period otherwise data of two accounting periods will get mix with each other.
Balance sheet: It shows the financial position of a firm. It consists of asset and liabilities.
1.
To prepare: Journal entries to record December transaction and posting them to ledger account.
Explanation of Solution
Solution:
Preparing journal entries:
Paid $1,025 for advertising cost:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 2 | Advertising Expense | 1,025 | ||
| Cash | 1,025 | |||
| (Being cash paid for advertising expense) |
Table (1)
- Advertising Expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit advertising expense account.
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is used to pay expense, asset is reduced. Hence, credit cash account.
Cash paid for minor repairs of the company’s computer:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 3 | Repair Expense | 500 | ||
| Cash | 500 | |||
| (Being cash spend on repairs) |
Table (2)
- Repair Expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit repair expense account.
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is used to pay expense, asset is reduced. Hence, credit cash account.
Cash received against the accounts receivable of November month:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 4 | Cash | 3,950 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 3,950 | |||
| (Being money received against accounts receivable ) |
Table (3)
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is received, it increases asset. Hence debit cash account
- Accounts receivable is an asset. Since, money is received, it reduces asset. Hence, credit accounts receivable account.
Paid cash for six days of work:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 10 | Wages Expense | 750 | ||
| Cash | 750 | |||
| (Being Wages paid for six days of work) |
Table (4)
- Wages Expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit wages expense account.
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is used to pay expense, asset is reduced. Hence, credit cash account.
Working notes:
Calculation of six days of wages,
Cash received in advance for a project:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 14 | Cash | 1,500 | ||
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |||
| (Being money received but not earned yet ) |
Table (5)
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is received, it increases asset. Hence debit cash account
- Unearned computer service revenue is a liability. Since, money is received but not earned yet, it increases liability. Hence, credit unearned computer service revenue account.
Purchased computer supplies on credit:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 15 | Computer supplies | 1,100 | ||
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |||
| (Being computer supplies purchased on credit ) |
Table (6)
- Computer supplies are an asset. Since, computer supplies is purchased, it increases asset. Hence debit computer supplies account.
- Accounts payable is a liability. Since, computer supplies is purchased but not paid yet, it increases liability. Hence, credit accounts payable account.
Sent a reminder to G. Company for payment of fees:
No entry, because it is just a reminder and no quantitative transaction occurred.
Cash received as a payment of a project:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 20 | Cash | 5,625 | ||
| Computer service revenue | 5,625 | |||
| (Being money received on completion of a project ) |
Table (7)
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is received, it increases asset. Hence debit cash account.
- Computer service revenue is an income. Since, money is received and earned, it increases income. Hence, credit computer service revenue account.
Took the week off for holidays:
No entry, because business was close due to holidays and no quantitative transaction occurred.
Cash received against the accounts receivable:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 28 | Cash | 3,000 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 3,000 | |||
| (Being money received against accounts receivable ) |
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is received, it increases asset. Hence debit cash account
- Accounts receivable is an asset. Since, money is received, it reduces asset. Hence, credit accounts receivable account.
Reimbursed S.R for business automobile mileage:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 29 | Mileage expense | 192 | ||
| Cash | 192 | |||
| (Being dividends paid using cash) |
Table (9)
- Mileage expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit mileage expense account.
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is used to pay mileage expense, asset is reduced. Hence, credit cash account.
Working notes:
Calculation of mileage expense,
Company paid $1,500 cash as dividends:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Dividends | 1,500 | ||
| Cash | 1,500 | |||
| (Being dividends paid using cash) |
Table (10)
- Dividend is distributed among shareholders. Since, it reduces equity, debit dividends account
- Cash is an asset. Since, cash is used to pay dividend, asset is reduced. Hence, credit cash account.
Post journal entries to ledger account:
| Cash Acct. No. 101 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 38,264 | 38,264 | ||
| December 2 | Advertising expense | 1,025 | 37,239 | ||
| December 3 | Repairs expense | 500 | 36,739 | ||
| December 4 | Accounts receivable | 3,950 | 40,689 | ||
| December 10 | Salary expense | 750 | 39,939 | ||
| December 14 | Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | 41,439 | ||
| December 20 | Computer service revenue | 5,625 | 47,064 | ||
| December 28 | Accounts receivable | 3,000 | 50,064 | ||
| December 29 | Mileage expense | 192 | 49,872 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 1,500 | 48,372 | ||
Table (11)
The ending balance is $48,372.
| Accounts Receivable Acct. No. 106 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 12,618 | 12,618 | ||
| December 4 | Cash | 3,950 | 8,668 | ||
| December 28 | Cash | 3,000 | 5,668 | ||
Table (12)
The ending balance is $5,668.
| Computer Supplies Acct. No. 126 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,545 | 2,545 | ||
| December 15 | Accounts payable | 1,100 | 3,645 | ||
Table (13)
The ending balance is $3,645.
| Prepaid Insurance Acct. No. 128 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,220 | 2,220 | ||
Table (14)
The ending balance is $2,220.
| Prepaid Rent Acct. No. 131 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 3,300 | 3,300 | ||
Table (15)
The ending balance is $3,300.
| Office Equipment Acct. No. 163 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 8,000 | 8,000 | ||
Table (16)
The ending balance is $8,000.
| Accumulated depreciation Office Equipment Acct. No. 164 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (17)
The ending balance is $0.
| Computer Equipment Acct. No. 167 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 20,000 | 20,000 | ||
Table (18)
The ending balance is $20,000.
| Accumulated depreciation Computer Equipment Acct. No. 168 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (19)
The ending balance is $0.
- Accounts Payable Acct. No. 201
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 15 | Computer supplies | 1,100 | 1,100 |
Table (20)
The ending balance is $1,100.
| Wages Payable Acct. No. 210 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (21)
The ending balance is $0.
| Unearned computer servicerevenue account Acct. No. 236 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 14 | Cash | 1,500 | 1,500 | ||
Table (22)
The ending balance is $1,500.
| Common Stock Acct. No. 307 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 73,000 | 73,000 | ||
Table (23)
The ending balance is $73,000.
| Retained Earnings Acct. No. 318 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (24)
The ending balance is $0.
| Dividends Acct. No. 319 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 5,600 | 5,600 | ||
| December 31 | Cash | 1,500 | 4,100 | ||
Table (25)
The ending balance is $4,100.
| Computer service revenue Acct. No. 403 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 25,659 | 25,659 | ||
| December 20 | Cash | 5,625 | 31,284 | ||
Table (26)
The ending balance is $31,284.
| Depreciation ExpenseOffice equipment Acct. No. 612 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (27)
The ending balance is $0.
| Depreciation ExpenseComputer equipment Acct. No. 613 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (28)
The ending balance is $0.
| Wages Expense Acct. No. 623 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,625 | 2,625 | ||
| December 10 | Cash | 750 | 3,375 | ||
Table (29)
The ending balance is $3,375.
| Insurance Expense Acct. No. 637 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (30)
The ending balance is $0.
| Rent Expense Acct. No. 640 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (31)
The ending balance is $0.
| Computer Supplies Expense Acct. No. 652 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (32)
The ending balance is $0.
| Advertising Expense Acct. No. 655 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 1,728 | 1,728 | ||
| December 2 | Cash | 1,025 | 2,753 | ||
Table (33)
The ending balance is $2,753.
| Mileage Expense Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 704 | 704 | ||
| December 29 | Cash | 192 | 896 | ||
Table (34)
The ending balance is $896.
| Miscellaneous Expense Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 250 | 250 | ||
Table (35)
The ending balance is $250.
| Repairs Expense-Computer Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 805 | 0 | ||
| December 3 | Cash | 500 | 1305 | ||
Table (36)
The ending balance is $1,305.
2.
To prepare: Adjusting entries.
Explanation of Solution
Solution:
a.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Computer Supplies Expense | 3,065 | ||
| Computer Supplies | 3,065 | |||
| (Being $3,065 worth of computer Supplies got exhausted) |
Table (37)
- Computer supplies expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit computer supplies expense account.
- Computer supplies are an asset. Since, some of asset used up, it reduces asset. Hence, credit computer supply account.
Working note:
Calculation of computer supply expense,
b.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Insurance Expense | 555 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | 555 | |||
| (Being insurance coverage worth $555has expired) |
Table (38)
- Insurance expense is a expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit insurance expense account.
- Prepaid Insurance is an asset. Since, some of the insurance is used up, it reduces asset. Hence, credit prepaid insurance account.
Working Note:
Calculation of Insurance expense,
c.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Wages Expense | 500 | ||
| Wages Payable | 500 | |||
| (Being salaries worth $600 due to be paid) |
Table (39)
- Wages expense is a expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit wages expense account.
- Wages Payable is a liability. Since, expense has occurred but not paid yet, it increases liability. Hence, credit wages payable account.
Working note:
Calculation of salary expense,
d.
To prepare: Adjusting entry.
Explanation of Solution
Solution:
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Depreciation Expense-Computer Equipment | 1,250 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation-Computer Equipment | 1,250 | |||
| (Being depreciation is recorded) |
Table (40)
- Depreciation Expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit depreciation expense-computer equipment account.
- Accumulated Depreciation-Computer equipment is a Contra asset. Since, it has a normal credit balance. Hence, credit accumulated depreciation-computer equipment account.
Working note:
Calculation of depreciation expense,
e.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Depreciation Expense-Office Equipment | 400 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation- Office Equipment | 400 | |||
| (Being depreciation is recorded) |
Table (41)
- Depreciation Expense is an expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit depreciation expense-office equipment account.
- Accumulated Depreciation-Office equipment is a Contra asset. Since, it has a normal credit balance. Hence, credit accumulated depreciation-office equipment account.
Working note:
Calculation of depreciation expense,
f.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| December 31 | Rent Expense | 2,475 | ||
| Prepaid Rent | 2,475 | |||
| (Being insurance coverage worth $2,475has expired) |
Table (42)
- Rent expense is a expense. Since, expense reduces equity, debit rent expense account.
- Prepaid rent is an asset. Since, some of the rent is used up, it reduces asset. Hence, credit prepaid rent account.
Working note:
Calculation of rent expense,
Post adjusting entries to ledger account:
| Cash Acct. No. 101 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 38,264 | 38,264 | ||
| December 2 | Advertising expense | 1,025 | 37,239 | ||
| December 3 | Repairs expense | 500 | 36,739 | ||
| December 4 | Accounts receivable | 3,950 | 40,689 | ||
| December 10 | Salary expense | 750 | 39,939 | ||
| December 14 | Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | 41,439 | ||
| December 20 | Computer service revenue | 5,625 | 47,064 | ||
| December 28 | Accounts receivable | 3,000 | 50,064 | ||
| December 29 | Mileage expense | 192 | 49,872 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 1,500 | 48,372 | ||
Table (43)
The ending balance is $48,372.
| Accounts Receivable Acct. No. 106 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 12,618 | 12,618 | ||
| December 4 | Cash | 3,950 | 8,668 | ||
| December 28 | Cash | 3,000 | 5,668 | ||
Table (44)
The ending balance is $5,668.
| Computer Supplies Acct. No. 126 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,545 | 2,545 | ||
| December 15 | Accounts payable | 1,100 | 3,645 | ||
| December 31 | Computer supplies expense | 3065 | 580 | ||
Table (45)
The ending balance is $580.
| Prepaid Insurance Acct. No. 128 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,220 | 2,220 | ||
| December 31 | Insurance expense | 555 | 1,665 | ||
Table (46)
The ending balance is $1,665.
| Prepaid Rent Acct. No. 131 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 3,300 | 3,300 | ||
| December 31 | Rent expense | 2,475 | 825 | ||
Table (47)
The ending balance is $825.
| Office Equipment Acct. No. 163 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 8,000 | 8,000 | ||
Table (48)
The ending balance is $8,000.
| Accumulated depreciation Office Equipment Acct. No. 164 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Depreciation expense-Office equipment | 400 | 400 | ||
Table (49)
The ending balance is $400.
| Computer Equipment Acct. No. 167 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 20,000 | 20,000 | ||
Table (50)
The ending balance is $20,000.
| Accumulated depreciation Computer Equipment Acct. No. 168 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Depreciation expense-computer equipment | 1,250 | 1,250 | ||
Table (51)
The ending balance is $1,250.
| Accounts Payable Acct. No. 201 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 15 | Computer supplies | 1,100 | 1,100 | ||
Table (52)
The ending balance is $1,100.
| Wages Payable Acct. No. 210 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Wages expense | 500 | 500 | ||
Table (53)
The ending balance is $600.
| Unearned computer servicerevenue account Acct. No. 236 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 14 | Cash | 1,500 | 1,500 | ||
Table (54)
The ending balance is $1,500.
| Common Stock Acct. No. 307 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 73,000 | 73,000 | ||
Table (55)
The ending balance is $73,000.
| Retained Earnings Acct. No. 318 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
Table (56)
The ending balance is $0.
| Dividends Acct. No. 319 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 5,600 | 5,600 | ||
| December 31 | Cash | 1,500 | 7,100 | ||
Table (57)
The ending balance is $7,100.
| Computer service revenue Acct. No. 403 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 25,659 | 25,659 | ||
| December 20 | Cash | 5,625 | 31,284 | ||
Table (58)
The ending balance is $31,284.
| Depreciation ExpenseOffice equipment Acct. No. 612 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Accumulated depreciation-Office Equipment | 400 | 400 | ||
Table (59)
The ending balance is $400.
| Depreciation ExpenseComputer equipment Acct. No. 613 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Accumulated depreciation-Computer Equipment | 1,250 | 1,250 | ||
Table (60)
The ending balance is $1,250.
| Wages Expense Acct. No. 623 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,625 | 2,625 | ||
| December 10 | Cash | 750 | 3,375 | ||
| December 31 | Wages payable | 500 | 3,875 | ||
Table (61)
The ending balance is $3,875.
| Insurance Expense Acct. No. 637 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid insurance | 555 | 555 | ||
Table (62)
The ending balance is $555.
| Rent Expense Acct. No. 640 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid rent | 2,475 | 2,475 | ||
Table (63)
The ending balance is $2,475.
| Computer Supplies Expense Acct. No. 652 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Computer supplies | 3,065 | 3,065 | ||
Table (64)
The ending balance is $3,065.
| Advertising Expense Acct. No. 655 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 1,728 | 1,728 | ||
| December 2 | Cash | 1,025 | 2,753 | ||
Table (65)
The ending balance is $2,753.
| Mileage Expense Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 704 | 704 | ||
| December 29 | Cash | 192 | 896 | ||
Table (66)
The ending balance is $896.
| Miscellaneous Expense Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 250 | 250 | ||
Table (67)
The ending balance is $250.
| Repairs Expense-Computer Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 805 | 0 | ||
| December 3 | Cash | 500 | 1,305 | ||
Table (68)
The ending balance is $1,305.
3.
To prepare: An adjusted trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
| B.S. Company | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| For the three month ended December 31, 2017 | ||
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer Supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,665 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 825 | |
| Office equipment | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- Office equipment | 400 | |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- Computer equipment | 1,250 | |
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages Payable | 500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| Common Stock | 73,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 0 | |
| Dividends | 7,100 | |
| Computer service revenue | 31,284 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Office equipment | 400 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Computer equipment | 1,250 | |
| Wages Expenses | 3,875 | |
| Insurance Expense | 555 | |
| Rent Expenses | 2,475 | |
| Computer Supply Expense | 3,065 | |
| Advertising Expense | 2,753 | |
| Mileage expense | 896 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 250 | |
| Repairs expense | 1,305 | |
| Total | 109,034 | 109,034 |
Table (69)
Thus, the total of adjusted trial balance on 31thDecember, 2017 is $109,034 .
4.
To prepare: Income statement.
Explanation of Solution
| B.S. Company | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the three month ended December 31, 2017 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Revenue: | ||
| Service Revenue | 31,284 | |
| Total Revenue | 31,284 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Depreciation Expense- Office equipment | 400 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Computer equipment | 1,250 | |
| Wages Expenses | 3,875 | |
| Insurance Expense | 555 | |
| Rent Expenses | 2,475 | |
| Computer Supply Expense | 3,065 | |
| Advertising Expense | 2,753 | |
| Mileage expense | 896 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 250 | |
| Repairs expense | 1,305 | 16,824 |
| Net income | 14,460 | |
Table (70)
Thus, net income of B.S. Company is $14,460 .
5.
To prepare: Retained Earnings Statement.
Explanation of Solution
| B.S. Company | ||
| Retained Earnings Statement | ||
| For the three month ended December 31, 2017 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | |
| Opening balance | 0 | |
| Net income | 14,460 | |
| Dividends | (7,100) | |
| Retained earnings | 7,360 | |
Table (71)
Therefore, retained earnings of B.S. Company are $7,360 .
6.
To prepare: Balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
| B.S. Company | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| December 31, 2017 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer Supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,665 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 825 | |
| Office equipment | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- Office equipment | (400) | 7,600 |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- Computer equipment | (1,250) | 18,750 |
| Total Assets | 83,460 | |
| Liabilities and Stockholder’s Equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages Payable | 500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| Stockholder’s Equity | ||
| Common Stock | 73,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 7,360 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 80,360 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholder’s equity | 83,460 | |
Table (72)
Thus, the balance sheet total is $83,460.
7.
To prepare: Closing entries.
Explanation of Solution
Service Revenue transfer to income summary account for closing.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| July 31 | Service Revenue | 31,284 | ||
| Income Summary | 31,284 | |||
| (Being service revenue transfer to income summary account) |
Table (73)
- Service revenue is revenue account. Since, revenue is transferred to income summary account, it reduces revenue. Hence, debit service revenue account.
- Income summary is a temporary account. Since, it is used for closing revenue account. Hence, credit income summary account.
All expenses transfer to income summary account for closing.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| July 31 | Income summary | 16,824 | ||
| Depreciation Expense- Office equipment | 400 | |||
| Depreciation Expense- Computer equipment | 1,250 | |||
| Wages Expenses | 3,875 | |||
| Insurance Expense | 555 | |||
| Rent Expenses | 2,475 | |||
| Computer Supply Expense | 3,065 | |||
| Advertising Expense | 2,753 | |||
| Mileage expense | 896 | |||
| Miscellaneous Expense | 250 | |||
| Repairs expense | 1,305 | |||
| (Being all expenses transfer to income summary account) |
Table (74)
- Income summary is a temporary account. Since, it is used for closing expense account. Hence, debit income summary account.
- All expenses are expenses. Since, expenses are transferred to income summary account, expenses is reduced. Hence, credit all expenses account
Income Summary transfer to income summary account for closing.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| July 31 | Income Summary | 14,460 | ||
| Retained Earning | 14,460 | |||
| (Being net income transfer to retained earnings) |
Table (75)
- Income summary is a temporary account. Since, it is used for transferring net income summary to retained account. Hence, debit income summary account.
- Retained earnings come under stockholder’s equity. Since, retained earning has increased. Hence, credit retained earning account.
Deduct dividend from retained earnings.
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| July 31 | Retained Earning | 7,100 | ||
| Dividend | 7,100 | |||
| (Being dividend distributed) |
Table (76)
- Retained earnings come under stockholder’s equity. Since, retained earnings is used to pay dividend, retained earnings has decreased. Hence, debit retained earnings account.
- Dividend is distributed from profit. Since it reduces retained earnings. Hence, credit dividend account.
Post closing entries to ledger account:
| Cash Acct. No. 101 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 38,264 | 38,264 | ||
| December 2 | Advertising expense | 1,025 | 37,239 | ||
| December 3 | Repairs expense | 500 | 36,739 | ||
| December 4 | Accounts receivable | 3,950 | 40,689 | ||
| December 10 | Salary expense | 750 | 39,939 | ||
| December 14 | Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | 41,439 | ||
| December 20 | Computer service revenue | 5,625 | 47,064 | ||
| December 28 | Accounts receivable | 3,000 | 50,064 | ||
| December 29 | Mileage expense | 192 | 49,872 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 1,500 | 48,372 | ||
Table (77)
The ending balance is $48,372.
| Accounts Receivable Acct. No. 106 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 12,618 | 12,618 | ||
| December 4 | Cash | 3,950 | 8,668 | ||
| December 28 | Cash | 3,000 | 5,668 | ||
Table (78)
The ending balance is $5,668.
| Computer Supplies Acct. No. 126 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,545 | 2,545 | ||
| December 15 | Accounts payable | 1,100 | 3,645 | ||
| December 31 | Computer supplies expense | 3065 | 580 | ||
Table (79)
The ending balance is $580.
| Prepaid Insurance Acct. No. 128 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,220 | 2,220 | ||
| December 31 | Insurance expense | 555 | 1,665 | ||
Table (80)
The ending balance is $1,665.
| Prepaid Rent Acct. No. 131 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 3,300 | 3,300 | ||
| December 31 | Rent expense | 2,475 | 825 | ||
Table (81)
The ending balance is $825.
| Office Equipment Acct. No. 163 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 8,000 | 8,000 | ||
Table (82)
The ending balance is $8,000.
| Accumulated depreciation Office Equipment Acct. No. 164 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Depreciation expense-Office equipment | 400 | 400 | ||
Table (83)
The ending balance is $400.
| Computer Equipment Acct. No. 167 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 20,000 | 20,000 | ||
Table (84)
The ending balance is $20,000.
| Accumulated depreciation Computer Equipment Acct. No. 168 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Depreciation expense-computer equipment | 1,250 | 1,250 | ||
Table (85)
The ending balance is $1,250.
| Accounts Payable Acct. No. 201 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 15 | Computer supplies | 1,100 | 1,100 | ||
Table (86)
The ending balance is $1,100.
| Wages Payable Acct. No. 210 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Wages expense | 500 | 500 | ||
Table (87)
The ending balance is $600.
| Unearned computer servicerevenue account Acct. No. 236 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 14 | Cash | 1,500 | 1,500 | ||
Table (88)
The ending balance is $1,500.
| Common Stock Acct. No. 307 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 73,000 | 73,000 | ||
Table (89)
The ending balance is $73,000.
| Retained Earnings Acct. No. 318 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 14,460 | |||
| December 31 | Dividends | 7,100 | 7,360 | ||
Table (90)
The ending balance is $7,360.
| Dividends Acct. No. 319 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 5,600 | 5,600 | ||
| December 31 | Cash | 1,500 | 7,100 | ||
| December 31 | Retained earnings | 7,100 | 0 | ||
Table (91)
The ending balance is $0.
| Computer service revenue Acct. No. 403 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 25,659 | 25,659 | ||
| December 20 | Cash | 5,625 | 31,284 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 31,284 | 0 | ||
Table (92)
The ending balance is $0.
| Depreciation ExpenseOffice equipment Acct. No. 612 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Accumulated depreciation-Office Equipment | 400 | 400 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 400 | 0 | ||
Table (93)
The ending balance is $0.
| Depreciation ExpenseComputer equipment Acct. No. 613 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Accumulated depreciation-Computer Equipment | 1,250 | 1,250 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 1,250 | 0 | ||
Table (94)
The ending balance is $0.
| Wages Expense Acct. No. 623 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 2,625 | 2,625 | ||
| December 10 | Cash | 750 | 3,375 | ||
| December 31 | Wages payable | 500 | 3,875 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 3,875 | 0 | ||
Table (95)
The ending balance is $0.
| Insurance Expense Acct. No. 637 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid insurance | 555 | 555 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 555 | 0 | ||
Table (96)
The ending balance is $0.
| Rent Expense Acct. No. 640 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid rent | 2,475 | 2,475 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 2,475 | 0 | ||
Table (97)
The ending balance is $0.
| Computer Supplies Expense Acct. No. 652 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 0 | 0 | ||
| December 31 | Computer supplies | 3,065 | 3,065 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 3,065 | 0 | ||
Table (98)
The ending balance is $0.
| Advertising Expense Acct. No. 655 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 1,728 | 1,728 | ||
| December 2 | Cash | 1,025 | 2,753 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 2,753 | 0 | ||
Table (99)
The ending balance is $0.
| Mileage Expense Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 704 | 704 | ||
| December 29 | Cash | 192 | 896 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 896 | 0 | ||
Table (100)
The ending balance is $0.
| Miscellaneous Expense Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 250 | 250 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 250 | 0 | ||
Table (101)
The ending balance is $0.
| Repairs Expense-Computer Acct. No. 684 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| December 1 | Balance b/f | 805 | 0 | ||
| December 3 | Cash | 500 | 1,305 | ||
| December 31 | Income summary | 1,305 | 0 | ||
Table (102)
The ending balance is $0.
8.
To prepare: Post closing trial balance.
Explanation of Solution
| B.S. Company | ||
| Post Closing Trial Balance | ||
| For the three month ended December 31, 2017 | ||
| Particulars | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Cash | 48,372 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 5,668 | |
| Computer Supplies | 580 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,665 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 825 | |
| Office equipment | 8,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- Office equipment | 400 | |
| Computer equipment | 20,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- Computer equipment | 1,250 | |
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Wages Payable | 500 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 1,500 | |
| Common Stock | 73,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 7,360 | |
| Dividends | 0 | |
| Computer service revenue | 0 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Office equipment | 0 | |
| Depreciation Expense- Computer equipment | 0 | |
| Wages Expenses | 0 | |
| Insurance Expense | 0 | |
| Rent Expenses | 0 | |
| Computer Supply Expense | 0 | |
| Advertising Expense | 0 | |
| Mileage expense | 0 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 0 | |
| Repairs expense | 0 | |
| Total | 85,110 | 85,110 |
Table (103)
Thus, the total of post closing trial balance on December 31, 2017 is $85,110 .
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING FUNDAMENTALS
- On October 1, 2019, Jay Pryor established an interior decorating business, Pioneer Designs. During the month, Jay completed the following transactions related to the business: Oct. 1. Jay transferred cash from a personal bank account to an account to be used for the business, 18,000. 4.Paid rent for period of October 4 to end of month, 3,000. 10.Purchased a used truck for 23,750, paying 3,750 cash and giving a note payable for the remainder. 13.Purchased equipment on account, 10,500. 14.Purchased supplies for cash, 2,100. 15.Paid annual premiums on property and casualty insurance, 3,600. 15.Received cash for job completed, 8,950. Enter the following transactions on Page 2 of the two-column journal: 21.Paid creditor a portion of the amount owed for equipment purchased on October 13, 2,000. 24.Recorded jobs completed on account and sent invoices to customers, 14,150. 26.Received an invoice for truck expenses, to be paid in November, 700. 27.Paid utilities expense, 2,240. 27.Paid miscellaneous expenses, 1,100. Oct. 29. Received cash from customers on account, 7,600. 30.Paid wages of employees, 4,800. 31.Withdrew cash for personal use, 3,500. Instructions 1. Journalize each transaction in a two-column journal beginning on Page 1, referring to the following chart of accounts in selecting the accounts to be debited and credited. (Do not insert the account numbers in the journal at this time.) Journal entry explanations may be omitted. 2. Post the journal to a ledger of four-column accounts, inserting appropriate posting references as each item is posted. Extend the balances to the appropriate balance columns after each transaction is posted. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance for Pioneer Designs as of October 31, 2019. 4. Determine the excess of revenues over expenses for October. 5. Can you think of any reason why the amount determined in (4) might not be the net income for October?arrow_forwardThe transactions completed by PS Music during June 2019 were described at the end of Chapter 1. The following transactions were completed during July, the second month of the businesss operations: July 1.Peyton Smith made an additional investment in PS Music by depositing 5,000 in PS Musics checking account. 1.Instead of continuing to share office space with a local real estate agency, Peyton decided to rent office space near a local music store. Paid rent for July, 1,750. 1.Paid a premium of 2,700 for a comprehensive insurance policy covering liability, theft, and fire. The policy covers a one-year period. 2.Received 1,000 cash from customers on account. 3.On behalf of PS Music, Peyton signed a contract with a local radio station, KXMD, to provide guest spots for the next three months. The contract requires PS Music to provide a guest disc jockey for 80 hours per month for a monthly fee of 3,600. Any additional hours beyond 80 will be billed to KXMD at 40 per hour. In accordance with the contract, Peyton received 7,200 from KXMD as an advance payment for the first two months. 3.Paid 250 to creditors on account. 4.Paid an attorney 900 for reviewing the July 3 contract with KXMD. (Record as Miscellaneous Expense.) 5.Purchased office equipment on account from Office Mart, 7,500. 8.Paid for a newspaper advertisement, 200. 11.Received 1,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 13.Paid 700 to a local audio electronics store for rental of digital recording equipment. 14.Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. Enter the following transactions on Page 2 of the two-column journal: 16.Received 2,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a wedding reception. 18.Purchased supplies on account, 850. July 21. Paid 620 to Upload Music for use of its current music demos in making various music sets. 22.Paid 800 to a local radio station to advertise the services of PS Music twice daily for the remainder of July. 23.Served as disc jockey for a party for 2,500. Received 750, with the remainder due August 4, 2019. 27.Paid electric bill, 915. 28.Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. 29.Paid miscellaneous expenses, 540. 30.Served as a disc jockey for a charity ball for 1,500. Received 500, with the remainder due on August 9, 2019. 31.Received 3,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 31.Paid 1,400 royalties (music expense) to National Music Clearing for use of various artists music during July. 31.Withdrew 1,250 cash from PS Music for personal use. PS Musics chart of accounts and the balance of accounts as of July 1, 2019 (all normal balances), are as follows: Instructions 1. Enter the July 1, 2019, account balances in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the Item column and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. (Hint: Verify the equality of the debit and credit balances in the ledger before proceeding with the next instruction.) 2. Analyze and journalize each transaction in a two-column journal beginning on Page 1, omitting journal entry explanations. 3. Post the journal to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting. 4. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance as of July 31, 2019.arrow_forwardThe transactions completed by PS Music during June 2019 were described at the end of Chapter 1. The following transactions were completed during July, the second month of the business's operations: July 1. Peyton Smith made an additional investment in PS Music by depositing 5,000 in PS Music's checking account. 1. Instead of continuing to share office space with a local real estate agency, Peyton decided to rent office space near a local music: store. Paid rent for July, 1,750. 1. Paid a premium of 2,700 for a comprehensive insurance policy covering liability, theft, and fire. The policy covers a one-year period. 2. Received 1,000 cash from customers on account. 3. On behalf of PS Music, Peyton signed a contract with a local radio station, KXMD, to provide guest spots for the next three months. The contract requires PS Music to provide a guest disc jockey for SO hours per month for a monthly fee of 3,600. Any additional hours beyond SO will be billed to KXMD at 40 per hour. In accordance with the contract, Peyton received 7,200 from KXMD as an advance payment for the first two months. 3. Paid 250 to creditors on account. 4. Paid an attorney 900 for reviewing the July 3 contract with KXMD. (Record as Miscellaneous Expense.) 5. Purchased office equipment on account from Office Mart, 7,500. 8. Paid for a newspaper advertisement, 200. 11. Received 1,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 13. Paid 700 to a local audio electronics store for rental of digital recording equipment. 11. Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. Enter the following transactions on Page 2 of the two-column journal: 16. Received 2,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a wedding reception. 18. Purchased supplies on account, 850. July 21. Paid 620 to Upload Music for use of its current music demos in making various music sets. 22. Paid 800 to a local radio station to advertise the services of PS Music twice daily for the remainder of July. 23. Served as disc jockey for a party for 2,500. Received 750, with the remainder due August 4, 2019. 27. Paid electric bill, 915. 28. Paid wages of 1,200 to receptionist and part-time assistant. 29. Paid miscellaneous expenses, 540. 30. Served as a disc jockey for a charity ball for 1,500. Received 500, with the remainder due on August 9, 2019. 31. Received 3,000 for serving as a disc jockey for a party. 31. Paid 1,400 royalties (music expense) to National Music Clearing for use of various artists' music during July. 31. Withdrew l,250 cash from PS Music for personal use. PS Music's chart of accounts and the balance of accounts as of July 1, 2019 (all normal balances), are as follows: 11 Cash 3,920 12 Accounts receivable 1,000 14 Supplies 170 15 Prepaid insurance 17 Office Equipment 21 Accounts payable 250 23 Unearned Revenue 31 Peyton smith, Drawing 4,000 32 Fees Earned 500 41 Wages Expense 6,200 50 Office Rent Expense 400 51 Equipment Rent Expense 800 52 Utilities Expense 675 53 Supplies Expense 300 54 music Expense 1,590 55 Advertising Expense 500 56 Supplies Expense 180 59 Miscellaneous Expense 415 Instructions 1.Enter the July 1, 2019, account balances in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the Item column and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. (Hint: Verify the equality of the debit and credit balances in the ledger before proceeding with the next instruction.) 2.Analyze and journalize each transaction in a two-column journal beginning on Page 1, omitting journal entry explanations. 3.Post the journal to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting. 4.Prepare an unadjusted trial balance as of July 31, 2019.arrow_forward
- Reece Financial Services Co., which specializes in appliance repair services, is owned and operated by Joni Reece. Reece Financial Services accounting clerk prepared the following unadjusted trial balance at July 31, 2019: The data needed to determine year-end adjustments are as follows: Depreciation of building for the year, 6,400. Depreciation of equipment for the year, 2,800. Accrued salaries and wages at July 31, 900. Unexpired insurance at July 31, 1,500. Fees earned but unbilled on July 31, 10,200. Supplies on hand at July 31, 615. Rent unearned at July 31, 300. Instructions 1. Journalize the adjusting entries using the following additional accounts: Salaries and Wages Payable, Rent Revenue, Insurance Expense, Depreciation ExpenseBuilding, Depreciation ExpenseEquipment, and Supplies Expense. 2. Determine the balances of the accounts affected by the adjusting entries and prepare an adjusted trial balance.arrow_forwardElite Realty acts as an agent in buying, selling, renting, and managing real estate. The unadjusted trial balance on March 31, 2019, follows: The following business transactions were completed by Elite Realty during April 2019: Apr. 1. Paid rent on office for month, 6,500. 2.Purchased office supplies on account, 2,300. 5.Paid insurance premiums, 6,000. 10.Received cash from clients on account, 52,300. 15.Purchased land for a future building site for 200,000, paying 30,000 in cash and giving a note payable for the remainder. 17.Paid creditors on account, 6,450. 20.Returned a portion of the office supplies purchased on April 2, receiving full credit for their cost, 325. 23.Paid advertising expense, 4,300. Enter the following transactions on Page 19 of the two-column journal: 27.Discovered an error in computing a commission; received cash from the salesperson for the overpayment, 2,500. 28.Paid automobile expense (including rental charges for an automobile), 1,500. 29.Paid miscellaneous expenses, 1,400. 30.Recorded revenue earned and billed to clients during the month, 57,000. 30.Paid salaries and commissions for the month, 11,900. 30.Withdrew cash for personal use, 4,000. 30.Rented land purchased on April 15 to local merchants association for use as a parking lot in May and June, during a street rebuilding program; received advance payment of 10,000. Instructions 1. Record the April 1, 2019, balance of each account in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account, write Balance in the item section, and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. 2. Journalize the transactions for April in a two-column journal beginning on Page 18. Journal entry explanations may be omitted. 3. Post to the ledger, extending the account balance to the appropriate balance column after each posting. 4. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance of the ledger as of April 30, 2019. 5. Assume that the April 30 transaction for salaries and commissions should have been 19,100. (a) Why did the unadjusted trial balance in (4) balance? (b) Journalize the correcting entry. (c) Is this error a transposition or slide?arrow_forwardOn July 1, a client paid an advance payment (retainer) of $5,000 to cover future legal services. During the period, the company completed $3,500 of the agreed-on services for the client. There was no beginning balance in the Unearned Revenue account for the period. Based on the information provided, A. Make the December 31 adjusting journal entry to bring the balances to correct. B. Show the impact that these transactions had.arrow_forward
- Good Note Company specializes in the repair of music equipment and is owned and operated by Robin Stahl. On November 30, 2019, the end of the current year, the accountant for Good Note prepared the following trial balances: Instructions Journalize the seven entries that adjusted the accounts at November 30. None of the accounts were affected by more than one adjusting entry.arrow_forwardOn October 31, the Vermillion Igloos Hockey Club received 800,000 in cash in advance for season tickets for eight home games. The transaction was recorded as a debit to Cash and a credit to Unearned Admissions. By December 31, the end of the fiscal year, the team had played three home games and received an additional 450,000 cash admissions income at the gate. a. Journalize the adjusting entry as of December 31. b. List the title of the account and the related balance that will appear on the income statement. c. List the title of the account and the related balance that will appear on the balance sheet.arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning  Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





