
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577213
Author: Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 30, Problem 30.6QAP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
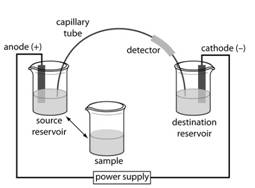
The time taken by the analyte cation to reach the detector needs to be determined, where the osmotic flow rate is given as 0.85mm/s and detector is placed 40cm from the injection end of capillary.
Concept introduction:
The instrumentation needs for capillary electrophoresis includes electric field, cathode and anode compartments which would contain the buffer solution and small vial that contains the sample, capillary tube and detector.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A 0.0200 gram blood sample was decomposed by a microwave digestion technique followed by dilution to 100.0 mL in a volumetric flask. Aliquots of the sample solution were treated with a lead complexing reagent and water as follows: Solution 1: 10.0 ml blood sample + 20.0 mL complexing agent + 30.0 mL H20. Solution 2: 10.0 ml blood sample + 20.0 mL complexing agent + 26.0 mL H20 + 4.00 mL of 78 ppb Pb2+ standard. The resulting solutions were analyzed by UV/Vis at 375 nm. Absorbance for solution 1 = 0.155 and for solution 2 = 0.216. Calculate the concentration of lead (ppb) in the original sample.
The data below was obtained with a Cl- ISE to prepare a plot of mV vs. log[Cl-]. Assume the unknown saltwater solution was diluted as in the procedure before being measured. What is the ppm Cl- of the undiluted unknown solution?
Cl- Concentration (ppm)
Potential (mV)
10
160
100
94
1000
40
Diluted Unknown Saltwater
132
An analyst wants to find out the active surface of his electrode before conducting his analyzes. To do this, he carried out a series of measurements by cyclic voltammetry (CV) using a 1 mM solution of K4Fe(CN)6 dissolved in 0.1M NaCl. He recorded the anodic peak intensity (ip) corresponding to the oxidation of Fe(II) to Fe(III) as a function of the scanning speed (v) of the CV (see table). What is the active surface of the electrode?
Data: Fe diffusion coefficient (CN)64-, D = 6.67x10-6 cm2/s
Randles-Sevcik equation ip = (2,69x105)n3/2ACD1/2v1/2
rate (v/s)
ip (A)
5,00E-02
5,75E-05
1,00E-01
7,68E-05
2,00E-01
9,94E-05
5,00E-01
1,42E-04
1,00E+00
2,07E-04
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Ali has measured the oxidative stability of palm oil sample under accelerated storage condition at 60*C for 6 days The following data were recorded for the peroxide value and p anisidine value of the palm oil after 5 days of storage time: Sample weight 1.0030 g Concentration of NazSzO3 = 0.001 N Volume of NazSzO3 titrated for sample solution = 1.35 ml Volume of NazSzO3 titrated for blank solution 0.20 ml Absorbance for sample solution = 0.907 Absorbance for blank solution 0.203 Calculate: i) peroxide value ii) p-anisidine value iii) TOTOX valuearrow_forwardFor Indirect Iodometric Analysis of Copper... ~0.0896g KIO3 necessary to consume 350mL of 0.1 M Na2S2O3, Na2S2O3 is stored in an amber glass bottle until ready for use. Primary Standard KIO3 has 2g of KI, 50mL of DI water, and 10 mL of 1.0M HCl is added then immediately titrated with Na2S2O3 until medium yellow or straw... then 5mL of starch indicator is added and titrated again until blue black color turns clear. Unknown CuO use 1.2G of Unknown, 20mL of HNO3 heated until sample dissolved, 25 mL of DI water added and boiled until clear light blue color, after cooling 1:1 NH3 added (~34.47 mL of NH4OH reagent) until permanent deep blue color amine complex, 2g of NH4HF2 added and swirled until dissolved, 3 g of KI is added then titrated immediately with Na2S2O3 until brown color of iodide is nearly gone (brown milk color), 2 g of KSCN and 3 mL of starch indicator is then added with titration continuing until disappearance of new blue black color. 1. Na2CO3 is often added to thiosulfate…arrow_forwardFor Indirect Iodometric Analysis of Copper... ~0.0896g KIO3 necessary to consume 350mL of 0.1 M Na2S2O3, Na2S2O3 is stored in an amber glass bottle until ready for use. Primary Standard KIO3 has 2g of KI, 50mL of DI water, and 10 mL of 1.0M HCl is added then immediately titrated with Na2S2O3 until medium yellow or straw... then 5mL of starch indicator is added and titrated again until blue black color turns clear. Unknown CuO use 1.2G of Unknown, 20mL of HNO3 heated until sample dissolved, 25 mL of DI water added and boiled until clear light blue color, after cooling 1:1 NH3 added (~34.47 mL of NH4OH reagent) until permanent deep blue color amine complex, 2g of NH4HF2 added and swirled until dissolved, 3 g of KI is added then titrated immediately with Na2S2O3 until brown color of iodide is nearly gone (brown milk color), 2 g of KSCN and 3 mL of starch indicator is then added with titration continuing until disappearance of new blue black color. 4. Why is the starch indicator solution…arrow_forward
- Lead in dry river sediment was extracted with 25 wt% HNO3 at incubation temperatures for 1 hr. Then 1 mL of filtered extract was combined with other reagents to a total of 4.60 mL. Pb+2 was measured by an electrochemical method by spiking with 2.50 ppm Pb2+. added vol. of 2.50ppm Pb2 signal 0 mL 1.10 0.025 mL 1.66 .050 mL 2.20 .075 mL 2.81 what is Sx based on Syarrow_forwardThe concentration of purified OXA-M290 is tested with a BCA assay. Serial dilutions of a bovine serum albumin (BSA) stock solution are prepared, then pipetted into a 96-well plate; each dilution of the BSA standard is tested in triplicate. Then, bicinchoninic acid and Cu2+ ions are added to all of the wells of the plate. After incubating the plate for 1 hour, a microplate reader is used to measure the absorbance of all of the wells in the plate at 560 nm. This generates the following data: BSA conc. (μg/mL), Replicate 1 Absorbance, Replicate 2 Absorbance, Replicate 3 Absorbance 40, 1.360, 1.403, 1.481 20, 0.750, 0.745, 0.810 10, 0.380, 0.344, 0.398 5, 0.198, 0.160, 0.183 2.5, 0.090, 0.100, 0.085 1.25, 0.038, 0.043, 0.051 0.625, 0.024, 0.028, 0.019 Prepare a calibration curve using these data. You can use Excel, R, SPSS or an equivalent graphing software. In this graph, plot absorbance (y-axis) against the concentration of the protein standard (x-axis). Calculate and plot…arrow_forwardA sample of body serum is to be analysed for sodium by flame emission spectroscopy. 1.00cm' aliquot of serum was pipetted into each of two 50.0cm' volumetric flasks. The first flask was diluted to volume with deionised water. The absorbance of this first solution was0.350. To the second flask 10.0 cm' of a 25.0 ppm sodium standard was added and the flask made up to volume with deionised water. The absorbance of this second solution was 0.720.(i) Calculate the concentration of the sodium in the body serum in mg dm-3.arrow_forward
- Determine the relationship between the observed/apparent value (EX) VERSUS that of the true value (ET) for the quantity being sought by writing either <, >, or = on the space provided Determination of the true concentration (ppm Fe) in a water sample using the iron-phenanthroline method. Dilution factor was not taken into account. EX _____ 1ETarrow_forwardQ) water hardness of each trial and average ppm with calculation, please. Hard Water Trial 1 Hard Water Trial 2 Hard Water Trial 3 Initial Syringe Reading 1.0ml 1.0ml 1.0ml Final Syringe Reading 0.88ml 0.84ml 0.85ml Volume of EDTA Consumed 0.12ml 0.16ml 0.15ml Water Hardness ppm CaCO3 Average ppmarrow_forwardCalculate the retardation factor (Rf) for dissolved Tetrachloroethene contamination given the bulk density of soil is 2.4 gm/cc, fraction organic content (foc) of soil is 0.005, and the Organic Carbon Partition Coefficient (Koc) is the number you look up in the table. HInt: Use Fetter Equation (Koc = Kd /foc to calculate Kd. Group of answer choices 1.4 to 2.7 l/gm 1.08 to 1.2 Cannot be calculated from given information. 3.25 to 4.5 1.05 to 1.2 l/gmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

