
Concept explainers
Figure P38.10 on the next page shows a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 575 nm incident on a slab of crown glass surrounded by air. Use a protractor to measure the angles of incidence and refraction. a. What is the speed of the beam of light within the glass slab? b. What is the frequency of the beam of light within the glass slab? c. What is the wavelength of the beam of light within the glass slab?
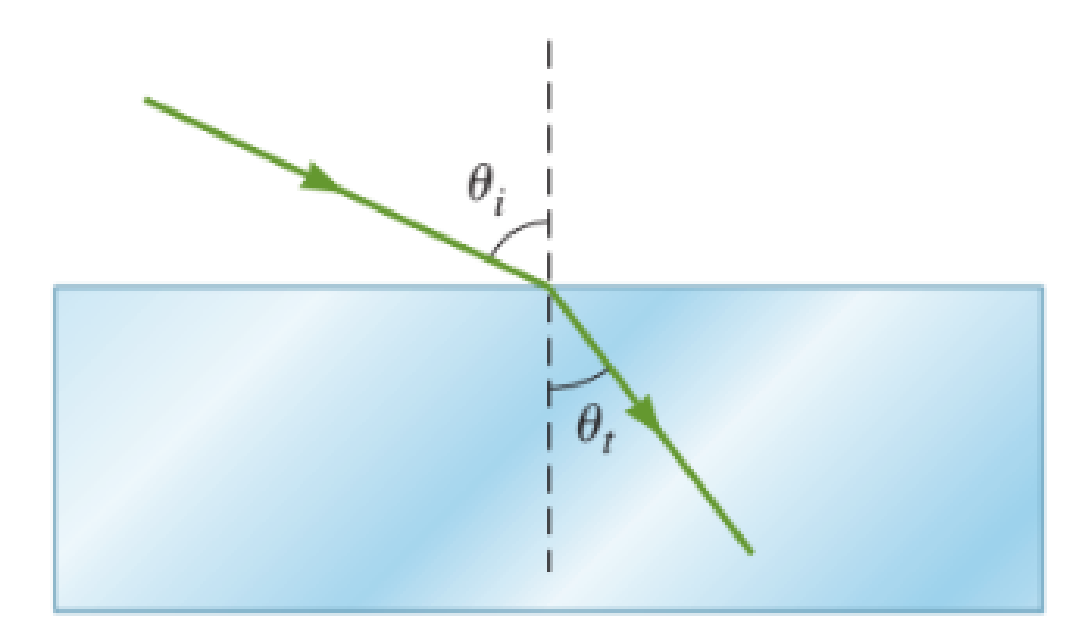
FIGURE P38.10
(a)
The speed of the beam of light within the glass slab.
Answer to Problem 10PQ
The speed of the beam of light within the glass slab is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression given by Snell’s for the light ray travelling in two different medium.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the speed of light.
Here,
Conclusion:
By the use of protractor the angle of incidence is measured as
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the speed of the beam of light within the glass slab is
(b)
The frequency of the beam of light within the glass slab.
Answer to Problem 10PQ
The frequency of the beam of light within the glass slab is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the frequency.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate the wavelength of the light travelling in the glass medium.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the frequency of the beam of light within the glass slab is
(c)
The wavelength of the beam of light within the glass slab.
Answer to Problem 10PQ
The wavelength of the beam of light within the glass slab is
Explanation of Solution
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, The wavelength of the beam of light within the glass slab is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 38 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- A technician directs a light ray through a transparent medium, toward one surface of an equilateral prism. (The ray travels, and remains in, the plane of the page.) Incident on Surface 1 at an angle ?1, the ray then encounters Surface 2 from within the prism. If the angle of incidence at Surface 2 equals ?c , the critical angle for this prism, what is the original incidence angle, ?1 (in degrees)? The critical angle in this case is ?c = 41.5°. answer in degreesarrow_forward(a) In the figure, light from ray A refracts from material 1 into a thin layer of material 2, crosses that layer, and is then incident at the critical angle on the interface between materials 2 and 3. (i) What is the value of incident angle θA? Draw a sketch of the situation. (ii) If θA is decreased, does part of the light refract into material 3? (b) Light from ray B refracts from material 1 into the thin layer, crosses that layer, and is then incident at the critical angle on the interface between materials 2 and 3. (iii) What is the value of incident angle θB? Draw a sketch of the situation. (iv) If θB is decreased, does part of the light refract into material 3? Answer: 54.3°, yes, 51.1°, noarrow_forwardA millipede sits 1.0 m in front of the nearest part of the surface of a shiny sphere of diameter 0.70 m. (a) How far from the surface does the millipede’s image appear? (b) If the millipede’s height is 2.0 mm,what is the image height? (c) Is the image inverted?arrow_forward
- A light source, S, is located 1.80 m below the surface of a swimming pool and 0.90 m from one edge of the pool. The pool is filled to the top with water.(a) At what angle does the light reaching the edge of the pool leave the water? °(b) What is the difference between the real depth and the apparent depth of the light source?arrow_forwardray of light strikes a flat block of glass at an incidence angle of ?1 = 38.6°. The glass is 2.00 cm thick and has an index of refraction that equals ng = 1.52. a.)What is the angle of refraction, ?2, that describes the light ray after it enters the glass from above? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) b.) With what angle of incidence, ?3, does the ray approach the interface at the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) c.) With what angle of refraction, ?4, does the ray emerge from the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 1 decimal place.) d.) The distance d separates the twice-bent ray from the path it would have taken without the glass in the way. What is this distance (in cm)? e.) At what speed (in m/s) does the light travel within the glass? f.) How many nanoseconds does the light take to pass through the glass along the angled path shown here?arrow_forwardA butterfly hovers 40 cm from a polished glass garden sphere of radius 10 cm. a) How far away will its image appear to the butterfly to be located? b) If the butterfly is 4 cm tall, how big will its reflection be?arrow_forward
- (a)What will be size of the angle of refraction if the index of refraction becomes smaller? (b)Among green, blue, and yellow block, when blue light is only on, which block reflects blue light? (c)In most materials, the smaller the wavelength of the light what will be the index of refraction?arrow_forwarda) A ray of light is incidented at angle of 30 degrees to the normal (perpendicular line or y-axis) to a surface of sea water.Using Snell’s Law,(i) Calculate the Reflected angle(ii) Calculate the Refracted angle(iii) Discuss the difference between the incidence angle and the refracted angle. b) If the same light ray in 3(a) above with the same incidence angle to a surface of Alcohol (propyl) and also using Snell’s Law,(i) Calculate the Reflected angle(ii) Calculate the Refracted angle(iii) Discuss your results and compare to the results in 3(a) above, and explain the differences.arrow_forwardA technician directs a beam of light through a transparent medium, toward one surface of an equilateral prism. (The beam travels, and remains in, the plane of the page.) Incident on Surface 1 at an angle ?1, the beam then encounters Surface 2 from within the prism. If the angle of incidence at Surface 2 equals ?c , the critical angle for this prism, what is the original incidence angle, ?1 (in degrees)? The critical angle in this case is ?c = 41.5°.arrow_forward
- A beam of white light is incident on the surface of a diamond at an angle θa�a.(Figure 1) Since the index of refraction depends on the light's wavelength, the different colors that comprise white light will spread out as they pass through the diamond. The indices of refraction in diamond are nred=2.410�red=2.410 for red light and nblue=2.450�blue=2.450 for blue light. The surrounding air has nair=1.000�air=1.000. Note that the angles in the figure are not to scale.arrow_forwardLight traveling through an optical fiber (n=1.44) reaches the end of the fiber and exits into air. (a) If the angle of incidence on the end of the fiber is 30o, what is the angle of refraction outside the fiber? (b) How would your answer be different if the angle of incidence were 50o?arrow_forwardAn optical fiber has an index of refraction n and diameter d. It is surrounded by vacuum. Light is sent into the fiber along its axis as shown. (a) Find the smallest outside radius Rmin permitted for a bend in the fiber if no light is to escape. (b) What If? What result does part (a) predict as d approaches zero? Is this behavior reasonable? Explain. (c) As n increases? (d) As n approaches 1? (e) Evaluate Rmin assuming the fiber diameter is 100 mm and its index of refraction is 1.40.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


