
(a)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
(a)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
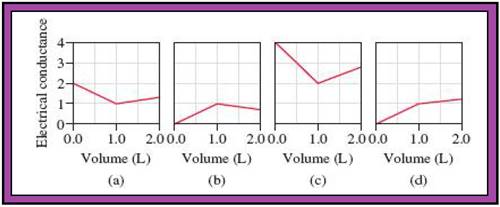
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
If Conductance unit of
(b)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
(b)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
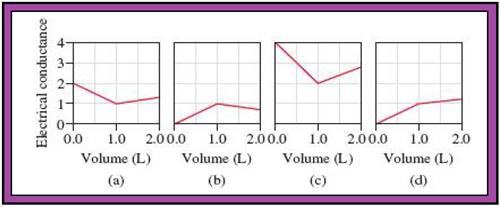
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(c)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
(c)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
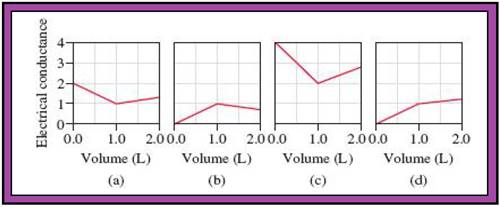
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(d)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
(d)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
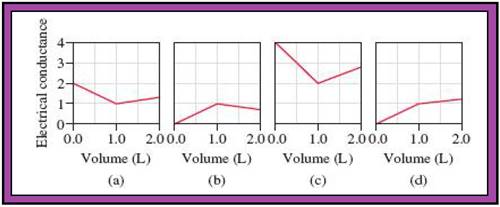
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(e)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
(e)
Answer to Problem 4.118SP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
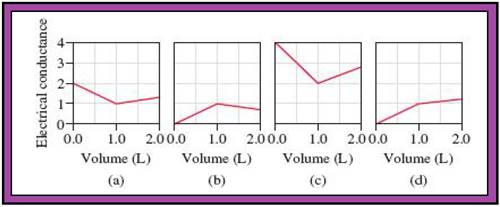
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
Match the calculated conductance unit of each reaction in given diagrams in Fig.1.
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
GENERAL CHEMISTRY LOOSE W/2SEM CONNECT
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





