
(a)
Interpretation:
The standard free energy of activation of reaction B is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The rate of the reaction is affected by the activation free energy of the reaction. The relationship between the activation free energy and
Where,
•
•
•
Answer to Problem 4.29P
The standard free energy of activation for reaction B is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that standard free energy of activation of reaction A is
The relative rates of two reactions are expressed as,
Where,
•
•
•
Substitute the activation energy for reaction A, the relative rate of A and B, gas constant and temperature in the given formula.
Rearrange the above equation for the calculation of activation energy of B as shown below.
Thus, standard free energy of activation for reaction B is
The standard free energy of activation for reaction B is
(b)
Interpretation:
The reaction free energy diagram for the two reactions showing the two values of
Concept introduction:
The transition state is formed during the conversion of reactants into products in the
Answer to Problem 4.29P
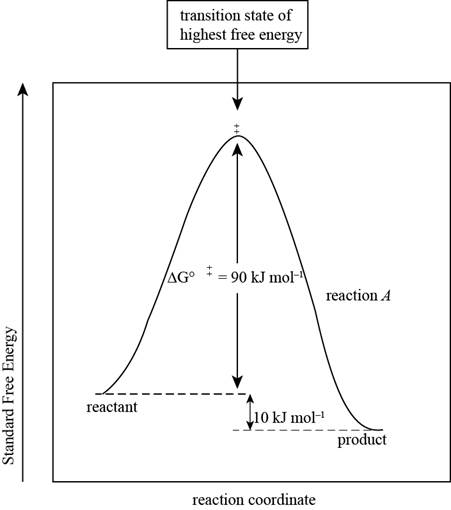
The reaction free-energy diagram for the reaction A showing the two values of
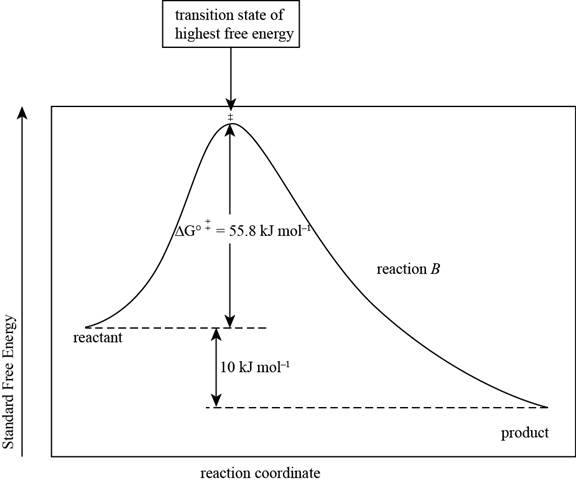
The reaction free-energy diagram for the reaction B showing the two values of
Explanation of Solution
It is given that standard free energy of activation of reaction A is
The reaction free-energy diagram for the reaction A showing the two values of
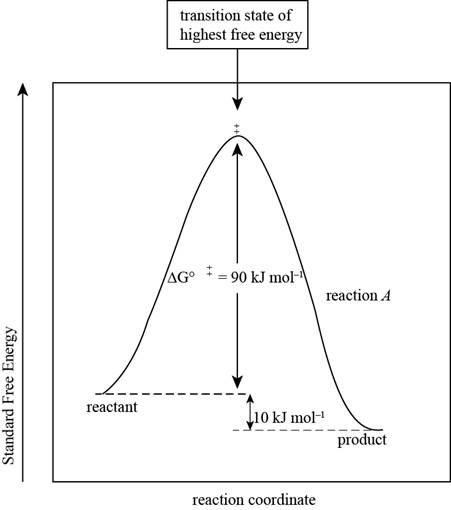
Figure 1
This diagram represents the plot between standard free energy and the reaction coordinates. The point at which the energy is maximum represents the transition state of the reaction.
The reaction free energy diagram for the reaction B showing the two values of
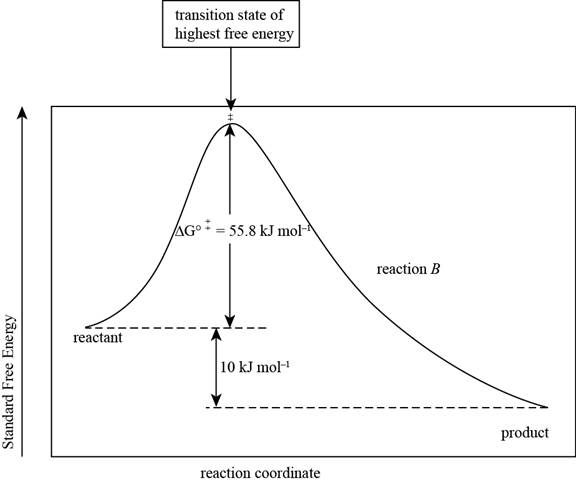
Figure 2
The reaction free-energy diagram for the two reactions showing the two values of
(c)
Interpretation:
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction in both reactions A and B is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The free energy diagram represents the plot between standard free energy and the reaction coordinates. The point at which the energy is maximum represents the transition state of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 4.29P
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction in both reactions A and B is
Explanation of Solution
It is given that standard free energy of activation of reaction A is
The products of each reaction are
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction A is,
Thus, the standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction A is
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction B is,
Thus, the standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction A is
The standard free energy of activation of the reverse reaction in both reactions A and B is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- The acid dissociation constant for a weak acid HX at 25°C is 1.9 10–6. Calculate the free energy of formation for X–(aq) at 25°C. The standard free energies of HX(aq) and H+(aq) at 25°C are –245.4 kJ/mol and 0, respectively.arrow_forwardWhat is the relationship between the standard free energy change and the equilibrium constant of the reaction?arrow_forwardChemistry determine enthalpy and entropy of activation.arrow_forward
- An important reaction in the production of energy from sugars (glycolysis) is the reduction of pyruvate to lactate by NADH. pyruvate + NADH + H+(aq) → lactate + NAD+ ΔrG°′ = ? Given the following reduction potentials, NAD+ + H+ + 2e− → NADH Ε°′ = −0.320 V pyruvate + 2H+ + 2e− → lactate Ε°′ = −0.190 V calculate the standard Gibbs free energy (at pH 7) for the reduction of pyruvate to lactate by NADH. (ΔrG°′ = −nFE°′; F = 96485 C/mol electrons)arrow_forwardIn addition, estimate the reaction enthalpy and predict the sign of reaction entropyarrow_forwardCalculate the free energy change that occurs when a reaction has an enthalpy of −315.2 kJ mol−1 and an entropy change of 224.7 J mol−1 K−1 at 211.3 ∘C. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction at this temperature? Will that constant increase or decrease as the temperature is increased?arrow_forward
- From the standard molar enthalpy of combustion of pentane at 298 K, calculate the value of Δr A° for the process. (For this reaction, ΔrH° = −3508.8 kJ·mol−1 and ΔrS° = −416.1 J·K−1·mol−1.)arrow_forwardThe standard free energy change for the reaction catalyzed by phosphoglucomutase is -7.1kJ/mol, (a) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction, (b) Calculate ΔG at 37°C when the concentration of glucose-1-phosphate is 1-mM and the concentration of glucose-6-phosphate is 25-mM, (c) Is the reaction spontaneous under these conditions?arrow_forwardAerobic respiration links the oxidation of glucose with the production of ATP form ADP.Given the following thermodynamic data, C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) ΔrH° = −2803 kJ/mol-rxn ATP + H2O(l) → ADP + HPO42-(aq) ΔrH° ≈ −24 kJ/mol-rxn calculate the enthalpy of reaction for the aerobic production of 25 ATP shown below.C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) + 25ADP + 25HPO42-(aq)→ 6CO2(g) + 25ATP + 31H2O(l) ΔrH° = ?arrow_forward
- How does temperature effect the following reaction in terms of its free energy?arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant for the dissociation of acetic acid is 1.8 × 10−5. What is the free energy change for the reaction?arrow_forwardWhat is the main importance for using change in free energy (ΔG) as the thermodynamic parameter for assessing spontaneity of reactions?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





