
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
(b)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
(c)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
(d)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
(e)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(e)
Explanation of Solution
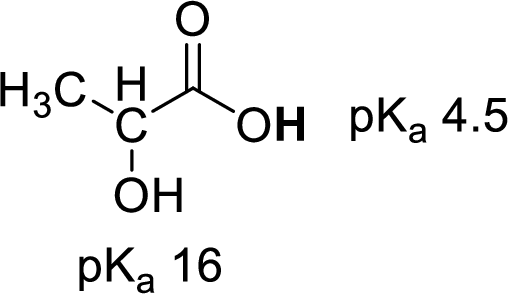
Given molecule,
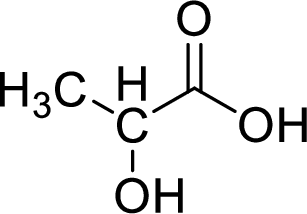
Increase in
(f)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
(g)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
(h)
Interpretation:
The most acidic hydrogen in given molecule has to be labelled and justify it using
Concept Introduction:
Position of equilibrium in acid-base reaction:
In an acid-base reaction, the position of equilibrium always favors reaction of the stronger acid and stronger base to form the weaker acid and weaker base. Therefore, the major species present at equilibrium in an acid-base reaction are weaker acid and weaker base. The reaction equilibrium shifts to a direction where weaker acid and weaker base is formed. Acids with greater
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule,
Increase in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- For the following molecules: circle the most acidic hydrogen(s). determine the approximate pKa of the hydrogen you circled rank the compounds from least (1) to most (5) acidic compound.arrow_forwardDrawing an SN2 product with More Complex Reactants Identify C, the product of an SN2 reaction in the synthesis of raloxifene, a drug used to reduce the risk of invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women.arrow_forward2) For the following groups of molecules (labeled A-C), rank the basicity of the molecules in order from least basic (3) to most basic (1). Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Identify the most acidic hydrogen(s) and draw its conjugated base in each offollowing moleculesarrow_forwardWhich among the given compounds are more basic than compound I? II and III IV and V III and IVarrow_forward(a) Rank A, B, and C in order of increasing SN2 reactivity. (b) Rank A, B, and C in order of increasing SN1 reactivity.arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements about an -NH2 group is FALSE? a. meta director b. activator towards EAS c. increases electron density on the aromatic ring d. stabilizes positively charged intermediates by resonance or inductive effectsarrow_forwardIn RPLC, Compound A is more polar than compound B. In which column will compound A be more retained than compound B? A. C18 B. C8 C. Phenyl bounded column D. All of the above E. None of the abovearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





