
(a)
The tension in the string.
(a)
Answer to Problem 52P
The tension in the string is
Explanation of Solution
Consider the free body diagram given below.
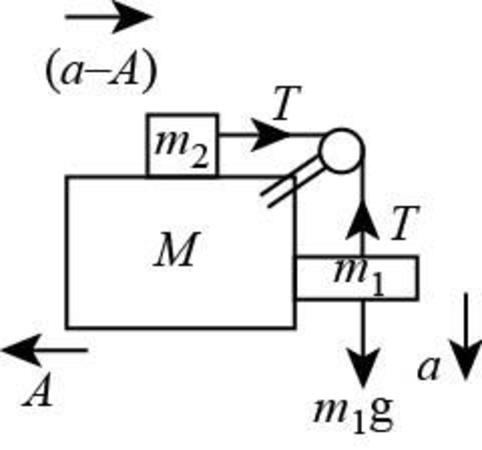
Figure I
Here,
Write the expression for the equilibrium condition for hanging block
Here,
Write the expression for the equilibrium condition for top block
Here,
Write the expression for the equilibrium condition for large block
Here,
Substitute
Further, solve it for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the tension in the string is
(b)
The acceleration of
(b)
Answer to Problem 52P
The acceleration of
Explanation of Solution
The force applied on the block of mass
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the acceleration of
(c)
The acceleration of
(c)
Answer to Problem 52P
The acceleration of
Explanation of Solution
The acceleration of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the acceleration of
(d)
The acceleration of
(d)
Answer to Problem 52P
The acceleration of
Explanation of Solution
The block of mass
Write the formula to calculate the acceleration of
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the acceleration of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- FIGURE P5.49 Problems 49 and 50. Suppose the system of blocks in Problem 49 is initially held motionless and, when released, begins to accelerate. a. If m1 = 7.00 kg, m2 = 2.00 kg, and the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks is 0.134 m /s2, find the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force between the second block and the ledge. b. What is the value of the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the ledge?arrow_forwardInitially, the system of objects shown in Figure P5.49 is held motionless. The pulley and all surfaces and wheels are frictionless. Let the force F be zero and assume that m1 can move only vertically. At the instant after the system of objects is released, Find (a) the tension T in the string, (b) the acceleration of m2, (c) the acceleration of M, and (d) the acceleration of m1. (Note: The pulley accelerates along with the cart.) Figure P5.49 Problems 49 and 53arrow_forwardSuppose mG and mh have equal masses. In this situation, do you expect the magnitude of the acceleration of the glider will be less than g or greater than g or equal to g? please explain the reason.arrow_forward
- You drop from rest from a platform 10.0 m10.0 m above the surface of a 6.00 m6.00 m deep pool. Assuming that you enter the water vertically and move through the water with constant acceleration, what is the minimum average force FF the water must exert on you to prevent you from hitting the bottom of the pool? Assume your mass is m=65.0 kgm=65.0 kg and that air resistance during the fall is negligible.arrow_forwardIf the only forces acting on a 2.0kg mass are F1=(3i-8j)N and F2=(5i+3j)N, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle?arrow_forwardThree objects are connected on a table as shown in Figure P5.31. The coefficient ofkinetic friction between the block of mass m2 and the table is 0.350. The objects havemasses of m1 = 4.00 kg, m2 = 1.00 kg, and m3 = 2.00 kg, and the pulleys are frictionless.(a) Draw a free-body diagram of each object. (b) Determine the acceleration of eachobject, including its direction. (c) Determine the tensions in the two cords. What If?(d) If the tabletop were smooth, would the tensions increase, decrease, or remain thesame? Explain.arrow_forward
- Consider the modified Atwood machine problem illustrated in Example 6.4 on page 274 of the book, and suppose m1 = 5kg and m2 = 10kg . Suppose I apply a horizontal force to the block on the table, so that both masses are at rest. What is the magnitude of the force I should apply? Group of answer choices 6.53 N 0.0 N 32.7 N 98.0 Narrow_forwardA cougar bites a llama of mass m and drags it across some rough horizontal ground. The cougar applies a horizontal force of magnitude F, and the llama is dragged at a constant velocity. The coefficient of kinetic friction is μk. While the cougar applies the force F, the magnitude of the kinetic friction force, fk , on the llama obeys: a)F > µk m g > fk b)F = fk = µk m gc)F = fk < µk m gd)cannot answer, not enough information givene) F > fk = µk m garrow_forwardA 9.00-kg hanging object is connected by a light, inextensible cord over a light, frictionless pulley to a 5.00-kg block that is sliding on a flat table (Fig. P5.7). Taking the coefficient of kinetic friction as 0.200, find the tension in the string. Figure P5.7arrow_forward
- Two objects, m1 = 3.00 kg and m2 = 8.50 kg, are attached by a massless cord passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P5.51. Assume the horizontal surface is frictionless. a. Draw a free-body diagram for each of the two objects. b. What is the tension in the cord? c. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the two objects? FIGURE P5.51 Problems 51 and 65.arrow_forwardIn Figure P4.53, the incline has mass M and is fastened to the stationary horizontal tabletop. The block of mass m is placed near the bottom of the incline and is released with a quick push that sets it sliding upward. The block stops near the top of the incline as shown in the figure and then slides down again, always without friction. Find the force that the tabletop exerts on the incline throughout this motion in terms of m, M, g, and .arrow_forwardAn object of mass M is held in place by an applied force F and a pulley system as shown in Figure P4.43. The pulleys are massless and frictionless. (a) Draw diagrams showing the forces on each pulley. Find (b) the tension in each section of rope, T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 and (c) the magnitude of F. Figure P4.43 44. Any device that allows you to increase the force you exert is a kind of machine. Some machines, such as the prybar or the inclined plane, are very simple. Some machines do not even look like machines. For example, your car is stuck in the mud and you cant pull hard enough to get it out. You do, however, have a long cable that you connect taut between your front bumper and the trunk of a stout tree. You now pull sideways on the cable at its midpoint, exerting a force f. Each half of the cable is displaced through a small angle from the straight line between the ends of the cable. (a) Deduce an expression for the force acting on the car. (b) Evaluate the cable tension for the case where = 7.00 and f = 100 N.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning




