
Biological Science (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134678320
Author: Scott Freeman, Kim Quillin, Lizabeth Allison, Michael Black, Greg Podgorski, Emily Taylor, Jeff Carmichael
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 45, Problem 14PIAT
Summary Introduction
To analyze:
The conclusion that can be drawn from the data given in the question.
Introduction:
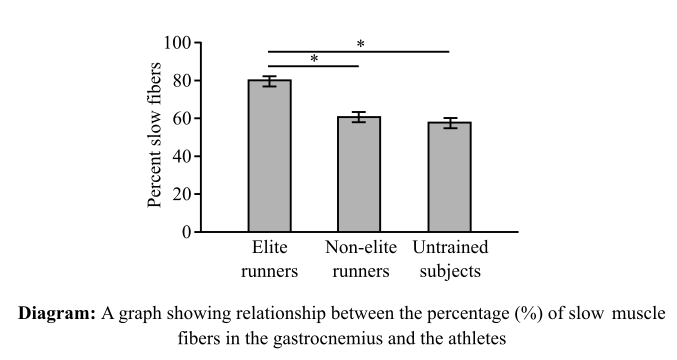
The muscle fibers are of three types: slow, fast, and intermediate. In the given experiment, the muscle fibers were categorized as fast and slow muscle fibers only. The absence of the intermediate muscle fibers during the time of the experiment was assumed. In an experiment given below, the biopsies of the gastrocnemius of 14 elite distance runners, 18 trained but nonelite runners, and 19 untrained subjects were obtained. Gastrocnemius is a muscle that forms the major bulk at the calf region present at the back of lower leg. A relationship was established between the muscle-fiber type and their performance, which is shown in the diagram below:
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
* The figure below is called the
It shows the
amount of tension generated by a muscle and the force of contraction
depends on how stretched or contracted it was before it was
stimulated. *
100
80
(d)
60
(e)
Normal
/range
40
(a)
20
1.2 μm 1.6 μm 2.1 μm
2.2 um
2.6μm
3.6 μη
Decreased length
Increased length
Optimal
resting length
Tension (percent of maximum)
The graphs below show the force-versus-shortening-velocity and power-versus-
shortening-velocity curves for four muscles in the human lower extremity. Note
that these curves show this relationship only for shortening activations (positive
shortening velocities), not lengthening activations. And, note that the values
displayed on the axes of the graphs are absolute (not normalized) values of force,
power, and velocity.
These graphs apply to the next three questions.
Force vs Shortening Velocity
Power vs Shortening Velocity
1,500
400
1,200
300
2 900
200
600
100
300
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
Shortening Velocity (m/s)
Shortening Velocity (m/s)
muscle 1
muscle 3
muscle 2
muscle 4
Force (N)
Power (W)
Explain how optimal skeletal muscle force (high muscle tension) can be achieved during a high intensity exercise. (Mention and explain how wave summation, motor recruitment summation, muscle length, and type of muscle fibers activated can affect muscle force).
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The motor unit firing patterns are measured in a human hand muscle using an electromyography (EMG) recording. Which one of the following statements is the best description of the EMG pattern observed as the individual voluntarily attempts to make a low-level force of contraction in the muscle and steadily increases the force of contraction? Low amplitude spikes visible on the EMG trace at low force. Larger amplitude spikes become visible with increasing force of contraction. Low frequency of small amplitude spikes on the EMG trace at low force. Spike frequency and amplitude increase with increasing force. A large single deflection in the trace as the individual contracts the muscle. The deflection gets larger with increasing force. Low frequency of spikes on the EMG trace at low force. The frequency of spikes becomes more frequent with increasing force.arrow_forwardA client asks your advice on how to best prevent lean body mass loss through diet. What evidence-based recommendation can you provide to optimize muscle synthesis? Question 75 options: a) Increase your protein intake at dinner to achieve a total of 1.5 g/kg/day b) Include protein shakes with breakfast each day c) Include 20-30 g of protein with each meal throughout the day d) Choose pasta-containing meals for dinner to promote carb loading and prevent muscle wasting during overnight fastingarrow_forwardWhat is the maximum distance that diffusion is effective for oxygenating a muscle cell? How does the diffusion rate of oxygen play a role in limiting the fiber diameter for oxidative fibers. Use online sources and present answer as equations or graphically, but be sure that the values are expressed in terms of times and dimensions that are relevant for muscle fibers.arrow_forward
- Describe in details the biochemical and mechanochemical series of events that enables motor neurons to trigger muscle contraction, using the biceps brachii as an example.arrow_forwardMuscle Contraction In an experiment, the strength of a neural stimulus and the resulting muscle contraction are compared. A single motor neuron that synapses with one muscle fibre is observed in this experiment. One end of the muscle fibre is attached to a mass. The following data were obtained from the experiment. Analyze the data and answer the following questions. Number of Trials Strength of Stimulus (mV) Mass Lifted by Muscle Contraction (g) 1 20 2 40 3 60 50 4 80 50 100 Not Tested 120 50 *note that the voltage applied is positive in order to raise potential from resting to threshold Identify the manipulated, responding and controlled variables in the experiment described above. Strength of Stimulus Number of Muscle Fibre Stimulated Mass Lifted by Muscle Contractionarrow_forwardReflect back on the Muscle Fatigue investigation we did earlier in this Activity. Choose one of your classmate’s interpretation to one of these questions: What happened to your energy & ability to pinch the clothespin as you progressed through each trial? Why? What might cause one to be able to get more squeezes, in other words, to have less fatigue? Explain in terms of biological concepts. Suggest how the amount of ATP produced cause your muscle cells to be less efficient. When did this change in the amount of ATP produced occur in this investigation? How could you tell? Your muscles would probably recover enough after 10 minutes to operate at the original efficiency. Explain why. Show how specific details from the steps of cellular respiration add details to answer this question.arrow_forward
- First, explain how resting membrane potential is established in terms of ion concentration and electric charge. Next, explain the process of neural signal transmission from an alpha motor neuron to the muscle fiber. Do this by explaining how an AP is generated (ions and membrane proteins) at the neuron, how the signal is propagated, what happens at the axon terminal, what happens at the motor endplate, and explain all the molecular events that occur to cause muscle contraction.arrow_forwardDefine hypertrophy of skeletal muscle. Explain skeletal muscle adaptations to strength training (over time, not acute). What are the mechanisms of action? What hormones are involved? What cell signaling occurs to produce hypertrophy? Identify two principles of resistance training and explain how they contribute to skeletal muscle adaptation. Provide at minimum, two reputable resources to back up your claims.arrow_forwardMuscle motor unit recruitment follows the pattern of the SO (I) fibers being recruited first followed by the FOG (IIa) and then ultimately by the FG (IIb) if and when workloads require this. Muscle fatigue follows the order that the FG fibers fatigue first, followed by the FOG fibers and finally (maybe never) the SO fibers. Explain how it makes sense physiologically that the last fibers to be recruited to contract are the first to fatigue, while the first fibers to be recruited to contract would be the last to fatigue.arrow_forward
- Fast oxidative glycolytic fibers in skeletal muscle are used Select one: O a. intermittently, for activities requiring more force output than the fast glycolytic fibers alone can produce. O b. constantly, for postural activities such as standing and sitting. O c. intermittently, for activities requiring more force output than the slow oxidative fibers alone can produce. O d. only for motions requiring maximum power output, such as jumping.arrow_forwardWhen utilizing microprocessor technology for testing muscle strength, you are typically looking at what form of muscle contraction? Concentric Isokinetic Isometric Eccentricarrow_forwardWhat methods can you use to test if someone has more fast twitch versus slow twitch muscle fibers? Remember the variances between fast twitch and slow twitch muscle fibers. Based on this, select a sport and a muscle group primarily used for that sport. Then share which muscle fiber type would be highest for that muscle group.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage LearningLifetime Physical Fitness & WellnessHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337677509Author:HOEGERPublisher:Cengage
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage LearningLifetime Physical Fitness & WellnessHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337677509Author:HOEGERPublisher:Cengage

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lifetime Physical Fitness & Wellness
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337677509
Author:HOEGER
Publisher:Cengage

GCSE PE - ANTAGONISTIC MUSCLE ACTION - Anatomy and Physiology (Skeletal and Muscular System - 1.5); Author: igpe_complete;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hm_9jQRoO4;License: Standard Youtube License