
To discuss:
The basic anatomy, physiology, and functions of the immune system.
Concept introduction:
The immune system comprised a network of cells that offer a defensive mechanism against a wide range of antigens. Any substance from the outside environment will be recognized as a foreign substance by the immune system. Tumor cells arise from the cells of normal tissue. These tumor cells contain chemical compounds on their exterior, which will be recognized as antigen by the immune system. Such antigens are known as tumor antigens.
Explanation of Solution
Humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity are the two major components of the immune system. Communication or interaction between these two systems of the immune system is significant. Antibodies produced (humoral response) by the B-lymphocytes attack the tumor cells. The destruction process of the tumor cells is carried out by the (cell-mediated response) T lymphocytes.
Humoral Immune System:
B lymphocytes are also called as B cells. These cells originate in the bone marrow; hence, they are named so. These cells remain inactive until the entry of an antigen. If an antigen binds to the surface of the receptor on the B cells, a signal will be sent to the B lymphocytes. The B cells will be converted into plasma cells. These plasma cells will produce antibodies. The antibodies will bind with the antigens, then inactivate them.
The immune system of the body is preprogrammed to be effective against millions of antigens. This ability further is developed by exposure to various antigens during lifetime. Antibodies produced from a single plasma cell are named as monoclonal antibodies. The 5 major types of antibodies or immunoglobulins present in the human body are immunoglobulins G, A, M, D, and E. Some of the B cells will become memory cells when B lymphocytes transform into plasma cells during an immune reaction.
The memory cell will remember the features of a new foreign antigen. If the same antigen attacks the host for the second time, a sturdy and fast response will be given by the memory cells.
The immune cells and antibodies involved in the humoral immune response are given below:
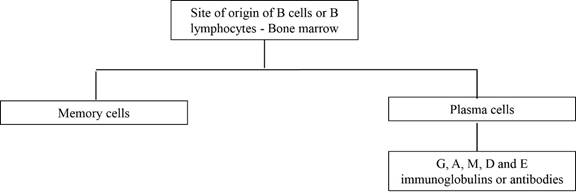
The cells involved in the cell mediated immune response are given below:
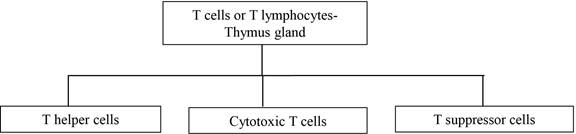
Functions of the various antibodies are given below:
IgA: Provides immunity to the newborn (baby). Present in the saliva, tears, colostrum and mucus lining the digestive and respiratory tracts.
IgG: Protects human body against toxins, bacterial, and fungal infections; provides immunity to the newborn (baby); mostly prevalent among other antibodies; and long-lasting memory about antigens.
IgM: First antibody released during an infection. It is responsible for blood (ABO grouping) transfusion reactions.
IgD: Effective against parasitic infections.
IgE: Involved in allergic responses.
Cell-mediated immune response:
T lymphocytes are the functional cells involved in cell-mediated immunity. They are also named as T cells because they mature in the thymus. Three different groups of T cells are T-helper cells, T-suppressor cells and cytotoxic T cells. These T cells are classified based on the functions that they perform. Cytotoxic T cells kill the pathogen by lysis.
The major controller of the cell-mediated immune response is done by T-helper cells. They direct the activities of various immune components (lymphokines and cytotoxic T cells). Cytokines are chemical mediators of different physiological functions. A subset of cytokines is known as lymphokines. T-suppressor cells suppress or control the immune response. The cancer cells are destroyed by the cell-mediated immune response. Macrophages, natural killer cells, and leukocytes are (other cells) involved in the cell-mediated immunity. These three cell types are involved in the destruction of cancer cells. Overactive suppressor T cells have a negative influence over the anti-tumor activity of the immune system. Therefore, these cells may be accountable for the growth of tumor cells.
The basic anatomy, physiology, and functions of the immune system are explained.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 47 Solutions
Pharmacology and Nursing Process (Custom Package)
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





