
Concept explainers
Estimating Cost Behavior Using Scattergraph and High-Low Methods
Camp Rainbow offers overnight summer camp programs for children ages 10 to 14 every summer during June and July. Each camp session is one week and can accommodate up to 200 children. The camp is not coed, so boys attend during the odd-numbered weeks and girls attend during the even-numbered weeks. While at the camp, participants make crafts, participate in various sports, help care for the Camp’s resident animals, have cookouts and hayrides, and help assemble toys for local underprivileged children.
The camp provides all food as well as materials for all craft classes and the toys to be assembled. One cabin can accommodate up to 10 children, and one camp counselor is assigned to each cabin. Three camp managers are on-site regardless of the number of campers enrolled.
Following is the cost information for Camp Rainbow s operations last summer
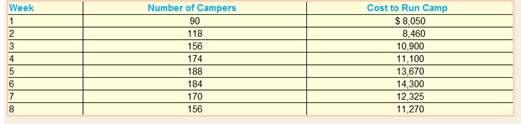
1. For each of the following items. Identify, whether the cost is variable, fixed, mixed, step-variable, or step-fixed. State any assumptions you make.
a. Cost of meals for campers.
b. Cost of camp counselor wanes.
c. Cost of crafting materials.
d.
e. Feed for the camp animals.
f. Electricity for the camp.
g. Camp managers’ salaries.
h. Cost of toys to be assembled by campers.
I. Housekeeping (e.g. cleaning cabins between sessions, laundering bed linens).
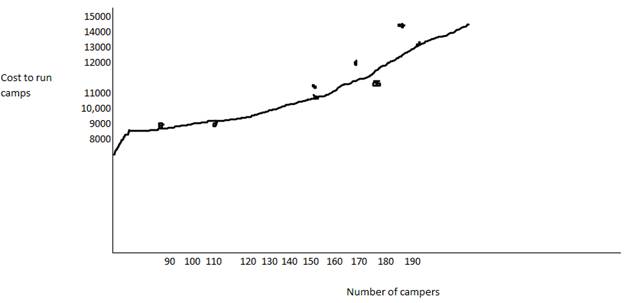
2. Prepare a scattergraph of Camp Rainbows operating cost and draw the line you believe best fits the data.
3. Based on this graph, estimate Camp Rainbow s total fixed costs per month.
4. Using the high-low method, calculate Camp Rainbow s total fixed operating costs and variable operating cost per child.
5. Using the high-low method results, calculate the camps expected operating cost if 170 children attend a session.
(a)
Concept introduction:
Variable cost:
Variable costs are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Example: Cloth (i.e., the raw material) used for producing shirt is a variable costs.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost is the cost which remains fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost is the cost which has some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example includes some production cost which remains fixed at $800 and also increases by $2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increases in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
The nature of given expenses.
Answer to Problem 10E
| a. | variable |
| b | step-fixed |
| c | step-variable |
| d | fixed |
| e | fixed |
| f | step-fixed |
| g | fixed |
| h | variable |
Explanation of Solution
| a. | Cost of meal will vary on the number of participants. |
| b | Camp counselor wages vary slightly depending on the number of participants. |
| c | Camp counselor wages will vary highly on the number of participants |
| d | Depreciation will remain fixed |
| e | feed of the camp animals will remain fixed |
| f | Electricity expenses remain fixed upto a certain limit |
| g | Camp manager's salary will remain fixed |
| h | Variable based on the number of participants |
Thus, thenature of expenses has been determined.
(b)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
To prepare:
The scatter-graph and estimate the fixed costs.
Answer to Problem 10E
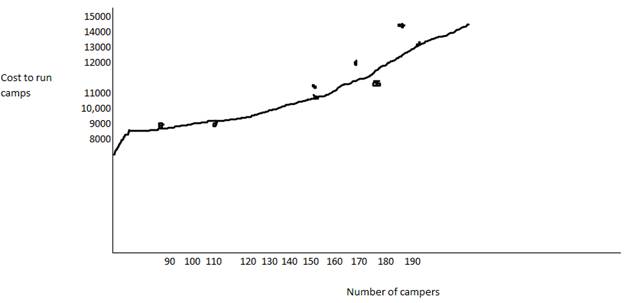
Explanation of Solution
The points have been plotted and a straight line has been drawn near the points.
Thus, the scatter-graph has been prepared
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
Requirement 3
To provide
The estimated fixed costs
Answer to Problem 10E
The estimated fixed cost is $7,000.
Explanation of Solution
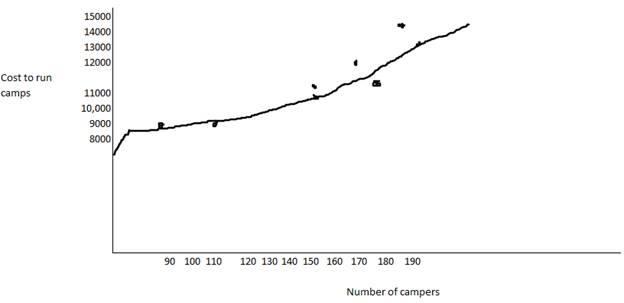
The intercept is at hence the fixed cost is estimated
Thus, the estimated fixed cost has been provided.
(d)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
To compute:
The fixed and variable cost using high low method.
Answer to Problem 10E
The fixed operating cost is $2839
The variable operating cost is $57.35/camper
Explanation of Solution
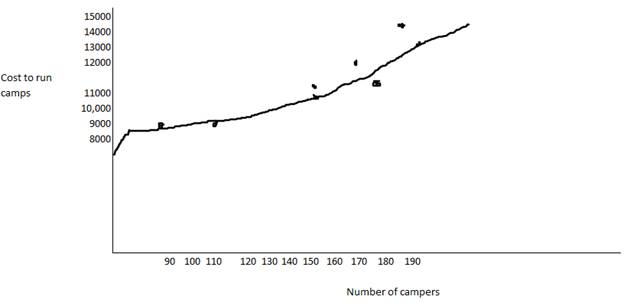
The highest point is 188campers with total cost $13,670
The lowest point is 90 campers with total cost $8050
So, variable cost per camper =
So, fixed cost for 90 camper=8050-(90*57.37) = 8050-5161.22=$2839
Hence, the fixed cost and variable cost has been determined.
(e)
Concept introduction:
Scatter-graph- Scatter-graph is the visual representation of the data on the graph with total costs on the y-axis and level of activity in the x-axis.
High-low method:
High-low method uses the most extreme values to determine the variable and fixed cost based on given trends.
Variable cost:
Variable cost are the cost that vary with the level of production and are directly related to the production volume. Examples include clothes in production of shirts is a variable costs the clothes and other accessories utilized can be directly traced to units of shirts produced.
Fixed cost:
Fixed cost are the cost which remain fixed over time or production volume and do not vary with the production level. Example include salaries and wages of officers, depreciation etc.
Mixed cost:
Mixed cost are the cost which have some part of cost fixed and some is variable. Example include some production cost which remain fixed at $800 and also increases by R$2 for every unit produced.
Step-variable cost- Step variable costs means the costs which is fixed over a very narrow range of activity and increase in many steps across the relevant range.
Step-fixed cost- Step fixed costs means the costs which is fixed over a very wide range of activity as compared to variable costs.
To compute:
The estimated cost at given number of units.
Answer to Problem 10E
The expected operating cost of 170 children using high-low method is $12,587
Explanation of Solution
The cost of 170 campers = 2839+(170*57.35) = $12,588
Hence, the estimated costs has been determined
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Product costing and decision analysis for a service company Blue Star Airline provides passenger airline service, using small jets. The airline connects four major cities: Charlotte, Pittsburgh, Detroit, and San Francisco. The company expects to fly 170,000 miles during a month. The following costs are budgeted for a month: Blue Star management wishes to assign these costs to individual flights in order to gauge the profitability of its service offerings. The following activity bases were identified with the budgeted costs: The size of the companys ground operation in each city is determined by the size of the workforce. The following monthly data are available from corporate records for each terminal operation: Three recent representative flights have been selected for the profitability study. Their characteristics are as follows: Instructions Determine the fuel, crew, and depreciation cost per mile flown. Determine the cost per arrival or departure by terminal city. Use the information in (1) and (2) to construct a profitability report for the three flights. Each flight has a single arrival and departure to its origin and destination city pairs.arrow_forwardA local picnic table manufacturer has budgeted these overhead costs: They are considering adapting ABC costing and have estimated the cost drivers for each pool as shown: Recent success has yielded an order for 1,000 tables. Assume direct labor costs per hour of $20. Determine how much the job would cost given the following activities:arrow_forwardTotal costs and unit costs, service setting. National Training recently started a business providing training events for corporations. In order to better understand the profitability of the business, the owners asked you for an analysis of costs—what costs are fixed, what costs are variable, and so on, for each training session. You have the following cost information: Trainer: $11,000 per session Materials: $2,500 per session and $35 per attendee Catering Costs (subcontracted): Food: $75 per attendee Setup/cleanup: $25 per attendee Fixed fee: $5,000 per training sessionNational Training is pleased with the service they use for the catering and have allowed them to place brochures on each dinner table as a form of advertising. In exchange, the caterer gives National Training a $1,000 discount per session. 1. Draw a graph depicting fixed costs, variable costs, and total costs for each training session versus the number of guests. 2. Suppose 100 persons attend the next event. What is…arrow_forward
- Objectives of Cost Allocation Dr. Fred Poston,"Dermatologist to the Stars," has a practice in southern California. The practice includes three dermatologists, three medical assistants, an office manager, and a receptionist. The office space, which is rented for $5,000 per month, is large enough to accommodate four dermatologists, but Dr. Poston has not yet found the right physician to fill the fourth spot. Dr. Poston developed a skin cleanser for his patients that is nongreasy and does not irritate skin that is still recovering from the effects of chemical peels and dermabrasion. The cleanser requires $0.50 worth of ingredients per eight-ounce bottle. A medical assistant mixes up several bottles at a time during lulls in her schedule. She waits until she has about 15 minutes free and then mixes 10 bottles of cleanser. She is paid $2,250 per month. Dr. Poston charges $5.00 per bottle and sells approximately 5,000 bottles annually. His accountant is considering various ways of costing…arrow_forwardSilver Law Firm – Case Study Silver Law firm provides litigation and mediation services to a variety of clients. Attorneys keep track of the time they spend on each case, which is used to charge fees to clients at a rate of $300 per hour. A management advisor commented that activity-based costing might prove useful in evaluating the costs of its legal services, and the firm has decided to evaluate its fee structure by comparing ABC to its alternative cost allocations. The following data relate to a typical month at the firm. During a typical month the firm handles seven mediation cases and three litigation cases.arrow_forwardQuestion Content Area A local picnic table manufacturer has budgeted these overhead costs: Purchasing $70,000 Handling Materials 34,580 Machine Setups 72,000 Inspections 30,600 Utilities 27,000 They are considering adapting ABC costing and have estimated the cost drivers for each pool as shown: Cost Driver Activity Orders 700 Material Moves 1,330 Machine Setups 16,000 Number of Inspections 6,000 Square Feet 180,000 Recent success has yielded an order for 1,000 tables. Assume direct labor costs per hour of $20. Activity Order, Units 1,000 Direct Materials 112,600 Machine Hours 15,300 Direct Labor Hours 5,200 Number of Purchase Orders 70 Number of Material Moves 750 Number of Machine Setups 100 Number of Inspections 450 Number of Square Feet Occupied 8,000 Determine how much the job would cost given the following activities: Do not round intermediate computations and round final answers to nearest whole number. Cost Assigned…arrow_forward
- 1. Using the monthly utilization information presented below, and omitting the Community College training packs, find the fixed and variable portion of costs through the high-low method. Note that the college only acquires packs in three months of the year: January, May, and September. These dates coincide with the start dates of their semesters and summer school 2. The reason the Education Coordinator needs to know how much of the cost is fixed is because she is supposed to collect the appropriate variable cost from the Community College for their packs. For her purposes, which computation do you believe is better? Why? Total Number of Total Community College Community College Month Training Packs Cost Number Packs Cost January 1,000 $6,200 200 $1,240 February 200 1,820 March 250 2,350…arrow_forwardLearnCo LearnCo manufactures and sells one product, an abacus for classroom use, with two models, the Basic model and the Deluxe model. The company began operations on January 1, 20Y1, and is planning for 20Y2, its second year of operations, by preparing budgets from its master budget. The company is trying to decide how many units to manufacture, how much it might spend on direct materials and direct labor, and what their factory overhead expenses might be. In addition, the company is interested in budgeting for selling and administrative costs, and in creating a budgeted income statement showing a prediction of net income for 20Y2. You have been asked to assist the controller of LearnCo in preparing the 20Y2 budgets. Sales Budget The sales budget often uses the prior year’s sales as a starting point, and then sales quantities are revised for various factors such as planned advertising and promotion, projected pricing changes, and expected industry and general economic conditions.…arrow_forwardNeed help using ABC product costing model. Grand Haven is a senior living community that offers a full range of services including independent living, assisted living, and skilled nursing care. The asssited living division provides residential space, meals, and medical services (MS) to its residents. The current costing system adds the cost of all of these services (space, meals, and MS) and divides by total resident days to get a cost per resident day for each month. Recognizing that MS tends to vary significantly among the residents, Grant Haven's accountant recommended that an ABC system be designed to calculate more accurated the cost of MS provided to residents. She decided that residents should be classified into four categories (A, B, C, D) based on the level of services received, with group A representing the lowest level of services and D representing the highest level of service. Two cost drivers being considered for measuring MS costs are number of assistance calls…arrow_forward
- The Gourmand Cooking School runs short cooking courses at its small campus. Management has identified two cost drivers it uses in its budgeting and performance reports—the number of courses and the total number of students. For example, the school might run two courses in a month and have a total of 62 students enrolled in those two courses. Data concerning the company’s cost formulas appear below: Fixed Cost per Month Cost per Course Cost per Student Instructor wages $ 2,930 Classroom supplies $ 270 Utilities $ 1,230 $ 65 Campus rent $ 5,200 Insurance…arrow_forwardThe Gourmand Cooking School runs short cooking courses at its small campus. Management has identified two cost drivers that it uses in its budgeting and performance reports—the number of courses and thetotal number of students. For example, the school might run two courses in a month and have a total of 50students enrolled in those two courses. Data concerning the company’s cost formulas appear below:Fixed Cost Cost per Cost perper Month Course StudentInstructor wages .................. $3,080Classroom supplies ............. $260Utilities ................................. $870 $130Campus rent ........................ $4,200Insurance ............................. $1,890Administrative expenses ...... $3,270 $15 $4For example, administrative expenses should be $3,270 per month plus $15 per course plus $4 per student.The company’s sales should average $800 per student.The actual operating results for September appear below:ActualRevenue .........................................…arrow_forwardThe Gourmand Cooking School runs short cooking courses at its small campus. Management has identified two cost drivers it uses in its budgeting and performance reports—the number of courses and the total number of students. For example, the school might run two courses in a month and have a total of 63 students enrolled in those two courses. Data concerning the company’s cost formulas appear below: Fixed Cost per Month Cost per Course Cost perStudent Instructor wages $ 2,960 Classroom supplies $ 300 Utilities $ 1,210 $ 90 Campus rent $ 5,000 Insurance $ 2,300 Administrative expenses $ 4,000 $ 43 $ 3 For example, administrative expenses should be $4,000 per month plus $43 per course plus $3 per student. The company’s sales should average $890 per student. The company planned to run four courses with a total of 63 students; however, it actually ran four courses with a total of only 53 students. The actual…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


