
GENETICS(LL)-W/CONNECT >CUSTOM<
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781260571561
Author: HARTWELL
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 49P
A diploid strain of yeast has a wild-type phenotype but the following genotype:
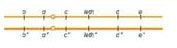
a, b, c, d, and e all represent recessive alleles that yield a visible phenotype, and leth represents a recessive lethal mutation. All genes are on the same chromosome, and a is very tightly linked to the centromere (indicated by a small circle). Which of the following
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In a wild-type fungus, protein E (encoded by the haplosufficient gene E) normally
dimerizes to catalyzes a biochemical reaction necessary for the production of a dark
pigment. Ed represents a mutant, dominant negative allele of gene E. What is the
predicted phenotype of a fungus cell of genotype E*/Ed, and why?
O wild type (normal production of the dark pigment), as E is haplosufficient
mutant (no pigment production), as no dimers will form in the heterozygous
mutant (no pigment production), as the mutant allele Eg is dominant
O wild type (normal production of the dark pigment), as dimers of wild-type and
mutant protein E will be formed in the heterozygous
To identify genes controlling the cell cycle in budding yeast, a genetic screen was carried out. In this screen, haploid yeast cells were exposed to a DNA damaging agent to introduce random mutations in the genome. By culturing cells at an elevated temperature (e.g. 37 degrees), where many mutated genes lose their function, scientists identified yeast mutants that showed growth defects and arrest at specific stages of the cell cycle (e.g. in mitosis with large buds). In this screen, mutants of the cyclin-dependent kinase were identified, but not mutants of cyclins. Explain the reason for this outcome.
A cross between yeast strains ab x AB produces the following unordered tetrads:
a. Label each group of tetrads as parental ditypes (PD), non-parental ditypes (NPD), or
tetratypes (T).
AB
AB
ab
ab
43
6
22
b. Are the genes linked or on separate chromosomes? Why?
aB
aB
Ab
Ab
Ab
AB
ab
aB
c. If the genes are linked determine the distance between them.
Chapter 5 Solutions
GENETICS(LL)-W/CONNECT >CUSTOM<
Ch. 5 - Choose the phrase from the right column that best...Ch. 5 - a. A Drosophila male from a true-breeding stock...Ch. 5 - Prob. 3PCh. 5 - The Punnett square in Fig. 5.4 shows how Mendels...Ch. 5 - In mice, the dominant allele Gs of the X-linked...Ch. 5 - In Drosophila, males from a true-breeding stock...Ch. 5 - If the a and b loci are 20 m.u. apart in humans...Ch. 5 - CCDD and ccdd individuals were crossed to each...Ch. 5 - In mice, the autosomal locus coding for the...Ch. 5 - In a particular human family, John and his mother...
Ch. 5 - Albino rabbits lacking pigment are homozygous for...Ch. 5 - In corn, the allele A allows the deposition of...Ch. 5 - If the a and b loci are 40 cM apart and an AA BB...Ch. 5 - Write the number of different kinds of phenotypes,...Ch. 5 - A DNA variant has been found linked to a rare...Ch. 5 - Figure 5.7a shows chromosomes during prophase of...Ch. 5 - Figure 5.7b shows bivalents in mouse primary...Ch. 5 - Cinnabar eyes cn and reduced bristles rd are...Ch. 5 - In Drosophila, the autosomal recessive dp allele...Ch. 5 - From a series of two-point crosses, the following...Ch. 5 - Map distances were determined for four different...Ch. 5 - In the tubular flowers of foxgloves, wild-type...Ch. 5 - In Drosophila, the recessive allele mb of one gene...Ch. 5 - A snapdragon with pink petals, black anthers, and...Ch. 5 - In Drosophila, three autosomal genes have the...Ch. 5 - Drosophila females heterozygous for each of three...Ch. 5 - Male Drosophila expressing the autosomal recessive...Ch. 5 - a. In Drosophila, crosses between F1 heterozygotes...Ch. 5 - A true-breeding strain of Virginia tobacco has...Ch. 5 - Prob. 30PCh. 5 - The following list of four Drosophila mutations...Ch. 5 - Do the data that Mendel obtained fit his...Ch. 5 - Two genes control color in corn snakes as follows:...Ch. 5 - A mouse from a true-breeding population with...Ch. 5 - Neurospora of genotype a c are crossed with...Ch. 5 - A cross was performed between one haploid strain...Ch. 5 - Prob. 40PCh. 5 - Prob. 41PCh. 5 - Indicate the percentage of tetrads that would have...Ch. 5 - Prob. 43PCh. 5 - This problem leads you through the derivation of a...Ch. 5 - a. In ordered tetrad analysis, what is the maximum...Ch. 5 - Prob. 46PCh. 5 - A single yeast cell placed on a solid agar will...Ch. 5 - Figure 5.29 shows mitotic recombination leading to...Ch. 5 - A diploid strain of yeast has a wild-type...Ch. 5 - In Drosophila, the yellow y gene is near the...Ch. 5 - Neurofibromas are tumors of the skin that can...Ch. 5 - Two important methods for understanding the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The STR DNA marker DS11 is located on the p arm of the chromosome #8 in humans. Molecular analysis has shown that Charlie Chaplin is a heterozygote for the STR marker (genotype DS11A and DS11B) Using this knowledge, provide a diagram of meiosis showing only the movements of chromosome 8 (assume no nondisjunction). Throughout, indicate where the marker may be found (in other words, label the chromosome to show where the STR markers can be found. (Show ONLY the chromosomes at interphase, metaphase 1, end of meiosis 1, metaphase 2, and end of meiosis 2). Suppose Charlie conceived a son with a chromosome 8 trisomy. Molecular analysis of the STR DS11 marker revealed that his son carried two copies of the DS11A marker and a DS11C marker. Based on the data, determine if the nondisjunction occurred in Charlie or in the mother? Provide your reasoning.arrow_forwardplease answer parts a and barrow_forwardIn a germline progenitor cell before DNA replication (2N), a translocation occurred between a telocentric and submetacentric chromosome resulting in a translocation heterozygote. The location of the translocation is illustrated below. Draw the Prophase I pairing conformation that would result from this translocation. The four types of chromosomes you have now can be labeled as follows: T-WT (telocentric wild type), T-TL (telocentric translocation), SM-WT (submetacentric wild type), and SM-TL (submetacentric translocation). Using these labels, list (please do not draw) the possible outcomes of Anaphase I and the possible phenotypes for each outcome. Please explain your reasoning for each phenotype in a few words. asaparrow_forward
- In the following schematic drawing of a Holliday junction,one chromatid is shown in red, and the homologous chromatidis shown in blue. The red chromatid carries a dominant allelelabeled A and a recessive allele labeled b, whereas the blue chromatidcarries a recessive allele labeled a and a dominant allelelabeled B. Where would the DNA strands have to be cut to produce recombinantchromosomes? Would they be cut at sites 1 and 3, or at sites2 and 4? What would be the genotypes of the two recombinantchromosomes?arrow_forwardVariations in Chromosome NumberAneuploidy Describe the process of nondisjunction and explain when it takes place during cell division.arrow_forward8.18 Irradiatioh of Drosophila sperm produces transloca- tions between the X chromosome and autosomes, between the Y chromosome and autosomes, and between different autosomes. Translotations between the X and Y chromosomes are not produced. Explain the absence of X-Y translocations. The birth of this child prompted the Dentons' physician to order a chromosome study of parents and child. The results of the study are shown in the accompanying fig- ure. Chromosome banding was done, and all chromo- somes were normal in these individuals, except some copies of number 6 and number 12. The number-6 and number-12 chromosomes of mother, father, and child are shown in the figure (the number 6 chromosomes are the larger pair): Child Mrs. Denton Mr. Denton a. Does either parent have an abnormal karyotype? If so, which parent has it, and what is the nature of the abnormality? b. How did the child's karyotype arise? (What pairing and segregation events took place in the parents?) e. Why is the child…arrow_forward
- The genotype of a Drosophila with a heterozygous translocation between chromosome 2 and chromosome 3 is shown below, where bw = brown eyes and e = ebony body: bw+ bw e Assume there is no crossing over in the female and that alternate = adjacent 1 = adjacent 2 disjunction. [Yes, these assumptions are incorrect, but they make the problem much easier!] Two individuals of the above genotype, i.e. both heterozygous for this 2;3 translocation and both heterozygous for bw (on chromosome 2) and e (on chromosome 3) are crossed. A (Only zygotes with balanced genomes will survive to adulthood. What proportion of F1 zygotes have a balanced genome? B. Draw the genotype(s) and state the phenotype(s) of the surviving progeny you mentioned in part A above. For each different genotype/phenotype indicate it's frequency among the surviving progeny.arrow_forwardImagine Drosophila genes C, D, and E are autosomal genes located close to each other on the same chromosome (same assumptions as the first problem). You cross a C D E homozygote with a c d e homozygote, then cross the F1 females with a c d e homozygous male. Of 400 progeny, you observe the following phenotypes: 135 CDE 139 cde 22 cDE 18 Cde 42 CdE 38 cDe 3 cdE 3 CDe a. What is the order of the genes? Calculate the distance between genes and draw a map to get the final answer. Question 2 options: 1.CED 2. DEC 3. ECD 4. DCEarrow_forwardTwo different strains of Drosophila melanogaster are mated in reciprocal crosses. When strain A males are crossed with strain B females, the progeny are normal. However, when strain A females are crossed with strain B males, there are many mutations and chromosome rearrangements in the gametes of the F1 progeny, and the F1 generation is effectively sterile. Explain these results.arrow_forward
- A Drosophila male is heterozygous for a reciprocaltranslocation between an autosome and the Y chromosome. The part of the autosome now present onthe Y chromosome contains the dominant mutationLyra (shortened wings); the other (normal) copyof the same autosome is Lyra+. This male is nowmated with a true-breeding, wild-type female. Whatkinds of progeny would be obtained, and in whatproportions?arrow_forward● ● Illustrate the chromosome changes in interphase and mitosis using a diploid cell that is 2n=4 (two large and two small chromosomes). Label the circles as G1 and G2 stages of interphase and each phase of mitosis (in order). Draw the chromosome in each circle using the following guidelines. 1) For unreplicated chromosome draw a line (/) and for replicated chromosome draw an X. 2) For simplicity, do not indicate that the chromosomes are decondensed chromatin during interphase. 3) Skip drawing the nuclear membrane or spindle fibers, since we are focusing on the chromosomes. Label genes in the resulting daughter cells as A/a and B/b. (These letters represent genes which are at particular places along the DNA molecule. Each chromosomes can have a thousand genes but we are focusing on these two.) Ask me Qs in class if anythign on this is not clear.arrow_forwardRice has a chromosome number of 2n = 24. If different euploids and anaeuploids are available in rice, identifythe chromosomal mutation, chromosome configuration, chromosome number, and/or type of gametes in each of the mutations below. Complete the table. Example: for 10B, the answer is "10 II + 2 I"arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY