
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
In the marked carbon atom, one s and three p orbital hybridize forming four
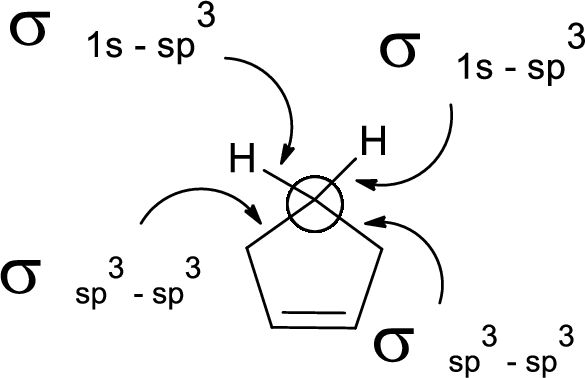
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(b)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(b)
Explanation of Solution
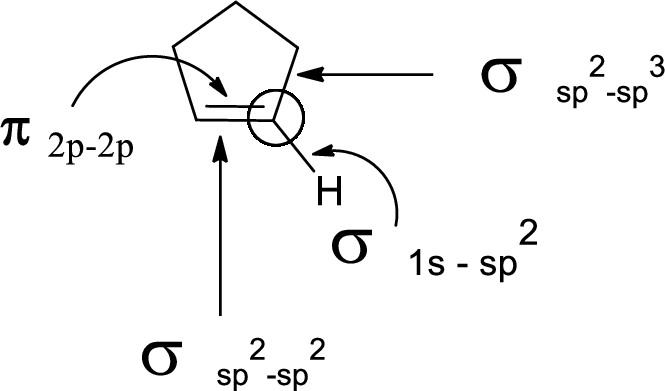
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(c)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(c)
Explanation of Solution
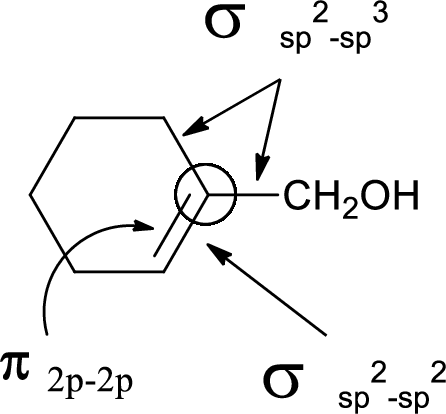
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
(d)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
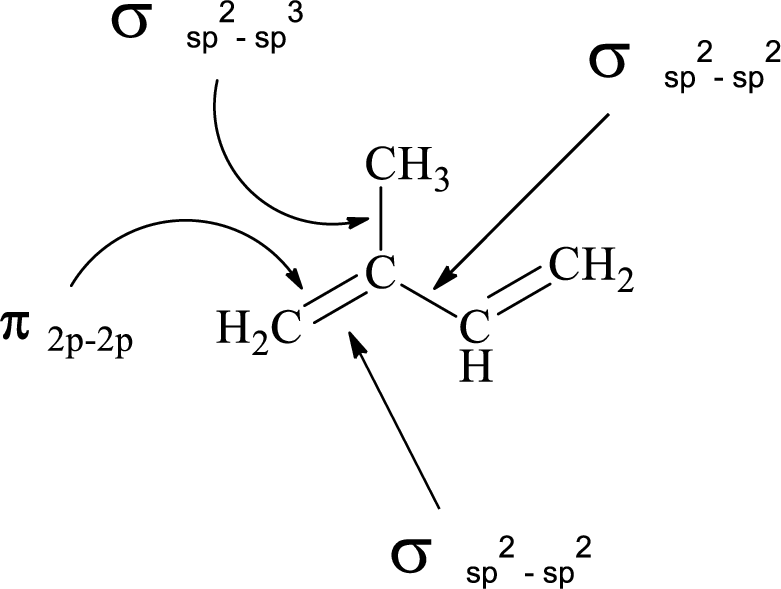
(e)
Interpretation:
Atomic orbitals which are used to form each
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is the mixing of valence atomic orbitals to get equivalent hybridized orbitals that having similar characteristics and energy.
Sigma (σ) bonds are the bonds in which shared hybrid orbital’s electron density are concentrated along the internuclear axis.
Pi (π) bonds are the bonds in which shared unhybridized orbital’s (p, d, etc) electron density are concentrated in above and below of the plane of the molecule.
Geometry of different types of molecule with respect to the hybridizations are mentioned are mentioned below,
(e)
Explanation of Solution
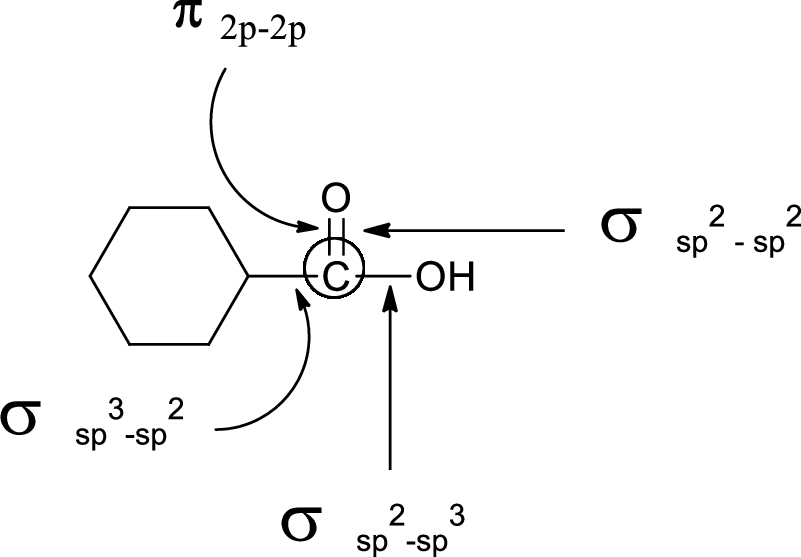
In the marked carbon atom, one s and one p orbital hybridize forming two
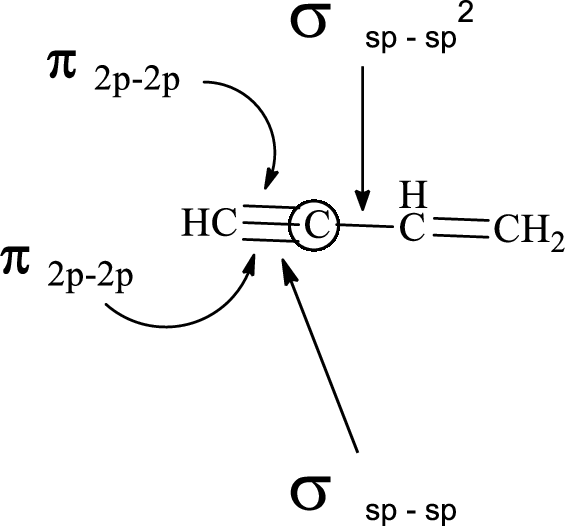
In the marked carbon atom, one s and two p orbital hybridize forming three
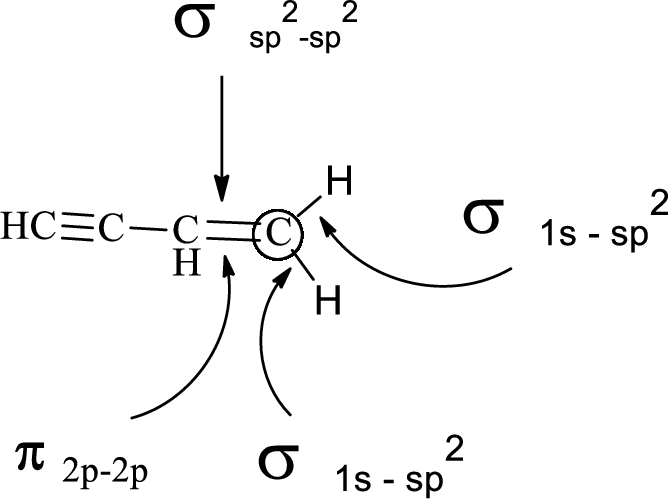
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Which atomic orbitals from carbon hybridize to form the bonds in CH₄?arrow_forwardWhat are all of the types of orbital overlaps that occur in the above structure. p-p overlap sp²-sp overlap s-sp² overlap sp²-sp² overlap s-sp overlap sp-sp overlap s-s overlap ---------- In cumulene, what are the C=C=C and H−C−H ideal bond angles, respectively?Enter the C=C=C bond angle followed by the H−C−H bond angle separated by a comma (no spaces, no º symbol required).arrow_forwardFor highlighted carbon atom , identify which atomic orbitals are used to form each σ bond and which are used to form each π bond.arrow_forward
- . Draw the Lewis diagram for acetamide. ( CH3CONH2) a. What is the electron geometry around each of the two carbon atoms. b. What is the hybridization type of each of the carbon atoms. c. What are the bond types and orbitals involved in bonding for all bonds between the C and O atoms.arrow_forwardDraw all of the constitutional isomers with molecular formula of C6H12 that possess one pi bond. Don't include cyclic structures.arrow_forwardDirections: Identify the functional group each compound represents. If the compound represents two or more functional groups, list all groups being represented. If the compound is a hydrocarbon, write the specific type of hydrocarbon class it belongs of the image 7, 8 and 9.arrow_forward
- How many secondary (2) degree carbons are found in 5 ethyl- 3,3,4 trimethylheptanearrow_forwardDraw a line-bond structure for a hydrocarbon that contains only two sp3 hybridized carbons and two sp hybridized carbons.arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between the hybridization of carbon atoms' valence orbitals in saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?arrow_forward
- Is the compound soluble or insoluble in water? What is the geometry around each carbon atom? What is the bond angle around each carbon atom? What is the hybridization of each carbon atom?arrow_forward1. What is resonance theory? State five conclusions that can be drawn from the theory. 2. State the two main experiments that were used to establish the extra stability of the benzene molecule? 3. What are the factors that confer aromaticity to an organic molecule? 4. What are the various ways by which alkenes may be synthesized.arrow_forwardWhat's the steric number , electron paid geometry, number of lone pairs, molecular geometry, and hybridization for 1. Dichlorodifluoromethane 2. Methanol 3. carbon dioxide 4. carbon disulfide 5. Germanium(II) bromide do all please and labelarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




