
a)
The mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
a)
Answer to Problem 5.6P
In the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium, Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 1/3 and (boxing) 2/3.
Explanation of Solution
In the study of
If all the playoffs are doubles, the table of battle of sexes will be,
| Husband | |||
| Wife | Ballet | Boxing | |
| Ballet | 4, 2 | 0, 0 | |
| Boxing | 0, 0 | 2, 4 |
Wife prefers the Ballet having the probability of w
Wife prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-w)
Equating both the equation, we get,
Husband prefers the Ballet having the probability of h
Husband prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-h)
Equating both the equation, we get,
From the above calculation, doubling of payoff never changes the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium. Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 1/3 and (boxing) 2/3.
Introduction: The game theory is preferable to oligopoly for better understanding. It is the detailed study of interactions between the players, business firms. The aim of this strategic decision is to deduce the responses to actions.
b)
The mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
b)
Answer to Problem 5.6P
In the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium, Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/5 and (boxing) 4/5. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3.
The new diagram is shown.
Explanation of Solution
In the study of game theory, the payoff is the numeric value that is involved with a possible outcome of a game. It represents the motivation of the players. A Strategy is the plan of action that provides the best payoff in a game.Nash equilibrium is one of the strategies and solutions for games.
If all the playoffs are doubles, the new playoff table will be,
| Husband | |||
| Wife | Ballet | Boxing | |
| Ballet | 4, 1 | 0, 0 | |
| Boxing | 0, 0 | 1, 2 |
Wife prefers the Ballet having the probability of w
Wife prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-w)
Equating both the equation, we get,
Husband prefers the Ballet having the probability of h
Husband prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-h)
Equating both the equation, we get,
From the above calculation, doubling of payoff never changes the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium. Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/5 and (boxing) 4/5. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/3.
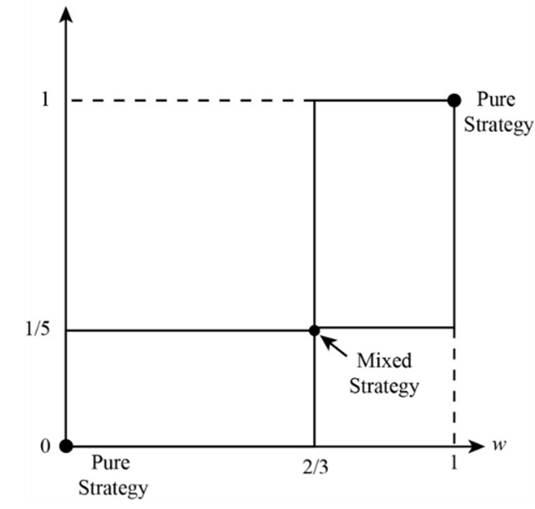
Introduction: The game theory is preferable to oligopoly for better understanding. It is the detailed study of interactions between the players, business firms. The aim of this strategic decision is to deduce the responses to actions.
c)
The mixed strategy Nash equilibrium
c)
Answer to Problem 5.6P
In the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium, Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/4 and (boxing) 3/4. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/4.
The new diagram is shown.
Explanation of Solution
In the study of game theory, the payoff is the numeric value that is involved with a possible outcome of a game. It represents the motivation of the players. A Strategy is the plan of action that provides the best payoff in a game.Nash equilibrium is one of the strategies and solutions for games.
If changes in the preferred activity from 0 to 1/2, the new playoff table will be,
| Husband | |||
| Wife | Ballet | Boxing | |
| Ballet | 2, 1 | 1/2, 0 | |
| Boxing | 1/2, 0 | 1, 2 |
Wife prefers the Ballet having the probability of w
Wife prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-w)
Equating both the equation, we get,
Husband prefers the Ballet having the probability of h
Husband prefers the boxing having the probability of (1-h)
Equating both the equation, we get,
From the above calculation, doubling of payoff never changes the mixed strategies of Nash Equilibrium. Wife is playing with probability (ballet) 1/4 and (boxing) 3/4. Husband is playing with probability (ballet) 2/3 and (boxing) 1/4.
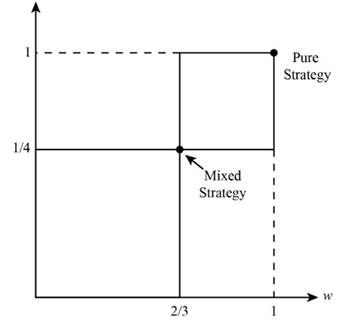
The above diagram is the new diagram
Introduction: The game theory is preferable to oligopoly for better understanding. It is the detailed study of interactions between the players, business firms. The aim of this strategic decision is to deduce the responses to actions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS AND ITS
- Consider the following sequential strategic situation, called the centipede game. The game has 100 stages. Two players take turns making decisions, starting with player 1. At stage t = 1,...,99, player 1 (if the stage is odd) or player 2 (if the stage if even) chooses whether to "Terminate the game" or to "Continue the game." If the game is terminated instage t = 1,...,99, the player terminating the game receives a payoff of t, while the other player receives a payoff of zero. Finally, at stage t = 100, player 2 chooses between action A with a payoff of 99 for each player, or action B with a payoff of zero for player 1 and a payoff of 100 for player 2. Draw the game tree for this situation. What is the SPNE?arrow_forwardRefer to the normal-form game of price competition in the payoff matrix below Firm B Low Price High Price Firm A Low Price 0, 0 50, −10 High Price −10, 50 20, 20 Suppose the game is infinitely repeated, and the interest rate is 20 percent. Both firms agree to charge a high price, provided no player has charged a low price in the past. This collusive outcome will be implemented with a trigger strategy that states that if any firm cheats, then the agreement is no longer valid, and each firm may make independent decisions. Will the trigger strategy be effective in implementing the collusive agreement? Please explain and show all necessary calculations.arrow_forwardConsider a simultaneous move game with two players. Player 1 has three possible actions (A, B, or C) and Player 2 has two possible actions (D or E.) In the payoff matrix below, each cell contains the payoff for Player 1 followed by the payoff for Player 2. Identify any pure strategy Nash Equilibria in this game. If there are none, state this clearly.arrow_forward
- Suppose two players play a two-period repeated game, where the stage game is the normal-form game shown below. Is there a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium in which the players select (A, X) in the first period? If so, fully describe such equilibrium. If not, explain why not. Player 1 has choice A, B; Player 2 has choice X, Y, Z. Payoff: (A,X)-(5,7), (A,Y)-(2,4), (A,Z)-(3,8), (B,X)-(1,4), (B,Y)-(3,5), (B,Z)-(1,4)arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothetical case. Only BMW and a competitor, Mazda, are considering launching a new, niche HPC in the Asian market. The issue is what price to charge. Both new cars are very similar in performance and production cost. Analyse the interaction between the two firms using game theory. Present a payoff matrix to model the situation and analyse it for Nash equilibrium. What can either of these firms do to make their best, most-preferred outcome more likely?arrow_forwardTwo players, Player 1 and Player 2, are playing a repeated prisoner’s dilemma. Payoffs are described in the following matrix. Answer which statement is correct: Select one: a. A trigger strategy will never support (A,A) as an equilibrium b. A tit-for-tat strategy will never support (A,A) as an equilibrium c. A tit-for-tat strategy will support (A,A) as an equilibrium if δ > 0.7 d. A trigger strategy will support (A,A) as an equilibrium if δ > 0.7arrow_forward
- The London Metro Bus is crowded for travel during peak hours. During such travel hours two daily passengers ‘James’ and ‘Robert’ enter the Metro. Luckily, two adjacent seats are free in the bus. Each of them must decide whether to sit or stand. For both, sitting alone is more comfortable than sitting next to the other person, which in turn is more comfortable than standing. consider James as ‘row player’ and Robert as ‘column player). a) Model the situation as a strategic game, assuming both ‘James’ and ‘Robert’ care only about their own comfort. Find the Nash equilibrium (equilibria) if it exists. Also, does a dominant strategy exist for either ‘James’ or ‘Robert’? show ALL steps and working in support to the answerarrow_forwardIn the collusion game, collusion was only sustainable in the infinite horizon repeated game. One Nash Equilibrium of that game can be found when all players play a “grim trigger” strategy, where they collude until an opponent chooses to compete, and then compete for all future rounds as a punishment. In such a game, if the one period bonus that comes from competing is low enough, firms always collude and the punishment is never triggered. Is the punishment (vowing to compete forever after one deviates) realistic, especially if firms can communicate freely? Why or why not? (Hint: Is a grim trigger Nash Equilibrium a Subgame Perfect Nash Equilibrium? What kinds of Nash Equilibria does Subgame erfection rule out in sequential games?)arrow_forwardTry to solve the following Extensive-form game by Backward Induction, then covert them into normal-form and find the Pure-strategy Nash equilibria in Normal form.arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc




