
Bad Debt Expense: Percentage of Credit Sales Method
The Glass House, a glass and china store, sells nearly half its merchandise on credit. During the past 4 years, the following data were developed for credit sales and losses from uncollectible accounts:
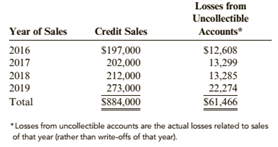
Required:
1. Calculate the loss rate for each year from 2016 through 2018. ( Note: Round answers to three decimal places.)
2. Determine whether there appears to be a significant change in the loss rate over time.
3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION If credit sales for 2020 are $400,000, determine what loss rate you would recommend to estimate
4. Using the rate you recommend, record bad debt expense for 2020.
5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Assume that the increase in The Glass House’s sales in
2020 was largely due to granting credit to customers who would have been denied credit in previous years. How would this change your answer to Requirement 4? Describe a legitimate business reason why The Glass House would adopt more lenient credit terms.
6. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Using the data from 2016 through 2019, estimate the increase in income from operations in total for those 4 years assuming (a) the average gross margin is 25% and (b) 50% of the sales would have been lost if no credit was granted.
(a)
Credit Sales Method:
The method named percentage of credit sales method is the method in which the bad debts are computed on the basis of percentage of sales.
Uncollectible accounts:
These are those accounts which reflect that amount of credit sales which is not to be collected i.e. bad debts.
To calculate:
The loss rate for each year from
Answer to Problem 83APSA
The loss Rate over the period is:
| Loss Rate Percentage | |
Explanation of Solution
The Glass House has a glass store which sells on credit. The data of past four years showing its credit sales and losses from uncollectible accounts are as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
|
| Total |
This is given in the question.
The loss rate from uncollectible accounts for the Glass House is as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
Loss Rate Percentage |
|
| Total |
(b)
Credit Sales Method:
The method named percentage of credit sales method is the method in which the bad debts are computed on the basis of percentage of sales.
Uncollectible accounts:
These are those accounts which reflect that amount of credit sales which is not to be collected i.e. bad debts.
To calculate:
The significant change in the loss rate.
Answer to Problem 83APSA
The significant change is observed in the year
Explanation of Solution
The Glass House has a glass store which sells on credit. The data of past four years showing its credit sales and losses from uncollectible accounts are as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
|
This is given in the question.
The changes in the loss rates over the period for the Glass House are as follows:
| Loss Rate Percentage | Increase or Decrease in the Loss Rate over the period | ||
| NOTE: The Base Year in this is taken to be |
|||
(c)
Credit Sales Method:
The method named percentage of credit sales method is the method in which the bad debts are computed on the basis of percentage of sales.
Uncollectible accounts:
These are those accounts which reflect that amount of credit sales which is not to be collected i.e. bad debts.
To calculate:
The loss rate for estimating the bad debt for
Answer to Problem 83APSA
The loss rate for estimating the bad debt in the year
Explanation of Solution
The Glass House has a glass store which sells on credit. The data of past four years showing its credit sales and losses from uncollectible accounts are as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
|
This is given in the question.
The loss rate for estimating the bad debt in the year
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
Loss Rate Percentage | Probability of Loss | Weighted Average of Loss | |
| Total |
(d)
Credit Sales Method:
The method named percentage of credit sales method is the method in which the bad debts are computed on the basis of percentage of sales.
Uncollectible accounts:
These are those accounts which reflect that amount of credit sales which is not to be collected i.e. bad debts.
To calculate:
The bad debt expense for
Answer to Problem 83APSA
The bad debt expense for
Explanation of Solution
The Glass House has a glass store which sells on credit. The data of past four years showing its credit sales and losses from uncollectible accounts are as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
|
This is given in the question.
The credit sales given in the question is
So, the bad debt expense to be recognised:
The journal entry for the Glass House is as follows:
| Date | Particulars | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Bad debt expense……… Allowance for Doubtful accounts.………(Record the entry of bad debt expense) |
(e)
Credit Sales Method:
The method named percentage of credit sales method is the method in which the bad debts are computed on the basis of percentage of sales.
Uncollectible accounts:
These are those accounts which reflect that amount of credit sales which is not to be collected i.e. bad debts.
The reason for adopting more lenient credit terms by the Glass House and its effect on the bad debt expense.
Answer to Problem 83APSA
The reasonable business reason for adopting the more lenient credit terms is that the business will increase their sales and revenue through this behaviour. The effect on bad debt will be that the bad debt will increase from this leniency.
Explanation of Solution
The leniency in the credit terms by the Glass House will increase the bad debt from
(f)
Credit Sales Method:
The method named percentage of credit sales method is the method in which the bad debts are computed on the basis of percentage of sales.
Uncollectible accounts:
These are those accounts which reflect that amount of credit sales which is not to be collected i.e. bad debts.
To calculate:
The increase in the operating income over those
Answer to Problem 83APSA
The incremental in the operating income is
Explanation of Solution
The Glass House has a glass store which sells on credit. The data of past four years showing its credit sales and losses from uncollectible accounts are as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
|
This is given in the question.
The increase in the income of the operations for the Glass House is as follows:
| Credit Sales |
Gross Profit |
Losses from Uncollectible Accounts |
Increase in Operation Income |
||
| Total |
Thus, the increase in the operation income is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
CORNERSTONES OF FINAN.ACCT.>CUSTOM<
- Allowance Method for Accounting for Bad Debts At the beginning of 2016, EZ Tech Companys Accounts Receivable balance was $140,000, and the balance in Allowance for Doubtful Accounts was $2,350 (Cr.). EZ Techs sales in 2016 were $1,050,000, 80% of which were on credit. Collections on account during the year were $670,000. The company wrote off $4,000 of uncollectible accounts during the year. Required Prepare summary journal entries related to the sale, collections, and write-offs of accounts receivable during 2016. Prepare journal entries to recognize bad debts assuming that (a) bad debts expense is 3% of credit sales and (b) amounts expected to be uncollectible are 6% of the year-end accounts receivable. What is the net realizable value of accounts receivable on December 31, 2016, under each assumption in part (2)? What effect does the recognition of bad debts expense have on the net realizable value? What effect does the write-off of accounts have on the net realizable value?arrow_forwardConner Pride reports year-end credit sales in the amount of $567,000 and accounts receivable of $134,000. Conner uses the balance sheet method to report bad debt estimation. The estimation percentage is 4.6%. What is the estimated balance uncollectible using the balance sheet method? A. $26,082 B. $6,164 C. $260,820 D. $61,640arrow_forwardBad Debt Expense: Percentage of Credit Sales Method Gilmore Electronics had the following data for a recent year: Cash sales $135,000 Credit sales 512,000 Accounts receivable determined to be uncollectible 9,650 The firms estimated rate for bad debts is 2.2% of credit sales. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry to write off the uncollectible accounts. 2. Prepare the journal entry to record the estimate of bad debt expense. 3. If Gilmore had written off $3,000 of receivables as uncollectible during the year, how much would bad debt expense reported on the income statement have changed? 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION If Gilmores estimate of bad debts is correct (2.2% of credit sales) and the gross margin is 20%, by how much did Gilmores income from operations increase assuming $150,000 of the sales would have been lost if credit sales were not offered?arrow_forward
- Average Uncollectible Account Losses and Bad Debt Expense The accountant for Porile Company prepared the following data for sales and losses from uncollectible accounts: Required: 1. Calculate the average percentage of losses from uncollectible accounts for 2015 through 2018. 2. Assume that the credit sales for 2019 are $1,260,000 and that the weighted average percentage calculated in Requirement 1 is used as an estimate of loses from uncollectible accounts for 2019 credit sales. Determine the bad debt expense for 2019 using the percentage of credit sales method. 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Do you believe this estimate of bad debt expense is reasonable? 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION How would you estimate 2019 bad debt expense if losses from uncollectible accounts for 2018 were What other action would management consider?arrow_forwardDetermining Bad Debt Expense Using the Aging Method At the beginning of the year, Tennyson Auto Parts had an accounts receivable balance of $31,800 and a balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts of $2,980 (credit). During the year, Tennyson had credit sales of $624,300, collected accounts receivable in the amount of $602,700, wrote off $18,600 of accounts receivable, and had the following data for accounts receivable at the end of the period: Required: 1. Determine the desired post adjustment balance in allowance for doubtful accounts. 2. Determine the balance in allowance for doubtful accounts before the bad debt expense adjusting entry is posted. 3. Compute bad debt expense. 4. Prepare the adjusting entry to record bad debt expense.arrow_forwardAllowance Method for Accounting for Bad Debts At the beginning of 2016, Miyazaki Companys Accounts Receivable balance was $105,000, and the balance in Allowance for Doubtful Accounts was $1,950. Miyazakis sales in 2016 were $787,500, 80% of which were on credit. Collections on account during the year were $502,500. The company wrote off $3,000 of uncollectible accounts during the year. Required Prepare summary journal entries related to the sales, collections, and write-offs of accounts receivable during 2016. Prepare journal entries to recognize bad debts assuming that (a) bad debts expense is 3% of credit sales and (b) amounts expected to be uncollectible are 6% of the year-end accounts receivable. What is the net realizable value of accounts receivable on December 31, 2016, under each assumption in part (2)? What effect does the recognition of bad debts expense have on the net realizable value? What effect does the write-off of accounts have on the net realizable value?arrow_forward
- McKinney Co. estimates its uncollectible accounts as a percentage of credit sales. McKinney made credit sales of 1,500,000 in 2019. McKinney estimates 2.5% of its sales will be uncollectible. Prepare the journal entry to record bad debt expense for McKinney at the end of 2019.arrow_forwardBad Debt Expense: Aging Method Glencoe Supply had the following accounts receivable aging schedule at the end of a recent year. The balance in Glencoes allowance for doubtful accounts at the beginning of the year was $58,620 (credit). During the year, accounts in the total amount of $62,400 were written off. Required: 1. Determine bad debt expense. 2. Prepare the journal entry to record bad debt expense. 3. If Glencoe had written off $90,000 of receivables as uncollectible during the year, how much would bad debt expense reported on the income statement have changed?arrow_forwardAllowance Method of Accounting for Bad Debts—Comparison of the Two Approaches Kandel Company had the following data available for 2016 (before making any adjustments): Required Prepare the journal entry to recognize bad debts under the following assumptions: (a) bad debts expense is expected to be 2% of net credit sales for the year and (b) Kandel expects it will not be able to collect 6% of the balance in accounts receivable at year-end. Assume instead that the balance in the allowance account is a $2,600 debit. How will this affect your answers to part (1)?arrow_forward
- Tonis Tech Shop has total credit sales for the year of 170,000 and estimates that 3% of its credit sales will be uncollectible. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a credit balance of 275. Prepare the adjusting entry at year-end for the estimated bad debt expense. (a) Based on an aging of its accounts receivable, Kyles Cyclery estimates that 3,200 of its year-end accounts receivable will be uncollectible. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a debit balance of 280 at year-end. Prepare the adjusting entry at year-end for the estimated uncollectible accounts.arrow_forwardUNCOLLECTIBLE ACCOUNTS-PERCENTAGE OF SALES Nicoles Neckties has total credit sales for the year of 380,000 and estimates that 2% of its credit sales will be uncollectible. Record the end-of-period adjusting entry on December 31, in general journal form, for the estimated bad debt expense. Assume the following independent conditions existed prior to the adjustment: 1. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a credit balance of 430. 2. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a debit balance of 295.arrow_forwardDoer Company reports year-end credit sales in the amount of $390,000 and accounts receivable of $85,500. Doer uses the income statement method to report bad debt estimation. The estimation percentage is 3.5%. What is the estimated balance uncollectible using the income statement method? A. $13,650 B. $2,992.50 C. $136,500 D. $29,925arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





