
Concept explainers
In Fig. 6-12, if the box is stationary and the angle θ between the horizontal and force
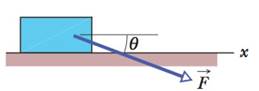
Figure 6-12 Question 1.
To find:
Whether the following quantities increase, decrease, or remain the same when an applied force is directed downward at an angle
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e) And, whether the magnitude of the frictional force on the box increases, decreases, or remains the same if the angle θ is increased.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solutions:
(a) The value of horizontal force
(b)
(c) The value of the normal force
(d)
(e) The friction force increases when the box slides and the angle between the surface and box also increases.
Explanation of Solution
Concepts
If the block slides, then kinetic frictional force is given by
Explanations:
Given Data:
In the problem (a) to (b): the box is stationary and the angle
Note: It is clear from Fig. 6-12, the angle
Formula used:
The free-body depiction for the inclined slope is provided below.
From Fig. (6-19) of the textbook and the free body diagram, we can draw:
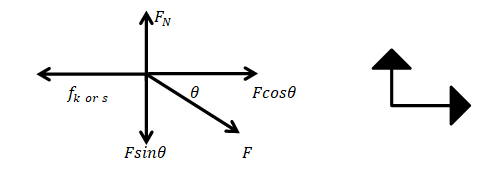
No acceleration in the first case (from (a) to (d)) as the box is in the stationary position. Hence, acceleration is zero.
Applying Newton’s 2nd law on the y-axis:
If the block slides, the kinetic frictional force:
If it does not slide, then the magnitude of maximum static friction:
Calculations: To find the magnitude of the different forces and their nature (increasing, decreasing, or no-change) when the angle (
(a) The horizontal component of the force is
(b) If a body does not move, the static frictional force and the component parallel to the surface are equal in magnitude, and is directed opposite that component. If the component decreases,
(c) The normal component of the force is given in Eq. (1).
The normal component of the force is
(d) From Eq. (3), the magnitude of the maximum static friction will also increase as
(e) In the sliding scenario, kinetic friction force can be explained by Eq. (2). This results in an increase in the kinetic frictional force. Thus, the friction force increases when the box slides and the angle between the surface and box increases.
Conclusion
If the value of the normal force
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
University Physics Volume 2
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Introduction to Electrodynamics
- A 47.4-kg box is being pushed a distance of 6.53 m across the floor by a force P whose magnitude is 149 N. The force P is parallel to the displacement of the box. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.222. Determine the work done on the box by (a) the applied force, (b) the friction force, (c) the normal force, and (d) by the force of gravity. Be sure to include the proper plus or minus sign for the work done by each force. (a) Number i (b) Number i (c) Number i (d) Number i eTextbook and Media Units Units Units Units > > <arrow_forwardA physics teacher has suspended a spring from a ceiling. When an object is attached to the spring's bottom end, the spring extends downward by an additional distance, d, measuring 7.50 cm. (That downward distance is relative to the unstretched position that the spring had previously held when in equilibrium, as shown by the horizontal dashed line in the figure below). Calculate the mass of the hanging object (in kg) if the spring constant k has the value 55.5 N/marrow_forwardYou are a member of an alpine rescue team and must get a box of supplies, with mass 2.20 kg , up an incline of constant slope angle 30.0 so that it reaches a stranded skier who is a vertical distance 3.10 m above the bottom of the incline. There is some friction present; the kinetic coefficient of friction is 6.00×10−2. Since you can't walk up the incline, you give the box a push that gives it an initial velocity; then the box slides up the incline, slowing down under the forces of friction and gravity. Take acceleration due to gravity to be 9.81 m/s2 . Use the work-energy theorem to calculate the minimum speed v that you must give the box at the bottom of the incline so that it will reach the skier. Express your answer numerically, in meters per second.arrow_forward
- A 45.9-kg box is being pushed a distance of 6.54 m across the floor by a force P whose magnitude is 168 N. The force P is parallel to the displacement of the box. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.208. Determine the work done on the box by (a) the applied force, (b) the friction force, (c) the normal force, and (d) by the force of gravity. Be sure to include the proper plus or minus sign for the work done by each force.arrow_forwardA box with a mass of 7.24 kg is held at the top of frictionless inclined plane of length L = 10.9 m and an inclination angle 0 = 26.9 degrees above the horizontal. The box is released from rest and stops at a distanced = 22.62 m from the bottom of the inclined plane along the rough horizontal surface. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the rough horizontal surface?arrow_forwardTwo identical elastic cords of negligible relaxed lengths are tied at one of their ends to fixed nails A and B that are equidistant from the origin O. The other ends of the strings are tied to a small ball. To hold the ball in equilibrium at a point P (4 m, 3 m), a force of magnitude F = 1000 N is required. Assuming free space conditions, find force constant of the cords?arrow_forward
- A spring with constant k in N / m is compressed to a length d in meters and a mass m in kilograms is placed at its free end, on a frictionless slope that forms an angle 0 with respect to the horizontal as shown in figure. After the spring is released, if the mass does not bind to the spring, it rises on the inclined plane to a height h1 measured relative to the floor. d m If we double the compression distance of the spring, keeping the spring constant, block mass and inclination angle. How does the new maximum height h, which the block would reach, compare to the height h1? Note: Height h2 is measured from the same reference level as height h1. a) It is not possible to compare the heights without more information. b) The height h2 would be the same as the height h1 c) The height h2 would be less than the height h1 d) The height h2 would be greater than the height h1arrow_forwardA 55.5-kg box is being pushed a distance of 8.48 m across the floor by a force P whose magnitude is 177 N. The force P is parallel to the displacement of the box. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.242. Determine the work done on the box by (a) the applied force, (b) the friction force, (c) the normal force, and (d) by the force of gravity. Be sure to include the proper plus or minus sign for the work done by each force. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Unitsarrow_forwardA 6.0-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force of magnitude 12 N.(A) Find the speed of the block after it has moved 3.0 m if the surfaces in contact have a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.15. (B) Suppose the force F→ is applied at an angle θ as shown in (8.8b). At what angle should the force be applied to achieve the largest possible speed after the block has moved 3.0 m to the right?arrow_forward
- If the net work done by external forces on a particle is zero, which of the following statements about the particle must be true? (a) Its velocity is zero. (b) Its velocity is decreased. (c) Its velocity is unchanged. (d) Its speed is unchanged. (e) More information is needed.arrow_forwardA block placed on a horizontal surface is being pushed by a force F making an angle 0 with the vertical. If the friction coefficient is u, how much force is needed to get the block just started. Discuss the situation when tane < Larrow_forwardP6arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

