
Concept explainers
(a)
The production process without capital input.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
A production function of a firm shows the relationship between the output and two inputs, capital and labor. In this case, the firm follows the Cobb‑Douglas production function.
Here, this production function clearly shows that the firm produces the output using the inputs, capital, and labor at an equal proportion. Therefore, producer cannot build any coffee tables without tools (capital). If did so, the output would be zero.
(b)
The production process without labor input.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
As described in part (a), the firm follows the Cobb‑Douglas production function where the firm uses the inputs, capital, and labor at an equal proportion to produce the given level of output. Therefore, the producer cannot build any coffee tables without labor inputs. If did so, the output would be zero.
(c)
The short run production function.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The production economies state that the short-run is the period of time during which one or more inputs into production cannot be changed, which mean that the short run production function of a firm holds variable inputs as well as fixed inputs. Therefore, the short run production function shows the output as a function of variable input and the fixed input.
In this case, the fixed input, capital, is given as 16. Now substitute the respective value into the given Cobb‑Douglas production function to get the short run production function of the firm.
Therefore, the short run production function is
Fixed inputs: The fixed inputs are inputs that cannot be changed in the short run
Variable inputs: The variable inputs are inputs that can be changed in the short run.
(d)
The graphical representation of the production function.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Short run production function is given below (Derived in subpart (c)).
Substitute the labor of 1 unit in Equation (1) to calculate the output at that particular level.
In the short run, output with one unit of labor is 16 units.
Table 1 shows the output of different levels of labor.
Table 2
| Labor | Output |
| 1 | 16 |
| 4 | 32 |
| 9 | 48 |
| 16 | 64 |
| 25 | 80 |
Figure 1 shows the short-run production function.
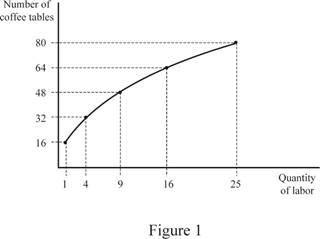
In Figure 1, the vertical axis shows the output and the horizontal axis shows the quantity of labor inputs. The production curve shows the possible level of output with different labor quantities.
(e)
The average and marginal product of labor.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The marginal product can be calculated using the following equation.
Now substitute the respective in Equation (1) to get the value of marginal product at 4 units of labor inputs.
Therefore, the value of marginal product at 4 units of labor is 5.33.
The average product can be calculated using the following equation.
Now substitute the respective values in Equation (3) to get the value of average product at 4 units of labor inputs.
Therefore, the value of the average product at 4 units of labor is 8.
Table 2 shows the values of total product, marginal product, and average product using Equations (1), (2), and (3).
Table 2
|
Number of workers | Total product | Marginal product | Average product |
| 1 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| 4 | 32 | 5.33 | 8 |
| 9 | 48 | 3.2 | 5.33 |
| 16 | 64 | 2.29 | 4 |
| 25 | 80 | 1.78 | 3.2 |
Marginal product: A marginal product is the additional output that a firm can produce using an additional unit of an input, holding use of the other input constant.
Average product: An average product is the quantity of output produced per unit of input.
(f)
The total product, average product, and marginal product.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
In this case, the capital was fixed at 16 units. If there is a fall of 7 machines, then the capital will be 9
Therefore, the new short run production function is
Table 3 shows the values of total product, marginal product, and average product at each level of new output using equation (1), (2), and (3).
Table 3
|
Number of workers | Total product | Marginal product | Average product |
| 1 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 4 | 24 | 4 | 6 |
| 9 | 36 | 2.4 | 4 |
| 16 | 48 | 1.71 | 3 |
| 25 | 60 | 1.33 | 2.4 |
Total product: The total product is the total quantity of output produced by a firm at the given time period.
Average product: An average product is the quantity of output produced per unit of input.
Marginal product: A marginal product is the additional output that a firm can produce using an additional unit of an input.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
LaunchPad for Goolsbee's Microeconomics (Six Month Access)

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





