
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton, in the given species, is to be identified, and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
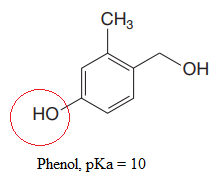
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
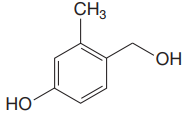
There are three protons that could be acidic. The proton attached to the carbon in methyl group, to the oxygen atom in alcohol, and the proton directly attached to the oxygen atom in phenol functional group are the protons that could be acidic.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having
The pKa value for the compound having
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid, and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
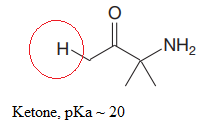
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
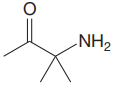
In the given structure, the proton attached to the nitrogen atom, and to the carbon atom next to the carbonyl group, could be the acidic protons.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid, and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(c)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
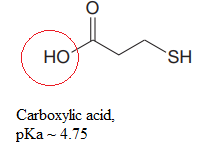
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
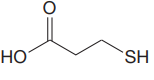
There are two protons that could be acidic. The proton attached to the oxygen atom which is directly bonded to the carbonyl group, and to the sulfur atom are the protons that could be acidic.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(d)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
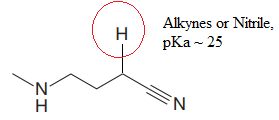
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
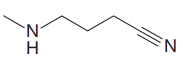
In the given structure, the proton attached to the nitrogen atom and to the triple bonded carbon atom could be the acidic protons.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(e)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
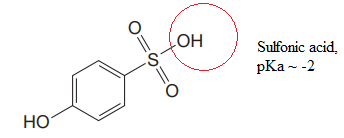
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
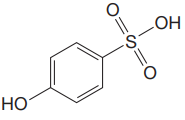
There are two protons that could be acidic. The proton attached to the carbon in methyl group, to the oxygen atom in alcohol, and the proton directly attached to the oxygen atom in phenol functional group are the protons that could be acidic.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(f)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
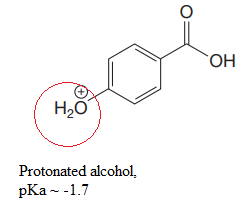
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
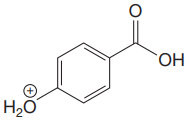
There are two protons that could be acidic. The proton attached to the carbon in methyl group, to the oxygen atom in alcohol, and the proton directly attached to the oxygen atom in phenol functional group are the protons that could be acidic.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having protonated
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid and the proton associated is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for protonated

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(g)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
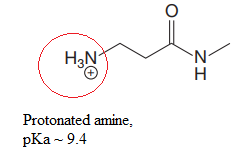
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
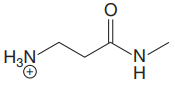
In the given structure, the proton attached to both nitrogen atoms could be acidic protons.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having protonated
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for protonated

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
(h)
Interpretation:
The most acidic proton in the given species is to be identified and its pKa value is to be estimated.
Concept introduction:
An Acidic proton is the one which is directly bonded to an electronegative atom. The acidity of a compound is governed largely by the functional group on which the acidic proton is found. Nearby structural features such as highly electronegative substituent or presence of a double or triple bond can alter the acidity significantly. The pKa value for a particular compound is explained based on structural similarities of the compound and the compounds listed in Table 6-1.
Answer to Problem 6.50P
The most acidic proton in the given species along with its estimated pKa value is:
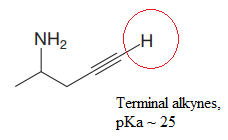
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
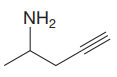
In the given structure, the protons attached to the terminal triple bonded carbon atom and to the nitrogen atom could be acidic protons.
According to Table 6-1, the relative pKa value of each of the protons is:
The pKa value for the compound having protonated
The pKa value for the compound having
Lower the pKa value, stronger is the acid and the proton associated with it is the most acidic proton. The lowest pKa value is for

The most acidic proton in the given structure is identified along with its estimated pKa value using Table 6-1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORG.CHEM W/TEXT+SOLU.MANUAL
- Please answer this NEATLY, COMPLETELY, and CORRECTLY for an UPVOTE. Arrange the intermediates below in order of increasing basicity:arrow_forwardidentify two basic sites and predict which one will be more reactivearrow_forwardWhich of the underlined protons for molecule 1 and 2 is more acidic and why?arrow_forward
- Which of the bases below would be best to ensure the following reaction was the major outcome?arrow_forwardOn the following two molecules, circle the most acidic proton, andrationalize your choice. Simply citing pKa values is not sufficient to answer this question. Include structures and a brief written explanation to support your choice.arrow_forwardSummarize the relationship between pKa and acid strength by completing the following sentences: a. The higher the pKa of an acid, the stronger or weaker the acid. b. The lower the pKa of an acid, the stronger or weaker the acid.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
