
Concept explainers
(a)
Find the z interval for
(a)
Answer to Problem 10P
The z interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Z score:
The number of standard deviations the original measurement x is from the value of
In the formula, x is the raw score,
The variable x is the weight of a fawn in kilograms. The weight of the body is
The z interval is,
Consider
Subtract 27.2 on both sides of the inequality.
Divide 4.3 on both sides of the inequality.
Hence, the z interval for
(b)
Find the z interval for
(b)
Answer to Problem 10P
The z interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For the z interval consider,
Subtract 27.2 on both sides of the inequality.
Divide 4.3 on both sides of the inequality.
Hence, the z interval for
(c)
Find the z interval for
(c)
Answer to Problem 10P
The z interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For the z interval consider,
Subtract 27.2 for each part of the inequality.
Divide 4.3 for each part of the inequality.
Hence, the z interval for
(d)
Find the x interval for
(d)
Answer to Problem 10P
The x interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The z score is,
For the x interval consider,
Multiply 4.3 on both sides of the inequality.
Add 27.2 on both sides of the inequality.
Hence, the x interval for
(e)
Find the x interval for
(e)
Answer to Problem 10P
The x interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For the x interval consider,
Multiply 4.3 on both sides of the inequality.
Add 27.2 on both sides of the inequality.
Hence, the x interval for
(f)
Find the x interval for
(f)
Answer to Problem 10P
The x interval for
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
For the x interval consider,
Multiply 4.3 for each part of the inequality.
Add 27.2 for each part of the inequality.
Hence, the x interval for
(g)
Identify whether the fawn weighing 14 kilograms is unusually small animal or not using z values and Figure 6-15.
(g)
Answer to Problem 10P
Yes, the fawn weighing 14 kilograms is unusually small animal.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The weight of the fawn is 14 kilograms. The z score is,
The weight of the fawn is 14 kilograms is 3.07 standard deviations below the mean value. The z score value is less than –3 indicating that the value is very unusual.
The figure 6-15 is the standard normal distribution curve. The z value is located on the curve as below.
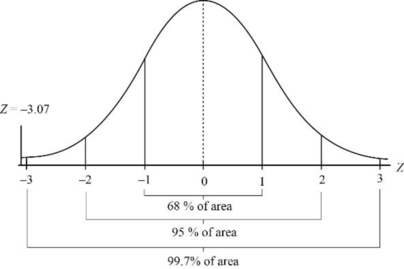
The z value that is far from the mean (zero) is considered as unusual. From the figure it can be observed that z value is very far from the value of mean indicating that it is very unusual. This shows that, fawn weighing 14 kilograms is unusually very small animal.
(h)
Explain whether the value of z for weight of the fawn would be closer to 0, –2, or 3 when fawn is unusually large.
(h)
Answer to Problem 10P
The value of z for weight of the fawn would be closer to 3 when fawn is unusually large.
Explanation of Solution
The z value that is far from the mean (zero) is considered as unusual. If the value is closer to –3 is usually very small and value closer to 3 is usually very large.
If the value of z for weight of the fawn is closer to 3 then the weight of the fawn usually would be very large.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Understandable Statistics: Concepts and Methods
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





