
Concept explainers
Absorption Costing Approach to Cost-Plus Pricing LO6—8
Martin Company uses the absorption costing approach to cost-plus pricing. It is considering the introduction of a new product. To determine a selling price, the company has gathered the following information:
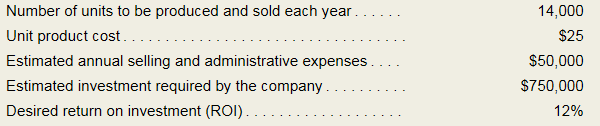
Required:
- Compute the markup percentage on absorption cost required to achieve the desired ROL.
- Compute the selling price per unit.
Concept Introduction:
Costing is a process of calculation of the cost of the product or service manufactured or provided by an organization. There are two methods of costing; absorption costing and variable costing.
As per nature, costs can be divided into three categories, i.e., variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
Requirement-1:
The markup percentage.
Answer to Problem 6A.1E
The markup percentage is 25.71%.
Explanation of Solution
The markup percentage is calculated as follows:
| Number of units (A) | $ 14,000 |
| Unit product cost (B) | $ 25 |
| Total absorption product cost (C) = (A*B) | $ 350,000 |
| Selling and admn expenses (D) | $ 50,000 |
| Total Cost (E) = (C+D) | $ 400,000 |
| Amount of investment (F) | $ 750,000 |
| Desired return on investment (G) | 12% |
| Desired markup (H) = (F*G) | $ 90,000 |
| Markup % (I) = (H/C) | 25.71% |
Concept Introduction:
Costing is a process of calculation of the cost of the product or service manufactured or provided by an organization. There are two methods of costing; absorption costing and variable costing.
As per nature, costs can be divided into three categories, i.e., variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
Requirement-2:
The selling price per unit.
Answer to Problem 6A.1E
The selling price per unit is $35.
Explanation of Solution
The selling price per unit is calculated as follows:
| Number of units (A) | $ 14,000 |
| Unit product cost (B) | $ 25 |
| Total absorption product cost (C) = (A*B) | $ 350,000 |
| Selling and admn expenses (D) | $ 50,000 |
| Total Cost (E) = (C+D) | $ 400,000 |
| Amount of investment (F) | $ 750,000 |
| Desired return on investment (G) | 12% |
| Desired markup (H) = (F*G) | $ 90,000 |
| Markup % (I) = (H/C) | 25.71% |
| Tota cost per unit (J) = (E/A) | $ 28.57 |
| Markup per unit (K) = (H/A) | $ 6.43 |
| Selling price (J+K) | $ 35.00 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- EA5. LO 2.2Rose Company has a relevant range of production between 10,000 and 25,000 units. The following cost data represents average cost per unit for 15,000 units of production. Using the cost data from Rose Company, answer the following questions: If 10,000 units are produced, what is the variable cost per unit? If 18,000 units are produced, what is the variable cost per unit? If 21,000 units are produced, what are the total variable costs? If 11,000 units are produced, what are the total variable costs? If 19,000 units are produced, what are the total manufacturing overhead costs incurred? If 23,000 units are produced, what are the total manufacturing overhead costs incurred? If 19,000 units are produced, what are the per unit manufacturing overhead costs incurred? If 25,000 units are produced, what are the per unit manufacturing overhead costs incurred?arrow_forwardQuestion Content Area Carmen Co. can further process Product J to produce Product D. Product J is currently selling for $23.95 per pound and costs $16.00 per pound to produce. Product D would sell for $36.45 per pound and would require an additional cost of $9.00 per pound to produce. The differential cost of producing Product D is?arrow_forwardQuestion A9 A company is using a relevant costing approach in producing a price for a tender for a one-off contract. The contract needs 15kg of material Y. It currently costs £100 per kg to purchase material Y. The company has 10kg of this material in stock from a previous contract, it cost £85 per kg when purchased two years ago and it will not be used in the ordinary course of business. If it is not used for this contract the company has found a buyer for the quantity of material Y held, they are willing to pay £90 per kg for the material although it will cost £50 to pack and ship the material to the buyer. What is the relevant cost of material Y for the contract?arrow_forward
- fixed cost =190000 variable cost per procedure 50 volume 10000 1) what revenue per visit is required to break even 2) what revenue per visit is required to provide a profit of 100000 3) using the answer to question 2 above,find the contribution margin required to provide a profit of 100000arrow_forwardQuestion Content Area Sales Mix and Break-Even Analysis Olmstead Company has fixed costs of $2,170,920. The unit selling price, variable cost per unit, and contribution margin per unit for the company's two products follow: Product Selling Price Variable Cost per Unit Contribution Margin per Unit QQ $700 $380 $320 ZZ 940 760 180 The sales mix for Products QQ and ZZ is 35% and 65%, respectively. Determine the break-even point in units of QQ and ZZ. If required, round your answers to the nearest whole number. a. Product QQ fill in the blank 1 unitsb. Product ZZ fill in the blank 2 unitsarrow_forwardExercise 1: From the following information calculate: (I) P/V Ratio (2) Break-Even Point (3) If the selling price is reduced to OMR. 80, calculate New Break-Even Point: Total sales OMR. 500,000 Selling price per unit OMR. 100 Variable cost per unit OMR. 60 Fixed cost OMR. 120,000arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


