
Concept explainers
(a)
The dimensional parameter generated by the given quantities.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
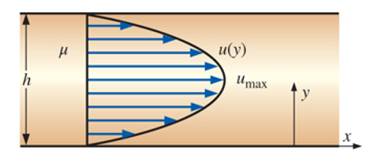
In the given question,
We use the method of variable to find the dimensionless quantity from the given data.
Total number of parameters given,
| n = 5 |
We define the function as,
Primary dimensions of all the given parameters,
The number of primary dimensions is (L, M, t).
Since the value of n is 5.
So,
J = 3,
And,
k = (N − J)
k = (5 − 3) = 2.
So, the number of pi-terms is two.
For further calculation we need to choose any three repeating quantities,
I choose
Thus, by using repeating variables, first independent pi- term is formed.
So, the substituting the values of variables to get a dimensionless relationship.
Thus, the required relationship is,
On simplifying,
(b)
The change in
Answer to Problem 97P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
From subpart a,
On simplifying,
When h is doubled,
(c)
The change in
Answer to Problem 97P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
From subpart a,
On simplifying,
When
(d)
The number of experiments required to describe complete relationship.
Answer to Problem 97P
The number of experiments required is 2.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
From previous problem,
There exist two pi-terms in the given question,
So, we need to perform two experiment for generation complete relationship between the given parameters.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, twodimensional velocity field V-›= (u, ? ) = (U0 + bx) i-›− byj-› where U0 is the horizontal speed at x = 0. Use the equation for volumetric strain rate to verify that this flow field is incompressiblearrow_forwardTheodore von Kármán in 1930 theorized that turbulentshear could be represented by τturb = ε du/dy, whereε= ρκ2y2|du/dy| is called the mixing-length eddy viscosityand κ ≈ 0.41 is Kármán’s dimensionless mixing-lengthconstant [2, 3]. Assuming that τturb ≈ τw near the wall,show that this expression can be integrated to yield thelogarithmic overlap la).arrow_forwardIn a steady, two-dimensional flow field in the xyplane, the x-component of velocity is u = ax + by + cx2 where a, b, and c are constants with appropriate dimensions. Generate a general expression for velocity component ? such that the flow field is incompressible.arrow_forward
- One of the corner flow patterns of Fig. 8.18 is given by thecartesian stream function ψ = A(3yx2 - y3). Which one?Can the correspondence be proved ?arrow_forwardThe velocity field for a line vortex in the r?-plane is given byur = 0 u? = K / rwhere K is the line vortex strength. For the case with K = 1.5 m/s2, plot a contour plot of velocity magnitude (speed). Specifically, draw curves of constant speed V = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5 m/s. Be sure to label these speeds on your plot.arrow_forwardConsider the following steady, incompressible, twodimensional velocity field: V-›= (u, ? ) = (4.35 + 0.656x) i-›+ (−1.22 − 0.656y) j-›Generate an analytical expression for the flow streamlines and draw several streamlines in the upper-right quadrant from x = 0 to 5 and y = 0 to 6.arrow_forward
- the differential equation for conservation of mass, the continuity equation. In cylindrical coordinates, and for steady flow, 1/ r ∂(rur) /∂r + 1/ r ∂u? /∂? + ∂uz /∂z = 0 Write the primary dimensions of each additive term in the equation, and verify that the equation is dimensionally homogeneous. Show all your work.arrow_forwardA viscous liquid of constant ρ and μ falls due to gravitybetween two plates a distance 2 h apart, as in Fig. P4.37. Thefl ow is fully developed, with a single velocity component w = w ( x ). There are no applied pressure gradients, onlygravity. Solve the Navier-Stokes equation for the velocityprofi le between the plates.arrow_forwardImagine a steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow that is purely circular in the xy- or r?-plane. In other words, velocity component u? is nonzero, but ur is zero everywhere. What is the most general form of velocity component u? that does not violate conservation of mass?arrow_forward
- Converging duct flow is modeled by the steady, twodimensional velocity field V-›= (u, ? ) = (U0 + bx) i-›− byj-› where U0 is the horizontal speed at x = 0 . As vertical line segment AB moves downstream it shrinks from length ? to length ? +Δ? assketchedin.Generateananalytical expression for the change in length of the line segment, Δ? . Note that the change in length, Δ? , is negative.arrow_forwardImagine a steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow that is purely radial in the xy- or r?-plane. In other words, velocity component ur is nonzero, but u? is zero everywhere. What is the most general form of velocity component ur that does not violate conservation of mass?arrow_forwardOil, of density ρ and viscosity μ , drains steadily down theside of a vertical plate, as in Fig. P4.80. After a developmentregion near the top of the plate, the oil fi lm willbecome independent of z and of constant thickness δ .Assume that w = w ( x ) only and that the atmosphere offersno shear resistance to the surface of the fi lm. ( a ) Solve theNavier-Stokes equation for w ( x ), and sketch its approximateshape. ( b ) Suppose that fi lm thickness δ and the slopeof the velocity profi le at the wall [ ∂ w /∂ x ] wall are measuredwith a laser-Doppler anemometer (Chap. 6). Find anexpression for oil viscosity μ as a function of ( ρ , δ , g ,[ ∂ w / ∂ x ] wall ).arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





