
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780073511214
Author: Francis A Carey Dr., Robert M. Giuliano
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 66P
As a method for the preparation of
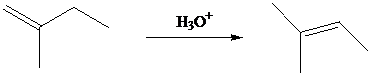
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Give the structural chemistry of active methylene, classify it asradical/intermediate/stable
organic compound, reagent of its production and role in alkylation
Pentafluorophenol is readily prepared by heating hexafluorobenzene with potassium hydroxide in tert-butyl alcohol:What is the most reasonable mechanism for this reaction? Comment on the comparative ease with which this conversion occurs.
3. Obtain acetophenone and acetaldehyde by reaction of glycols with periodic acid. Justify your answer with the reaction mechanism.
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
Ch. 8.1 - What three alkenes yield 2-methylbutane on...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 5PCh. 8.4 - Give a structural formula for the carbocation...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 8.6 - Instead of the three-step process of Mechanism...Ch. 8.6 - The rates of hydration of the two alkenes shown...Ch. 8.6 - Is the electrophilic addition of hydrogen chloride...
Ch. 8.7 - You can calculate the equilibrium constant for the...Ch. 8.7 - Does the presence or absence of a catalyst such as...Ch. 8.7 - The gas phase reaction of ethanol with hydrogen...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 14PCh. 8.8 - Hydroborationoxidation of -pinene, like its...Ch. 8.10 - Arrange the compounds 2-methyl-1-butene,...Ch. 8.10 - Give the structure of the product formed when each...Ch. 8.11 - Prob. 18PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 19PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 23PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 24PCh. 8 - How many alkenes yield...Ch. 8 - Prob. 26PCh. 8 - Catalytic hydrogenation of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 28PCh. 8 - Prob. 29PCh. 8 - Prob. 30PCh. 8 - Prob. 31PCh. 8 - A single epoxide was isolated in 7984% yield in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33PCh. 8 - Prob. 34PCh. 8 - On catalytic hydrogenation over a rhodium...Ch. 8 - Prob. 36PCh. 8 - Prob. 37PCh. 8 - Prob. 38PCh. 8 - Prob. 39PCh. 8 - 1-Butene has a higher heat of hydrogenation than...Ch. 8 - Match the following alkenes with the appropriate...Ch. 8 - The heats of reaction were measured for addition...Ch. 8 - Complete the following table by adding + and -...Ch. 8 - Match the heats of hydrogenation (107 kJ/mol,...Ch. 8 - The iodination of ethylene at 25 C is...Ch. 8 - Specify reagents suitable for converting...Ch. 8 - (a) Which primary alcohol of molecular formula...Ch. 8 - Identify compounds A and B in the retrosynthesis...Ch. 8 - Identify compounds A and B in the retrosynthesis...Ch. 8 - Prob. 50PCh. 8 - On being heated with a solution of sodium ethoxide...Ch. 8 - Compound A (C7H15Br) is not a primary alkyl...Ch. 8 - Prob. 53PCh. 8 - Prob. 54PCh. 8 - A mixture of three alkenes (A, B, and C) was...Ch. 8 - Reaction of 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene with hydrogen...Ch. 8 - Dehydration of 2,2,3,4,4-pentamethyl-3-pentanol...Ch. 8 - Prob. 58PCh. 8 - East Indian sandalwood oil contains a hydrocarbon...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - On the basis of the mechanism of acid-catalyzed...Ch. 8 - As a method for the preparation of alkenes, a...Ch. 8 - Which of the following is the most reasonable...Ch. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Oxymercuration Concerns about mercurys toxicity...Ch. 8 - Prob. 70DSPCh. 8 - Prob. 71DSPCh. 8 - Prob. 72DSPCh. 8 - Prob. 73DSPCh. 8 - Oxymercuration Concerns about mercurys toxicity...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Quinolines, heterocyclic compounds that contain a pyridine ring fused to a benzene ring, are commonly synthesized by a method known as the Skraup synthesis, in which aniline reacts with glycerol under acidic conditions. Nitrobenzene is added to the reaction mixture to serve as an oxidizing agent. The first step in the synthesis is the dehydration of glycerol to propenal. a. What product would be obtained if para-ethylaniline were used instead of aniline? b. What product would be obtained if 3-hexen-2-one were used instead of glycerol? c. What starting materials are needed for the synthesis of 2,7-diethyl-3-methylquinoline?arrow_forwardNerol, a natural product from lemongrass, can be converted to α-cyclogeraniol upon treatment with chlorosulfonic acid(an acid catalyst). Write a stepwise mechanism for this process. The reaction involves a carbocation intermediate.arrow_forwardAcid-catalyzed dehydration of 2,2-dimethyl-1-hexanol gave a number of isomeric alkenes including 2-methyl-2-heptene as shown in the following equation.(a) Write a stepwise mechanism for the formation of 2-methyl-2-heptene, using curved arrows to show the flow of electrons. (b) What other alkenes do you think are formed in this reaction?arrow_forward
- Alkene can be prepared from alcohol using acid catalyzed dehydration reaction a. Draw and label the main aparatus and general important reagents that involved in the distillation process for this reaction. b. Suggest three (3) laboratory safety rules while conducting the reaction in 2(a) c. The prepared alkene reacts with bromine water with the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid. Suggest the reaction and explain your answer.arrow_forwardThe intramolecular Claison Condensation (Dieckmann Cyclization) of the double ester, diethyl 3-methylheptandioate, gives a mixture of two β-keto esters. What are their structures and why is a mixture formed?arrow_forwardTwo moles of organic compound ‘A’ on treatment with a strong base gives two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ on dehydrogenation with Cu gives ‘A’ while acidification of ‘C’ yields carboxylic acid ‘D’ with molecular formula of CH2O2. Identify the compounds A, B, C and D and write all chemical reactions involved.arrow_forward
- Compound A is an alcohol that undergoes oxidation to produce compound B.Compound B is a ketone that gives positive triiodomethane reaction. Compound B isthen reacted with phenyl magnesium bromide, C6H5MgBr in the presence of aqueousacid to form compound C. Compound C has the molecular formula of C9H12O. Deducethe structure for compound A, B and C. PLEASE PROVIDE CLEAR DRAWINGS AND EXPLANATIONSarrow_forwardDescribe the ozonolysis of alkenes one mole of a hydrocarbon(A) reacts with one mole of beomine giving a dibromo compound C5H10Br2.Substance A on treatment with cold dilute kMnO4 solution forms a compound C5C12O2(C5H12O2) on ozonolysis A,gives equimolar quantities of propanone and ethanol.Deduce the structure of substance A.arrow_forwardStearolic acid, C18H32O2, yields stearic acid on catalytic hydrogenation and undergoes oxidative cleavage with ozone to yield nonanoic acid and nonanedioic acid. What is the structure of stearolic acid?arrow_forward
- An organic compound A which has a characteristic odour is treated with 50% NaOH to give B (C7H8O)and C which is a sodium salt of an organic acid . Oxidation of B gives back A. Heating C with soda lime yields an aromatic hydrocarbon D . Deduce the structures of A,B,C and Darrow_forwardArrange the following in the increasing order of property shown : (i) Methanol, Ethanol, Diethylether, Ethylene-glycol. (Boiling points) (ii) Phenol, o-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol, p-nitrophenol. (Acidic strength) (iii) Dimethylether, ethanol, phenol. (Solubility in water) (iv) n-butanol, 2-methylpropan-1-ol, 2-methylpropan-2-ol. (Acidic strength)arrow_forwardAn unknown hydrocarbon A with the formula C6H12 reacts with 1 molar equivalent ofH2 over a palladium catalyst. Hydrocarbon A also reacts with OsO4 to give diol B. When oxidized with KMnO4 in acidic solution, A gives two fragments. One fragmentis propanoic acid, CH3CH2CO2H, and the other fragment is ketone C. What are thestructures of A, B, and C? Write all reactions and show your reasoning.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
07 Physical Properties of Organic Compounds; Author: Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UjlSgwq4w6U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY