
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a. 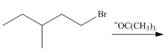 e.
e. 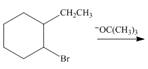 h.
h. 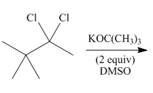
b. ![]() f.
f. 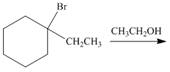 i.
i. 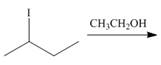
c. 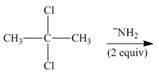 g.
g. ![]() j.
j. 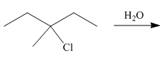
d. 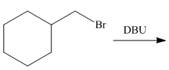
(a)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
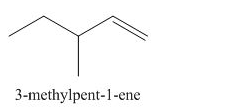
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves primary alkyl halide and strong bulky base. Primary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong and bulky; it undergoes elimination reaction through
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
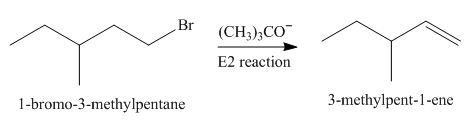
Figure 1
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic products formed in the given reaction are shown below.
![]()
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the alkyl halide is primary and ethoxide ion is a strong base. Primary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong, and also a strong nucleophile, the given halide undergoes substitution reaction through
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 2.
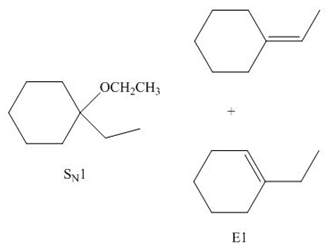
(c)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A carbon atom bonded to two halogen groups is called germinal dihalides. Geminal dihalides undergo double dehydrohalogenation reaction in the presence of excess base to form alkyne as the final product. The reaction prefers elimination pathway.
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
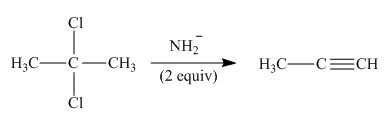
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, germinal dihalide is the starting material and amine base is strong, negatively charged and present in excess amount
The corresponding reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
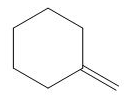
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the alkyl halide is primary and base is strong, but non-nucleophilic. Primary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong and non-nucleophilic, it undergoes elimination reaction through E2 pathway.
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
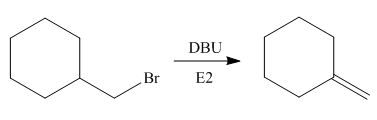
Figure 4
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
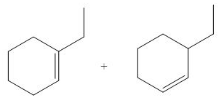
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the alkyl halide is secondary and base is a strong, negatively charged bulky base. Secondary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong and bulky it undergoes elimination reaction through E2 pathway.
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
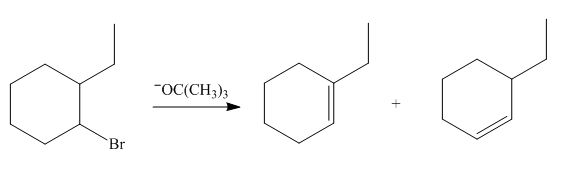
Figure 5
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves tertiary alkyl halide, weak base that is also a weak nucleophile. These conditions make the given halide (tertiary) suitable to undergo either substitution by
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
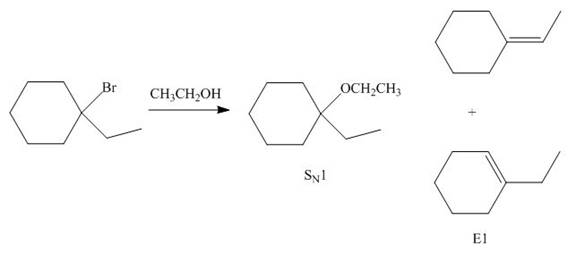
Figure 6
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of sodamide
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
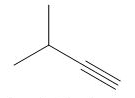
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is vicinal dihalide.
Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of sodamide
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
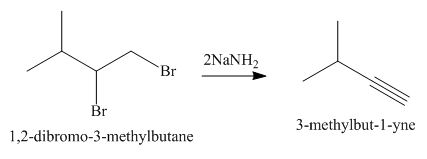
Figure 7
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of sodamide
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
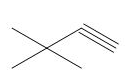
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is vicinal dihalide.
Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of DMSO.
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
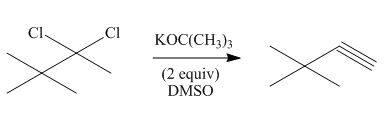
Figure 8
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
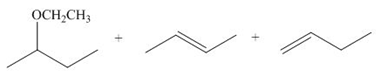
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves secondary alkyl halide and a base that is also a weak nucleophile. These conditions make the given halide (secondary) suitable to undergo either substitution by
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
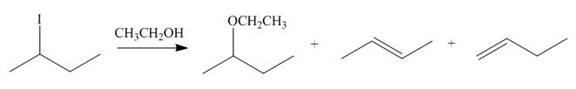
Figure 9
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
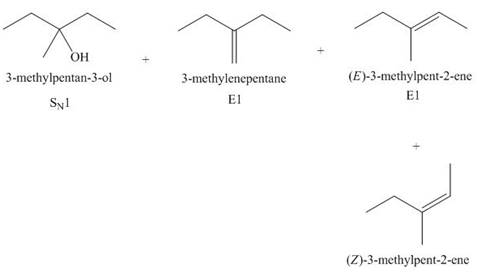
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is tertiary. Water is a weak base. These conditions make the given halide (tertiary) suitable to undergo substitution as well as elimination reaction
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
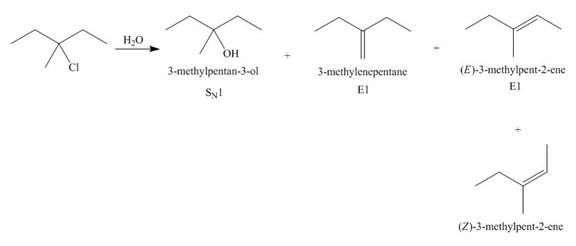
Figure 10
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
KCTCS Organic Chemistry Value Edition (Looseleaf) - Text Only
- Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reduction.arrow_forwardDraw a stepwise mechanism for the attached reaction that forms ether D. D can be converted to the antidepressant fluoxetine (trade name Prozac) in a single steparrow_forwardAcid hydrolysis of esters produces____ and____?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

