
(a)
Interpretation:
To draw the mixture of enantiomers A and B obtained from cis and Trans isomers of 1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with KOC (CH3)3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
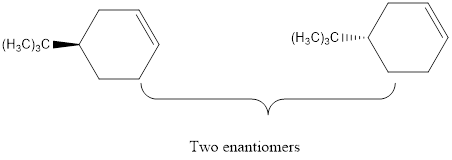
Explanation of Solution
The elimination of the Br from the reactant using base to form the respective

(b)
Interpretation:
To determine the isomer that reacts faster with KOC(CH3)3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
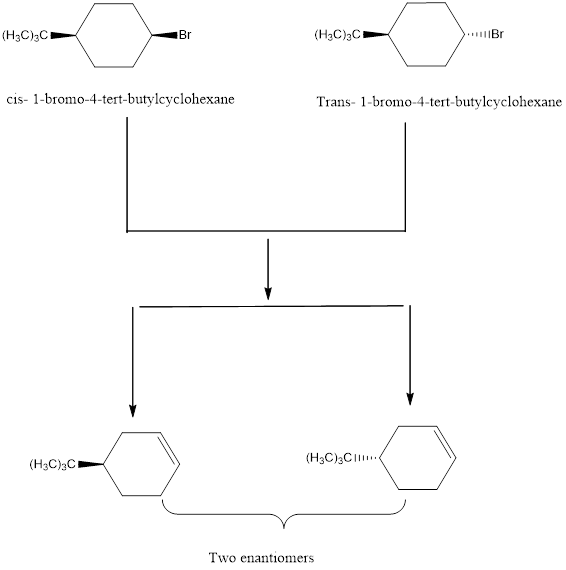
The bulky tert-butyl group in the cyclohexane ring is in the equatorial position.

In the cis-isomer, the Br is in the axial position. So cis-isomer is faster than the trans-isomer.
Explanation of Solution

The bulky tert-butyl group in the cyclohexane ring is in the equatorial position. The cis isomer has the Br in the axial position while in the trans isomer the Br is in the equatorial position. For the dehydrogenation to occur, the halogen must be in the axial position to afford trans diaxial elimination of H and X. Thus the cis isomer react faster than trans where the Br lies in the equatorial position.
Thus cis-isomer is faster than the trans-isomer due to axial position of Br in the structure.
(c)
Interpretation:
To draw the structures for C and D from cis and trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product
![]()
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product
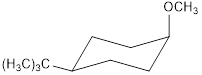
Explanation of Solution
The major products C and D formed when cis and trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane reacts with NaOCH3 is shown. The respective reaction takes place by SN2 reaction mechanism that is by backside attack of the nucleophile.
.
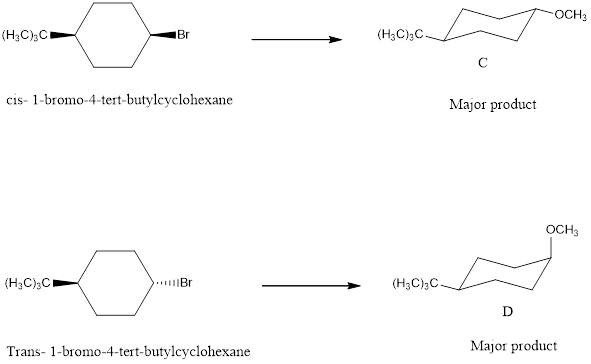
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product.
![]()
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3 forms the product.

(d)
Interpretation:
To determine the isomer that reacts faster with NaOCH3.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
The cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane reacts faster when compared to trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane.
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3.
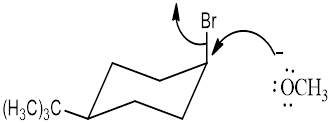
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3
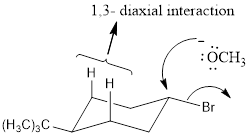
Explanation of Solution
NaOCH3, is a strong nucleophile. The reaction follows the SN2 in which the backside attack occurs. With the cis isomer the nucleophile can attack by the equatorial position to avoid the 1, 3-diaxial interaction. Moreover only the cis isomer has the Br and Β carbon in the anti periplanar that is in trans diaxial arrangement when compared to trans isomer. Thus the cis isomer reacts faster than trans isomer.
cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3
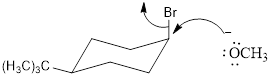
trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane with NaOCH3

Thus the cis -1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane reacts faster when compared to trans-1-bromo-4-tert-butylcyclohexane
(e)
Interpretation:
To explain why there is different products formed when the alkyl halides uses two different alkoxides.
Concept introduction:
The most common mechanism for dehydrohalogenation is the E2 mechanism. An E2 reaction exhibits a second-order kinetics, in which the reaction is bimolecular and both the alkyl halide and the base appear in the rate equation. The most straightforward explanation for the second-order kinetics is a concerted reaction: all bonds are broken and formed in a single step. In other words simultaneously all bonds are broken and formed.
The transition state of an E2 reaction consists of four atoms from the alkyl halide-one hydrogen atom, two carbon atoms, and the leaving group (X)-all aligned in the same plane. There are two ways for the C-H and C-x bonds to be coplanar. When the H and X atoms oriented on the same side of the molecule. This geometry is called syn periplanar. While the H and X atoms oriented on opposite sides of the molecule. This geometry is called anti periplanar. The dihedral angle for the C-H and C-X bonds equals 0° for the syn periplanar arrangement and 180° for the anti periplanar arrangement.
Whereas the E1 reaction is a twostep reaction of first order kinetics. The two steps reaction is the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed.
Answer to Problem 8.57P
The bulky base –OC(CH3)3 favours the elimination by an E2 reaction mechanism, to get a mixture of enantiomers A and B. The strong nucleophile –OCH3 favours nucleophile substitution by an SN2 mechanism. Inversion of configuration results from backside attack of the nucleophile. Thus different product are formed.
Explanation of Solution
-OCH3, is a strong nucleophile. The reaction follows the SN2 in which the backside attack occurs. With the cis isomer the nucleophile can attack by the equatorial position to avoid the 1, 3-diaxial interaction. Moreover only the cis isomer has the Br and Β carbon in the anti periplanar that is in trans diaxial arrangement when compared to trans isomer. Thus the cis isomer reacts faster than trans isomer. The bulky base –OC(CH3)3 favours the elimination by an E2 reaction mechanism, to get a mixture of enantiomers A and B.
Thus different product are formed when the alkyl halides uses two different alkoxides are used.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
KCTCS Organic Chemistry Value Edition (Looseleaf) - Text Only
- Explain why the addition of HBr to alkenes A and C is regioselective, forming addition products B and D, respectively.arrow_forwardExplain why the addition of HBr to alkenes A and C is regioselective,forming addition products B and D, respectively.arrow_forwardWhich group in each pair is assigned the higher priority? a. – CH3, – CH2CH3 b. – I, – Br c. – H, – D d. – CH2Br, – CH2CH2Br e. – CH2CH2Cl, – CH2CH(CH3)2 f. – CH2OH, – CHOarrow_forward
- 1. Using Br2 in C2H4Br2 will result in HBr and ______. a. C2H3Cl3 b. C2H4Cl3 c. C2H2Cl3 d. none of the above 2. How many halogenation are posible in propane? a. 3 b. 8 c. 6 d. 10 3.Sulfonation of pentane will result in ________ and water. a. C5H11SO3H b. C5H12SO3H c. C5H14SO3H d. none of the above 4.Nitration of hexane will result in ________ and water. a. C6H13SO3H b. C6H15NO2 c. C6H13NO2 d. C6H14NO2 5.How many moles of O2 in heating a C12H26 (dodecane) a. 27 b. 37 c. 24 d. none of the abovearrow_forwardShow all steps and reagents needed to convert cyclohexane into each compound: (a) the two enantiomers of trans-1,2- dibromocyclohexane; and (b) 1,2-epoxycyclohexane.arrow_forward(a) What product(s) are formed when the E isomer of C6H5CH = CHC6H5 is treated with Br2, followed by one equivalent of KOH? Label the resulting alkene(s) as E or Z. (b) What product(s) are formed when the Z isomer of C6H5CH = CHC6H5 is subjected to the same reaction sequence? (c) How are the compounds in parts (a) and (b) related to each other?arrow_forward
- 4-Chloro-2-pentene has a double bond that can have either the E or the Z configuration and a stereogenic center that can have either the R or the S configuration. How many stereoisomers arepossible altogether? Draw the structure of each, and group the pairs of enantiomers.arrow_forwardExplain the characteristics of electrophilic addition of HX to alkenes ?arrow_forwarda. Draw three-dimensional representations for all stereoisomers of 2-chloro-3- methylpentane, and label pairs of enantiomers.b. Considering dehydrohalogenation across C2 and C3 only, draw the E2 product that results from each of these alkyl halides. How many different products have you drawn?c. How are these products related to each other?arrow_forward
- 1)Chemistry students are taking an experimental course in organic chemistry at a public university. During an experiment involving conjugated dienes, some doubts arose when discussing the results obtained so far: (a) A student obtained two products from the reaction of 1,3-cyclohexadiene with Br2. His lab partner was surprised to get only one product from the reaction of 1,3 - cyclohexadiene with HBr. Explain these distinct results. (b) One student, seeing the discussion of colleagues, commented that she obtained two distinct products when reacting 1,3,5-hexatriene with HBr, with different yields just by changing the reaction temperature. Explain the results she obtained using reaction mechanism and based on kinetic and thermodynamic control involving conjugated dienes.arrow_forwardThe 1,2‑dibromide is synthesized from an alkene starting material. Draw the alkene starting material. Clearly, show stereochemistry of the alkene.arrow_forwardWhen you react ammonia with a halogenated Alkane will you get only one organic product? Why or why notarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
