
(a)
Interpretation:
The configuration of the substitution products formed from the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
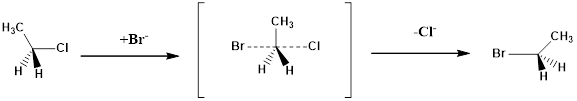
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
Solvolysis: The reaction is defined as solvolysis reaction if solvent acts as nucleophile in the given reaction.
Configuration of a molecule: The configurations of a molecule arise due to the spatial arrangement of atoms. The configuration can be assigned by following CIP rules as follows.
Assign numbering to the groups which are bonded to the chiral carbon based on the molecular weight and electronegativity.
If the sequence of the numbering follows clockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as R configuration.
If the sequence of the numbering follows anticlockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as S configuration.
(b)
Interpretation:
The configuration of the substitution products formed from the given reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
Transition State: The state which defines the highest potential energy with respect to reaction co-ordinate between reactant and product. It is usually denoted by using the symbol ‘≠’.
Nucleophile: donates pair of electrons to positively charged substrate resulting in the formation of
Configuration of a molecule: The configurations of a molecule arise due to the spatial arrangement of atoms. The configuration can be assigned by following CIP rules as follows.
Assign numbering to the groups which are bonded to the chiral carbon based on the molecular weight and electronegativity.
If the sequence of the numbering follows clockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as R configuration.
If the sequence of the numbering follows anticlockwise direction the chiral atom is assigned as S configuration.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- Which of the following reaction conditions will NOT FAVOR SN1 reaction? a. Sterically hindered alkyl halides b. All of these conditions will favor SN1 c. Reaction with strong base d. Reaction with alcoholsarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product of the SN1SN1 reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the structure of a dibromide that could be used to prepare the following alkyne via elimination. More than one dibromide may be possible.arrow_forward
- Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction that illustrates how two substitution products are formed. Explain why 1-bromohex-2-ene reacts rapidly with a weak nucleophile (CH3OH) under SN1 reaction conditions, even though it is a 1° alkyl halide.arrow_forwardexplain why carbonyl compounds are so attractive to both nucleophiles and electrophilesarrow_forwardWhich nucleophile would prefer simple addition over conjugate addition? CH3MgBr NaCN CH3CH2NH2 (CH3CH2)2CuLiarrow_forward
- Intramolecular reactions are also observed in Friedel–Crafts alkylation. Draw the intramolecular alkylation product formed from each of the following reactants.arrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction of bromoethane with each of the following nucleophiles? - (CH3)3N -CH3CH2S−arrow_forwardWhat two sets of reagents (each consisting of a carbonyl compound and phosphonium ylide) can be used for the synthesis of the following alkene? a. What alkyl halide is required to prepare each of the phosphonium ylides? b. What is the best set of reagents to use for the synthesis?arrow_forward
- Which alkyl halide is more reactive in an SN2 reaction with a given nucleophile?arrow_forwardE2 elimination takes place under the same conditions as SN2 substitution and the reactions compete with each other. Which of the following statements is true? a) E2 elimination and SN2 substitution proceed through the same intermediate step b) E2 elimination is only possible for compounds that react with the SN2 mechanism c) In competition, a strong base favors a substitution reaction d) Steric hindrance favors E2 eliminationarrow_forwardRank the following compounds towards nucleophiles. (1-most reactive - 4- least reactive)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
