
(a)
Interpretation: In the oxymercuration-demercuration reaction, a nucleophile other than water can be used. In the given reaction mechanism, the product is to be interpreted.
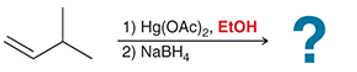
Concept introduction:
Addition reactions are the
(b)
Interpretation: In the oxymercuration-demercuration reaction, a nucleophile other than water can be used. In the given reaction mechanism, the product is to be interpreted.
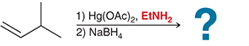
Concept introduction:
Addition reactions are the chemical reactions that show the addition of a certain group or molecule to the unsaturated carbon atoms. Alkenes are the unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one double bond between the carbon atoms. Therefore, they tend to give addition reactions. Some examples of addition reactions are acid-catalyzed hydration, oxymercuration-demercuration, etc.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WILEYPLUS ACCESS>I<
- Draw the most stable resonance form for the intermediate in the following electrophilic substitution reaction. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. Include all valence lone pairs in your answer.arrow_forwarda) Consider the reaction of HBr with ethylene and propylene. At roomtemperature the reaction of propylene with HBr is much faster than thereaction with ethylene.Using reaction energy diagrams and your knowledge of carbocationstability explain why this is so. b) Xylene (dimethylbenzene) is a commonly used chemical in the printingindustry and as a cleaning solvent for oily waste. It is also used whenpreparing histological samples to remove waxes from biological samples.Draw the three possible structures for this compound and give the UPACnames for each. Define which structures are ortho, meta, and para.arrow_forwardWrite the mechanism and all the products to this reactionarrow_forward
- The following compounds are major products of an elimination reaction with an alkyl halide. Determine the structure of the alkyl halide and write the overall reaction mechanism.arrow_forwardIn a polar reaction mechanism, the atom that gives away electrons in an uncharged nucleophile will end up as a/an anion neutral cation radicalarrow_forwardWhich mechanism(s) would be favored under the following reaction conditions?arrow_forward
- Your answer is incorrect. Predict the relative rates of these reactions. That is, select 1 next to the reaction with the fastest rate, 2 next to the reaction with the next fastest rate, and so on. Note for advanced students: you may assume these reactions all take place in a polar aprotic solvent, like DMSO. Incorrect Your answer is incorrect. Predict the relative rates of these reactions. That is, select I next to the reaction with the fastest rate, 2 next to the reaction with the next fastest rate, and so on. Note for advanced students: you may assume these reactions all take place in a polar aprotic solvent, like DMSO. Reaction Relative Rate G + H₂O - OH₂ 2 Br + H₂S - + Br 3 + H₂S SHI + ci I (fastest) Br + H₂O OM₂ + Br 4 (slowest)arrow_forwardFor the following reactions, design the experimental conditions that willlead to the suggested major products. Suggest actual reagents, solvents, nucleophile/base, concentration of nucleophile/base and what mechanism it is. Do not just use descriptors.arrow_forwardIndicates the product in the next reaction as well as the nucleophile and the electrophilearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





