
Concept explainers
(a)
The force on the cables.
Answer to Problem 13PE
The force in the cables is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of the bridge is
The mass of the car is
The distance of weight of the bridge from point
The distance of weight of the car from point
The distance of weight of the bridge from point
The length of the bridge is
The angle of force from point
Formula used:
The relation between the weight and the mass of the bridge is
The relation between the weight and the mass of the car is
The relation between the torque and weight of bridge is
The relation between the torque sand weight of car is
The relation between torque of cable is
The relation between the torque of car, bridge and cable is
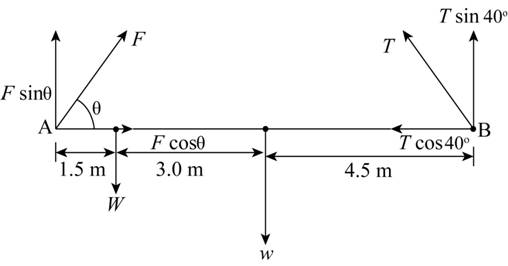
Figure-(1)
Calculation:
Substituting the given values in equation (1), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (2), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (3), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (4), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (5), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (6), we get
Conclusion:
Thus, the force in the cables is
(b)
The direction and magnitude of force exerted by the hinges on the bridge.
Answer to Problem 13PE
The magnitude of force exerted by the hinges on the bridge is
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
The relation between force in the horizontal direction and torque is
The relation between force in the vertical direction and torque is
The relation between the force and vertical and horizontal forces is
The relation between the angle made by force and vertical and horizontal forces is
Calculation:
Substituting the given values in equation (7), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (8), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (9), we get
Substituting the given values in equation (10), we get
Conclusion:
Thus, the magnitude of force exerted by the hinges on the bridge is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS (OER)
- A uniform plank of length 5 m and weight 200 N rests horizontally on two supports with 1.1 m of the plank hanging over the right support. To what distance x, can a person who weights 430 N walk on the overhanging part of the plank before it just starts to tip? What is the net torque around the pivot point (take the FR support as the pivot point)?arrow_forwardA sculpture is 4.00 m tall and has its center of gravity located 1.80 m above the center of its base. The base is a square with a side of 1.10 m. To what angle, theta, can the sculpture be tipped before it falls over?arrow_forwardWhat is the horizontal distance of the center of gravity of the person-ladder system from the point where the ladder touches the ground?arrow_forward
- A museum of modern art is displaying an irregular 426-N sculpture by hanging it from two thin vertical wires, A and B, that are 1.25 m apart. The center of gravity of this piece of art is 48.0 cm from its extreme right tip. Find the tension in each wire.arrow_forwardFind the x and y-coordinates of the center of gravity of a 4.00-ft by 8.00-ft uniform sheet of plywood with the upper right quadrant removed as shown in the figure below. Hint: The mass of any segment of the plywood sheet is proportional to the area of that segment.arrow_forwardA hiker, wo weights 911 N, is strolling through the woods and crosses a small horizontal bridge. The bridge is uniform, weighs 3440 N, and rests on two concrete supports, one of each end. He stops 1/5 of the way along the bridge. What is the magnitude of the force that a concrete support exerts on the bridge (a) at the near end and (b) at the far end?arrow_forward
- A 1.90-m-long barbell has a 21.0 kg weight on its left end and a 32.0 kg weight on its right end. If you ignore the weight of the bar itself, how far from the left end of the barbell is the center of gravity? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Where is the center of gravity if the 9.00 kg mass of the barbell itself is taken into account? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardIn order to balance a meterstick at the 27 cm mark, how much weight would you need to hang at the 10 cm mark? Assume the stick weighs 200 g and its center of mass is at 50 cm.arrow_forwardA small 1295-kg SUV has a wheelbase of 3.2 m. If 62% of its weight rests on the front wheels, how far behind the front wheels is the wagon's center of mass?arrow_forward
- A uniform plank 6 m long and 30 kg in mass rests horizontally on a scaffold. If 1.5 m of the plank protrudes from one end of the scaffold. How far can a 60 kg broad brush painter walk on the overhang before the plank tips over?arrow_forwardA stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = ℓ. A painter of mass m stands on the ladder a distance d from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately. Figure P10.73 Problems 73 and 74.arrow_forwardA stepladder of negligible weight is constructed as shown in Figure P10.73, with AC = BC = = 4.00 m. A painter of mass m = 70.0 kg stands on the ladder d = 3.00 m from the bottom. Assuming the floor is frictionless, find (a) the tension in the horizontal bar DE connecting the two halves of the ladder, (b) the normal forces at A and B, and (c) the components of the reaction force at the single hinge C that the left half of the ladder exerts on the right half. Suggestion: Treat the ladder as a single object, but also treat each half of the ladder separately.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




