
Concept explainers
(a)
The force exerted on the floor by each hand to do pushups.
Answer to Problem 37PE
The force exerted on the floor by each hand to do pushups is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of the woman is
The acceleration due to gravity is
Formula used:
The free body diagram is as shown below.
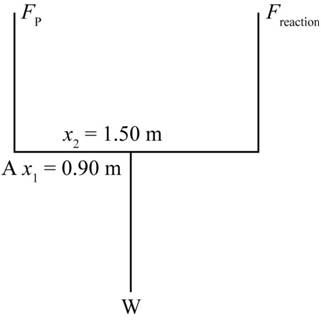
Figure (1)
Apply second condition of equilibrium; the net torque around the pivot is zero.The force is same on each arm.
The relation between weight and mass of the woman is
By second condition of equilibrium,
The force on each arm is
Calculation:
The weight of the woman is calculated as
The reaction force is calculated as
The force on each arm is calculated as
Conclusion:
The force exerted on the floor by each hand to do the pushups is
(b)
The magnitude of force in each triceps muscle and the ratio of forces between the triceps muscle to the weight.
Answer to Problem 37PE
The magnitude of force in each triceps muscle is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The reaction force is
Formula used:
The torque around the pivot point gives the relation between the forces in triceps muscles
The ratio between the forces in the triceps muscle to the weight is
Calculation:
The force in each triceps muscle is calculated as
The ratio is calculated as
Conclusion:
The magnitude of force in each triceps muscle is
(c)
The work done by the women.
Answer to Problem 37PE
The work done by the women is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The height from the floor when the centre of mass rises her body is
Formula used:
The work done by the woman to raise her centre of mass is given by
Calculation:
The work done by the woman is calculated as
Conclusion:
The work done by the women is
(d)
The useful power of the women.
Answer to Problem 37PE
The useful power output of the women is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The work done by the woman is
The number pushups the woman do in one minute is
Formula used:
The time taken by the woman to do one pushup is
The relation between the work done, the time taken to complete the work and the power is
Calculation:
The time taken by the woman to do one pushup is calculated as
The power output is calculated as
Conclusion:
The useful power output of the women is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS (OER)
- Check your Understanding Repeat Example 12.3 using the left end of the meter stick to calculate the torques; that is by placing the pivot at the left end of the meter stick.arrow_forwardThe following figure represents a bicep curl maneuver where the center of mass (CoM) of a 23 kg dumbbell is 0.29 m from the elbow joint (pivot). The mass of the arm is 5 kg and acts 0.17 m from the elbow joint, and the biceps tendon acts at a distance of 0.01 m from the elbow joint. What is the required magnitude of the resultant joint reaction force (JRF) at the elbow in newtons (N) for the scenario described above in a) where static equilibrium is achieved.arrow_forwardA spade is modelled as a uniform rod, of mass 2kg and length 90cm, attached to a uniform square lamina, of side 20cm and mass 0.5kg. A gardener holds the spade horizontally with hands 30cm and 60cm from the end of the rod. Find the vertical forces exerted by the gardener's hands. Im stuck on this q, pls help.arrow_forward
- When opening a door, you push on it perpendicularly with a force of 63.2 N at a distance of 0.864m from the hinges. What torque are you exerting relative to the hinges? (Does it matter if you push at the same height as the hinges?)arrow_forwardThe forearm of length Larm=35.4 cm shown in the figure is positioned at an angle θ with respect to the upper arm, and a 5.30-kg ball is held in the hand. The total mass ?totalmtotal of the forearm and hand is 3.00 kg, and their center of mass is located at LCM=14.6 cm from the elbow. The biceps muscle attaches to the forearm at a distanceLbiceps=3.5 cm from the elbow. What is the magnitude of the force Fbiceps that the biceps muscle exerts on the forearm for ?=49∘? What is the magnitude of the force Fjoint that the forearm exerts on the elbow joint for ?=49∘?arrow_forwardA sculpture is 4.00 m tall and has its center of gravity located 1.80 m above the center of its base. The base is a square with a side of 1.10 m. To what angle, theta, can the sculpture be tipped before it falls over?arrow_forward
- In using the spring scale to find the equilibrant, why does one hold it horizontally on its body and not on its (topmost) handle?arrow_forwardA beam of length 5.4 meters is attached to the ground by a pin and is being held up by a horizontal wire. A block is hanging off the beam with x = 3.6 meters from the pin as shown. If the horizontal wire has a tension of 986 Newtons and theta = 53.9 degrees, what is the magnitude of the torque exerted by the horizontal wire on the beam about the pin?arrow_forwardA uniform plank of length 2.00m and mass 30.0kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in figure p8.27. Find the tension in each rope when a 700-N person is d=0.500m from the left end.arrow_forward
- If a baseball player pushes with 250N due North at a point 8.0cm due southeast of the pivot point of a horizontal bat, calculate the torque they exert, T (Tau) = r × Farrow_forwardA person bending forward to lift a load “with his back”(Fig. P8.23a) rather than “with his knees” can be injured bylarge forces exerted on the muscles and vertebrae. The spinepivots mainly at the fifth lumbar vertebra, with the principalsupporting force provided by the erector spinalis muscle inthe back. To see the magnitude of the forces involved, and tounderstand why back problems are common among humans,consider the model shown in Figure P8.23b of a person bendingforward to lift a 200.-N object. The spine and upper bodyare represented as a uniform horizontal rod of weight 350. N,pivoted at the base of the spine. The erector spinalis muscle,attached at a point two-thirds of the way up the spine, maintainsthe position of the back. The angle between the spineand this muscle is 12.0°. Find (a) the tension in the back muscleand (b) the compressional force in the spine.arrow_forwardIf you are trying to balance a seesaw and you have a higher mass on the left, should the mass on the right be placed at a greater distance or lower distance to balance it? Why?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill


