
Concept explainers
A small 0.65-kg box is launched from rest by a horizontal spring as shown in Figure P9.50. The block slides on a track down a hill and comes to rest at a distance d from the base of the hill. Kinetic friction between the box and the track is negligible on the hill, but the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the horizontal parts of track is 0.35. The spring has a spring constant of 34.5 N/m, and is compressed 30.0 cm with the box attached. The block remains on the track at all times.
a. What would you include in the system? Explain your choice.
b. Calculate d.
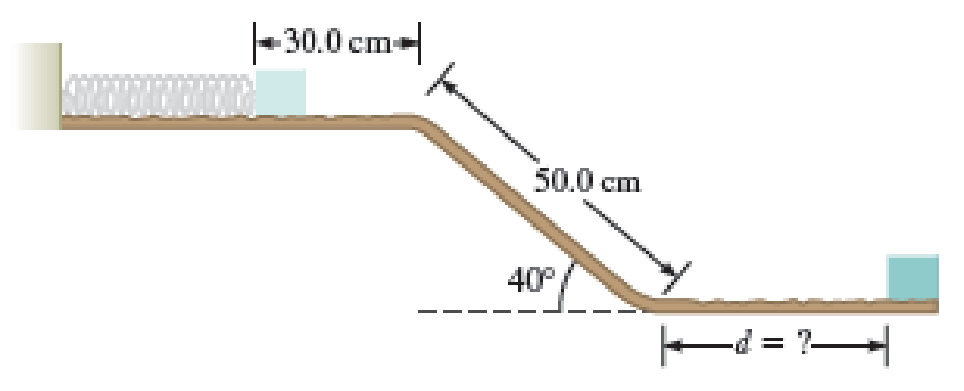
(a)
The items included in the system and explain the choice.
Answer to Problem 50PQ
The items included are the box and the tracks surface because the kinetic friction increases the thermal energies and included this thermal energy internal to the system.
Explanation of Solution
In order to keep all the thermal energy into the system, it is better to include both the box and the tracks surface so that it will increase the kinetic friction which leads to the increase in the thermal energies and including both keeps all of this thermal energy internal to the system.
If Earth and spring are the choices, to account for them in terms of changes in gravitational and elastic potential energy without letting anything outside the system to do work.
Figure 1 show the graph of the initial and final energies which will help to organize the energies needed to be taken into account.
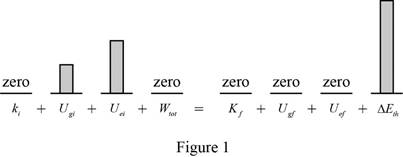
Conclusion:
Therefore, the items included are box and the tracks surface because the kinetic friction increases the thermal energies and included this thermal energy internal to the system.
(b)
The value of
Answer to Problem 50PQ
The value of
Explanation of Solution
The reference configuration for the spring is when it is relaxed, and for gravity it is when the box is at the bottom of the ramp. The box is initially at rest
The energy conservation equation for a system is,
Here,
In this problem, Equation (I) will changes to (since all other energies are zero),
Write the expression for the initial gravitational potential energy.
Here,
Write the expression for the initial potential energy of the spring.
Here,
Write the expression for the thermal energy.
Here,
The total path length will be
Kinetic friction is proportional to the normal force which equals the weight.
Here,
Write the expression for the normal force.
Use equation (VIII) in equation (VI),
Use equation (VIII) in (VI), and solve for
Conclusion:
The displacement
Substitute
Therefore, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- Review. Consider the system shown in Figure P10.36 with m1 = 20.0 kg, m2 = 12.5 kg, R = 0.200 m, and the mass of the pulley M = 5.00 kg. Object m2 is resting on the floor, and object m1 is 4.00 m above the floor when it is released from rest. The pulley axis is frictionless. The cord is light, does not stretch, and does not slip on the pulley. (a) Calculate the time interval required for m1 to hit the floor. (b) How would your answer change if the pulley were massless?arrow_forwardTo give a pet hamster exercise, some people put the hamster in a ventilated ball andallow it roam around the house(Fig. P13.66). When a hamsteris in such a ball, it can cross atypical room in a few minutes.Estimate the total kinetic energyin the ball-hamster system. FIGURE P13.66 Problems 66 and 67arrow_forwardThe puck in Figure P11.46 has a mass of 0.120 kg. The distance of the puck from the center of rotation is originally 40.0 cm, and the puck is sliding with a speed of 80.0 cm/s. The string is pulled downward 15.0 cm through the hole in the frictionless table. Determine the work done on the puck. (Suggestion: Consider the change of kinetic energy.) Figure P11.46arrow_forward
- A block is placed on top of a vertical spring, and the spring compresses. Figure P8.24 depicts a moment in time when the spring is compressed by an amount h. a. To calculate the change in the gravitational and elastic potential energies, what must be included in the system? b. Find an expression for the change in the systems potential energy in terms of the parameters shown in Figure P8.24. c. If m = 0.865 kg and k = 125 N/m, find the change in the systems potential energy when the blocks displacement is h = 0.0650 m, relative to its initial position. FIGURE P8.24arrow_forwardA giant swing at an amusement park consists of a 365-kg uniform arm 10.0 m long, with two seats of negligible mass connected at the lower end of the arm (Fig. P8.53). (a) How far from the upper end is the center of mass of the arm? (b) The gravitational potential energy of the arm is the same as if all its mass were concentrated at the center of mass. If the arm is raised through a 45.0 angle, find the gravitational potential energy, where the zero level is taken to be 10.0 m below the axis, (c) The arm drops from rest from the position described in part (b). Find the gravitational potential energy of the system when it reaches the vertical orientation. (d) Find the speed of the seats at the bottom of the swing.arrow_forwardReview. As shown in Figure P8.26, a light string that does not stretch changes from horizontal to vertical as it passes over the edge of a table. The string connects m1, a 3.50-kg block originally at rest on the horizontal table at a height h = 1.20 m above the floor, to m2, a hanging 1.90-kg block originally a distance d = 0.900 m above the floor. Neither the surface of the table nor its edge exerts a force of kinetic friction. The blocks start to move from rest. The sliding block m1 is projected horizontally after reaching the edge of the table. The hanging block m2 stops without bouncing when it strikes the floor. Consider the two blocks plus the Earth as the system. (a) Find the speed at which m1 leaves the edge of the table. (b) Find the impact speed of m1 on the floor. (c) What is the shortest length of the string so that it does not go taut while m1 is in flight? (d) Is the energy of the system when it is released from rest equal to the energy of the system just before m1 strikes the ground? (e) Why or why not? Figure P8.26arrow_forward
- A small 0.65-kg box is launched from rest by a horizontal spring as shown in Figure P9.50. The block slides on a track down a hill and comes to rest at a distance d from the base of the hill. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the track is 0.35 along the entire track. The spring has a spring constant of 34.5 N/m, and is compressed 30.0 cm with the box attached. The block remains on the track at all times. a. What would you include in the system? Explain your choice. b. Calculate d. c. Compare your answer with your answer to Problem 50 if you did that problem.arrow_forwardA horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant of k = 850 N/m. A block of mass m = 1.00 kg is attached to the spring and rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface as in Figure P8.35. (a) The block is pulled to a position xi = 6.00 cm from equilibrium and released. Find the elastic potential energy stored in the spring when the block is 6.00 cm from equilibrium and when the block passes through equilibrium. (b) Find the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium point. (c) What is the speed of the block when it is at a position xi/2 = 3.00 cm? (d) Why isnt the answer to part (c) half the answer to part (b)? Figure P8.35arrow_forwardAn inclined plane of angle = 20.0 has a spring of force constant k = 500 N/m fastened securely at the bottom so that the spring is parallel to the surface as shown in Figure P7.47. A block of mass m = 2.50 kg is placed on the plane at a distance d = 0.300 m from the spring. From this position, the block is projected downward toward the spring with speed v = 0.750 m/s. By what distance is the spring compressed when the block momentarily comes to rest? Figure P7.47 Problems 47 and 48.arrow_forward
- In a laboratory experiment, 1 a block of mass M is placed on a frictionless table at the end of a relaxed spring of spring constant k. 2 The spring is compressed a distance x0 and 3 a small ball of mass m is launched into the block as shown in Figure P11.22. The ball and block stick together and are projected off the table of height h. Find an expression for the horizontal displacement of the ballblock system from the end of the table until it hits the floor in terms of the parameters given. FIGURE P11.22arrow_forwardAn 85 kg man stands in a very strong wind moving at 14 m/s at torso height. As you know, he will need to lean in to the wind, and we can model the situation to see why. Assume that the man has a mass of 85 kg, with a center of gravity 1.0 m above the ground. The action of the wind on his torso, which we approximate as a cylinder 50 cm wide and 90 cm long centered 1.2 m above the ground, produces a force that tries to tip him over backward. To keep from falling over, he must lean forward. a. What is the magnitude of the torque provided by the wind force? Take the pivot point at his feet. Assume that he is standing vertically.b. At what angle to the vertical must the man lean to provide a gravitational torque that is equal to this torque due to the wind force?arrow_forwardConsider a fruit hanging on a twig with potential energy of 150 J. If the fruit suddenly falls to the ground, what is the kinetic energy of the fruit as it lands?a. 150.0 Jb. 0 Jc. 1470 Jd. 159.8 Jarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





