
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given

Explanation of Solution
In the given
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.

(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given
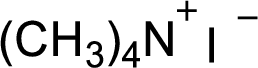
Explanation of Solution
In the given
In this reaction formed quaternary ammonium ion is stabilized by iodine ion so the product is an iodine salt of quaternary ammonium ion.
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.

(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(c)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given
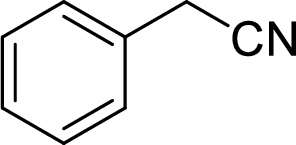
Explanation of Solution
In the given
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.
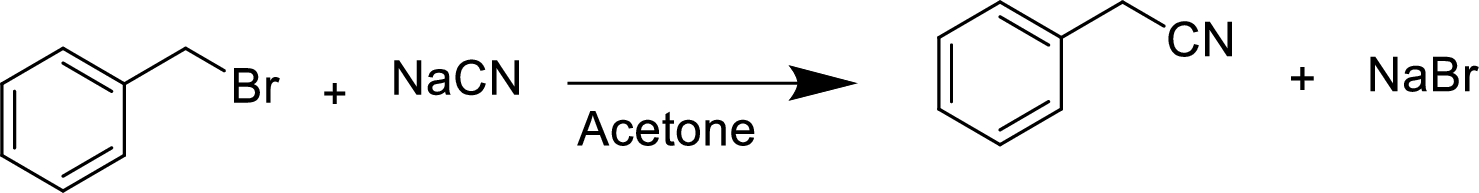
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(d)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given
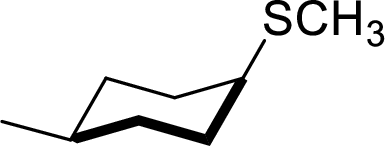
Explanation of Solution
In the given
Given reactant has an equatorial chlorine hence, the product is axial.

(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(e)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given
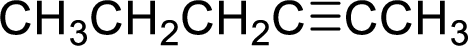
Explanation of Solution
In the given
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.

(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(f)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given
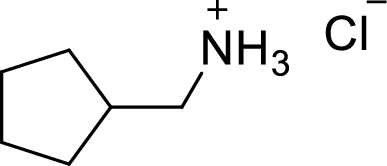
Explanation of Solution
In the given
In this reaction formed ammonium ion is stabilized by chorine ion so the product is a chlorine salt of ammonium ion.
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.
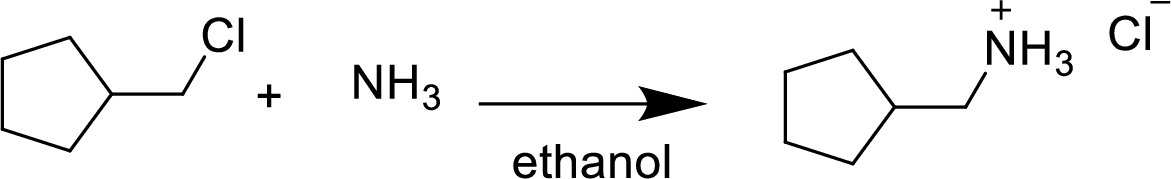
(g)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(g)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given
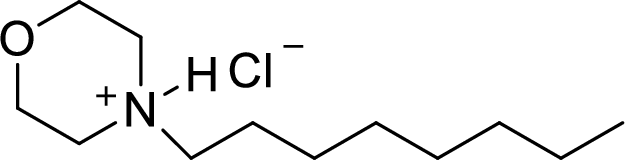
Explanation of Solution
In the given
In this reaction formed ammonium ion is stabilized by chorine ion so the product is a chlorine salt of ammonium ion.
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.

(h)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of given
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
(h)
Answer to Problem 9.13P
The structural formula for the product of given

Explanation of Solution
In the given
Given reactant is non-chiral so product also non-chiral.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- In an advanced synthetic chemistry experiment, a researcher prepares a compound, ZY-7, by reacting a ketone (C5H10O) with hydroxylamine (NH2OH), followed by heating in the presence of an acid catalyst. The resulting compound, ZY-7, is then treated with a solution of sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) at low temperature. Identify the class of compound that ZY-7 most likely belongs to after this series of reactions." A) Amide B) Oxime C) Nitro compound D) Diazonium salt E) Ester Don't use chatgpt please provide valuable answerarrow_forwardstructural formula (3E, 6S)-6, 7, 7-trimethyl-4-phenyloct-3-enoic acidarrow_forwardbutene-1 acts on a combination of three reactants.Write the corresponding reactions a) Cl2, CO2, H2SO4arrow_forward
- An unknown hydrocarbon A with the formula C6H12 reacts with 1 molar equivalent of H2 over a palladium catalyst. Hydrocarbon A also reacts with OsO4 to give diol B. When oxidized with KMnO4 in acidic solution, A gives two fragments. One fragment is propanoic acid, CH3CH2CO2H, and the other fragment is ketone C. What are the structures of A, B, and C? Write all reactions, and show your reasoning.arrow_forwardStarting with acetylene and ethylene oxide as the only sources of carbon atoms, show how to prepare the compound Q.)1,6-Hexanediolarrow_forwardDraw the structure of each product from the reaction of benzene with 2-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane using AlCl 3 as the catalyst and Identify the major product.arrow_forward
- 7. The following compounds are isomeric esters derived from acetic acid, each with formula C5H10O2. Draw the structures of the two esters?arrow_forward5. Compound A, C 10H 18O, undergoes reaction with dilute H 2SO 4 at 50 °C to yield a mixture of two alkenes, C 10H 16. The major alkene B, gives only cyclopentanone after ozone treatment followed by reduction with zinc in acetic acid. Which of the following reactions are correct.arrow_forward(5d-301) Consider the bromination of 2-pentene. What would be the product of such a reaction? Draw 2-pentene and the bromination product. Also, give the IUPAC name for the product.arrow_forward
- (CH3)2C=CHCH2CH3 and Ozone (o)3 /Zn product?arrow_forwardHydrocarbon A, C8H12 absorbs 3 equiv. of hydrogen to give B, C8H18 when hydrogenated over a Pd/C catalyst. Treatment of A with aqueous H2SO4 and Hg(II) gives a single ketone, C. Oxidation of A with KMnO4 gives CO2 and the two carboxylic acids D & E shown below. What would be a structure for A?arrow_forwardCompound A, C5H11Br, on treatment with alcoholic KOH, gives two isomeric compoundsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
