
Concept explainers
(a)
Calculate the consolidation settlement inone year.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.20CTP
The consolidation settlement in one year
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of sand layer
The thickness of clay layer
The moisture content
The specific gravity of soil solids
The compression index
The coefficient of consolidation
The unit weight of sand is
The unit weight of fill
The depth of the compacted fill
Calculation:
Consider the unit weight of water
Calculate the initial void ratio
Substitute
Calculate the saturated unit weight
Substitute
At the middle of the clay layer:
Calculate the effective overburden pressure
Substitute
Calculate the increase in vertical pressure
Substitute
Calculate the final primary consolidation settlement
Substitute
Calculate the time factor
Substitute
Refer Table 9.3 “Variation of Time Factor with Degree of consolidation” in the Text Book.
Take the value of Uas
Take the value of Uas
Calculate the value of U for the value
Calculate the final consolidation settlement
Substitute
Therefore, the consolidation settlement in one year is
(b)
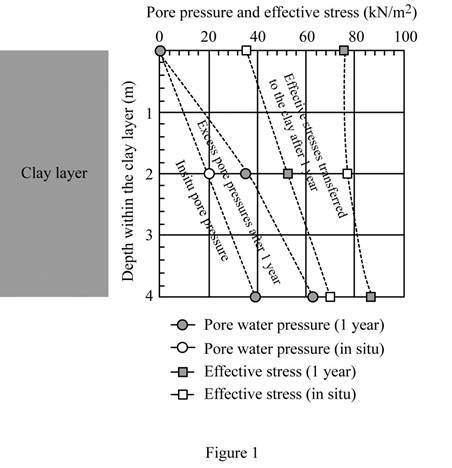
Plot the in situ variation of pore water pressure and effective stress with depth for the clay layer.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of sand layer
The thickness of clay layer
The moisture content
The specific gravity of soil solids
The compression index
The coefficient of consolidation
The unit weight of sand is
The unit weight of fill
The depth of the compacted fill
Calculation:
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water pressure
Substitute
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water pressure
Substitute
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Show the variation of pore water pressure and effective stress with depth for the clay layer as in Figure 1.
(c)
Plot the variation of pore water pressure and effective stress with depth after on year.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of sand layer
The thickness of clay layer
The moisture content
The specific gravity of soil solids
The compression index
The coefficient of consolidation
The unit weight of sand is
The unit weight of fill
The depth of the compacted fill
Calculation:
Consider the degree of consolidation
Refer to part (a).
The time factor
Calculate the effective stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water
Substitute
Calculate the ratio of height of soil to the maximum drainage depth as shown below.
Substitute
Refer Figure 9.20 “Variation of
Take the value of
Calculate the effective stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water
Substitute
At the bottom of the clay layer, after one year:
Calculate the ratio of height of soil to the maximum drainage depth;
Substitute
Refer Figure 9.20 “Variation of
Take the value of
Calculate the effective stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water
Substitute
Show the variation of the pore water pressure and the effective stress with depth as in Figure 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- For a normally consolidated soil, the following is given: Determine the following: a. The compression index, Cc. b. The void ratio corresponding to pressure of 200 kN/m2arrow_forwardFor a normally consolidated clay layer in the field, the following values are given:Thickness of clay layer = 8.5 ftVoid ratio ?? = 0.8Compression index ?? = 0.28Average effective pressure on the clay layer ??′ = 2650 lb ft2 ⁄∆?′ = 970 lb ft2 ⁄Secondary compression index ?? = 0.02What is the total consolidation settlement of the clay layer five years after the completionof primary consolidation settlement? (Note: Time for completion of primary settlement= 1.5 years.)arrow_forwardFor a given consolidated clay: Gs= 2.71; LL= 45; In situ average effective overburden pressure = 120 kPa; In situ void ratio= 0.80 ; Thickness of clay layer = 4m ; average increase of effective stress on clay layer= 40 kPa; Effective pressure at the mid-height of clay layer= 60 kPa; Swell Index (Cs)= 1/5 Cc. Compute the primary consolidation settlement in mm. a.87.64 b.49 c.92.9 d.100.5arrow_forward
- A normally consolidated clay layer, 3 m thick, has the following properties : Initial void ratio, e0= 0.8 Compression index, Cc = 0.25 Average effective pressure, σ’0 = 125 Kpa Expected pressure increase, Δσ’ = 45 Kpa Secondary compression index, Ca = 0.02 Time of completion of primary settlement = 1.5 years What is the total settlement of the clay layer five years after the completion of the primary settlement?arrow_forwardQuestion-3: A soil profile is shown in Figure 3.1. If a uniformly distributed load, ∆σ, is applied at the ground surface, calculate the settlement of the clay layer caused by primary consolidation, if Cc = 0.27 and Cr = 0.045 and a. The clay is normally consolidated b. The preconsolidation pressure, σ′c = 190 kN/m2 c. σ′c = 170 kN/m2arrow_forwardThe soil profile at a site consists of a 3-m thick sand layer (moist unit weight = 16.5 kN/m^3, saturated unit weight = 18.5 kN/m^3) underlain by a 6-m thick clay layer (w = 27%, Gs = 2.70, mv = 0.31 MPa^-1, Cv = 2.6 m^3/year), which is underlain by a gravel layer as shown in the figure. A 3 m compacted fill with a unit weight of 20 kN/m^3 is required to be placed at ground level.a) What would be the final consolidation settlement, in mm rounded to the first decimal place?b) How long will it take for 50 mm consolidation settlement, in months rounded to the first decimal place?c) What would be the consolidation settlement in one year, in mm rounded to nearest whole number?arrow_forward
- PROBLEM 50: Compute the compression index of undisturbed clay having a plastic limit of 32% and a plasticity index of 8%arrow_forwardA normally consolidated clay layer has the following properties: Soil layer thickness: 3.7 m Initial void ratio: 0.63Compression index: 0.29 Average effective pressure: 133 kPa Expected pressure increase: 58.7 kPa Secondary compression index: 0.02 Time for completion of primary settlement: 3 yearsa. Determine the void ratio at the start of the secondary consolidation. b. What is the total settlement of the clay layer 9 years after the start of primary consolidation settlement?arrow_forwardFor a given consolidated clay: Gs= 2.71; LL= 45; In situ average effective overburden pressure = 120 kPa; In situ void ratio= 0.80 ; Thickness of clay layer = 4m ; average increase of effective stress on clay layer= 40 kPa; Effective pressure at the mid-height of clay layer= 60 kPa; Swell Index (Cs)= 1/5 Cc. Compute the pre-consolidation pressure in kPa. a. 92.9 b. 49 c. 87.64 d. 100.5arrow_forward
- A normally consolidated clay has the following values void ratio e = 1.2, k(cm/sec) = 0.2 x 10^-6 And void ratio e = 1.9, 0.91x10^-6. Estimate the magnitude k of the clay at a void ratio (e) of 0.9. Use k = C (e^n)/1+e.arrow_forwardquestion 5 A rectangular footing (4.67 x 4.45 m.) is placed 1.62 m. below the ground surface. The soil arrangement is composed of sand (ground) for the first 6.22 meters and followed by clay for the next 5.85 meters. The force acting on the footing is 10,929 kN. Determine the settlement of the consolidating layer in mm. Assume a 2V:1H pressure diagram. Unit weight of sand = 16.6 kN/m3. Clay has the following properties: Unit weight = 18.6 kN/m3, Void ratio = 28, Liquid limit = 43. Round off to two decimal places.arrow_forwardA three-layer soil has the following properties: Layer 1: k = 2.77 x 10^-3 cm/s, H = 3.17 m. Layer 2: k = 1.6 x 10^-2 cm/s, H = 4.97 m. Layer 3: k = 3.06 x 10^-3 cm/s, H = 4.25 m. Determine the equivalent vertical coefficient of permeability of the soil arrangement. Layer 1 is on top of layer 2 while layer 2 is on top of layer 3. Round off to four decimal places.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning


