
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.46AP
The products formed when
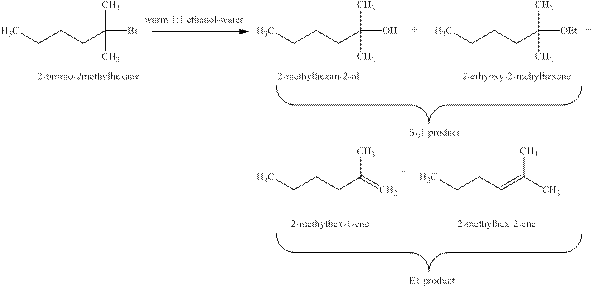
Explanation of Solution
The types of reactions which
The products that are obtained via

Figure 1
The
An
The products formed when
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.46AP
The products expected when

Explanation of Solution
An
The products formed for this reaction are shown below.

Figure 2
An
The products expected when
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.46AP
The products expected when
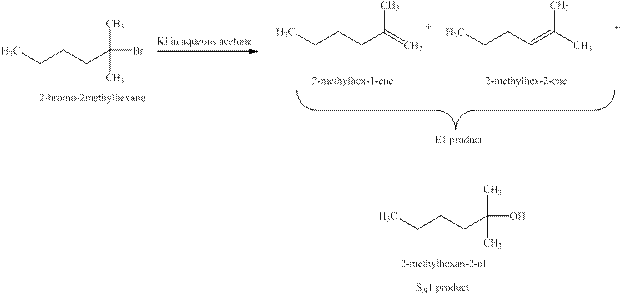
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions which
The products that are obtained via

Figure 3
The
An
The products expected when
(d)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
Concept introduction:
An
Answer to Problem 9.46AP
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
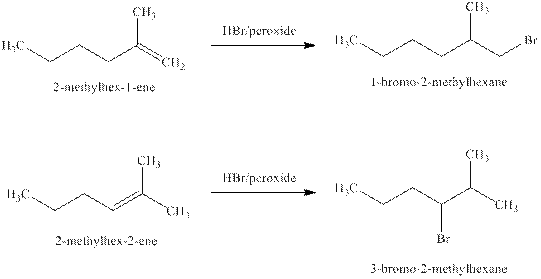
Explanation of Solution
Some reactions follow the rule of Markonikov’s addition but some do not. Markonikov’s gave the rule purely on the basis of the observation of products received by him when performed the addition reaction on alkene.
Some reactions do not follow the rule because they follow the stability of the intermediate formed in the mechanism of that particular reaction.
The reaction of alkenes (
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and

Figure 4
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
(e)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
Concept introduction:
An alkene undergoes addition reactions due to the presence of unsaturated bond in it. Markonikov’s gave a rule for the addition of protic acids or protic compounds takes place in such a way that proton goes to carbon having the highest number of hydrogen and anion goes to other carbon.
Answer to Problem 9.46AP
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
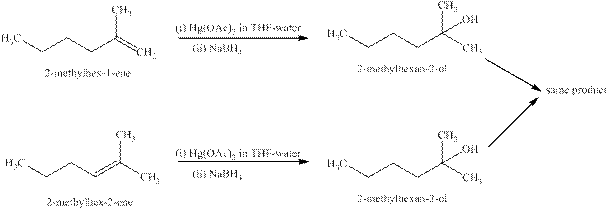
Explanation of Solution
Some reactions follow the rule of Markonikov’s addition but some do not. Markonikov’s gave the rule purely on the basis of the observation of products received by him when performed the addition reaction on alkene.
Some reactions do not follow the rule because they follow the stability of the intermediate formed in the mechanism of that particular reaction.
The reaction of alkenes (
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and

Figure 5
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
(f)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
Concept introduction:
An alkene undergoes addition reactions due to the presence of unsaturated bond in it. Markonikov’s gave a rule for the addition of protic acids or protic compounds takes place in such a way that proton goes to carbon having the highest number of hydrogen and anion goes to other carbon.
Answer to Problem 9.46AP
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
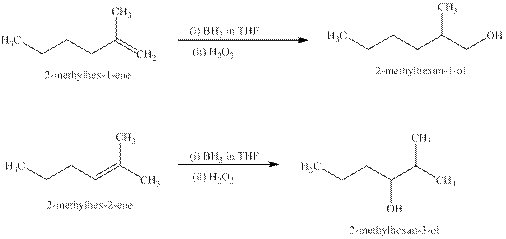
Explanation of Solution
Some reactions follow the rule of Markonikov’s addition but some do not.
Markonikov’s gave the rule purely on the basis of the observation of products received by him when performed the addition reaction on alkene.
Some reactions do not follow the rule because they follow the stability of the intermediate formed in the mechanism of that particular reaction.
The reaction of alkenes (
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and

Figure 6
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (b) and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





