
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of the reaction between methyl iodide and ethanol solution containing nucleophiles
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which a group is substituted by an incoming nucleophile. These
The
Answer to Problem 9.66AP
The major product of the
Explanation of Solution
The
In polar protic solvents, the reaction occurs due to the presence of polar hydrogen atom. Therefore, the more basic nucleophiles undergo slower reaction giving minor products in competition with less basic nucleophiles and vice-versa for
The reaction of methyl iodide with both the nucleophiles undergoes via
The reaction products are shown below.
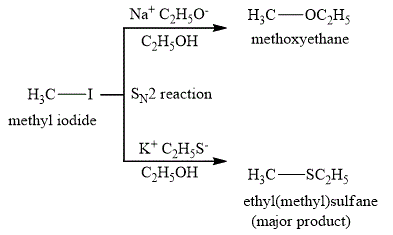
Figure 1
The major product of the reaction between methyl iodide and
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of the reaction between methyl iodide and the ethanol solution containing
Concept introduction:
The nucleophilic substitution reactions are the reactions in which a group is substituted by an incoming nucleophile. These rate of reaction depend upon the nucleophilicity and concentration of the incoming nucleophile.
The
Answer to Problem 9.66AP
The major product of the
Explanation of Solution
The
In polar protic solvents there undergoes due to the presence of polar hydrogen atom. Therefore, the more basic nucleophiles undergo slower reaction giving minor products in competition with less basic nucleophiles and vice-versa for polar aprotic solvents.
The reaction of methyl iodide with both the nucleophiles undergoes via
DMSO is a polar aprotic solvent. Sodium ethoxide
The reaction products are shown below.
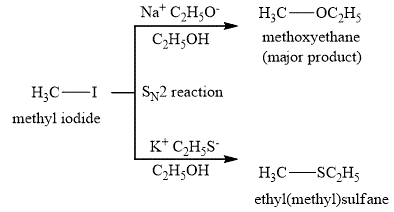
Figure 2
The major product obtained when
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





