
For Problems 7-21, please provide the following information.
(a) What is the level of significance? Stale the null and alternate hypotheses, (b) Check Requirements What sampling distribution will you use? Do you think the sample size is sufficiently large? Explain Compute the value of the sample test statistic and corresponding z value. (c) Find the P-value of the test statistic Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
(d) Based on sour answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistic ally significant at level
(c) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
Focus Problem: Benford's Law Please read the Focus Problem at the beginning of this chapter. Recall that Benford's Lam claims that numbers chosen from very large data files lend to have " 1“ as the first nonzero digit disproportionately often. In fact, research has shown that if you randomly draw a number from a very large data file, the probability of getting a number with "1" as the leading digit is about 0.301 (sec the reference in this chapter's Focus Problem).
Now suppose you are an auditor for a very large corporation. The revenue report involves millions of numbers in a large computer file. Let us say you took a random sample of n = 215numerical entries from the file, and r = 46 of the entries had a first nonzero digit of 1. Let p represent the population proportion of all numbers in the corporate file that have a first nonzero digit of 1.
Test the claim that p is less than 0.301 Use
If p is in fact less than 0.301, would it make you suspect that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading Is? Could this indicate that the books have been “cooked" by “pumping up" or inflating the numbers? Comment from the view point of a stockholder. Comment from the perspective of the Federal Bureau of Investigation as ii looks for money laundering in the form of false profits.
iii. Comment on the following statement “If we reject the null hypothesis at level of significance
(i)
(a)
The level of significance, null and alternative hypothesis.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The level of significance is
Explanation of Solution
The level of significance is defined as the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, it is denoted by
Null hypothesis
Alternative hypothesis
(b)
To find: The sampling distribution that should be used and compute the z value of the sample test statistic.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The sampling distribution
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The
The standardized sample test statistic for
(c)
To find: The P-value of the test statistic and sketch the sampling distribution showing the area corresponding to the P-value.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The P-value of the test statistic is 0.0027.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
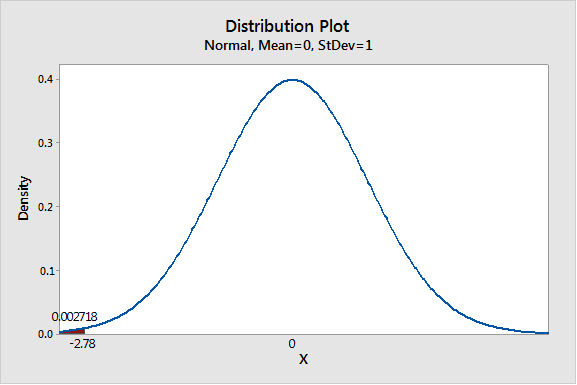
We have z = -2.78
Using Table 3 from the Appendix to find the specified area:
Thus P- value is 0.0027.
Graph:
To draw the required graphs using the Minitab, follow the below instructions:
Step 1: Go to the Minitab software.
Step 2: Go to Graph > Probability distribution plot > View probability.
Step 3: Select ‘Normal’ and enter Mean 0 and Standard deviation 1.
Step 4: Click on the Shaded area > X value.
Step 5: Enter X-value as -2.78 and select ‘Left tail’.
Step 6: Click on OK.
The obtained distribution graph is:
(d)
Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesisand whether the data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.01.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The P-value
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0027 is less than the level of significance (
(e)
The interpretation for the conclusion.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: There is enough evidence to conclude that population proportion of numbers with leading “1” in the revenue file is less than the probability 0.301 predicted by Benford’s law.
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0027 is less than the level of significance (
(ii)
To explain: Whether it is suspect that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: Yes. The revenue data file seems to include more numbers with higher first nonzero digits than Benford's law predicts.
Explanation of Solution
There are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's than Benford's law predicts. So, we cannot say that it is an indication of the books have been “cooked” by “pumping up” or inflating the numbers. From the viewpoint of a stockholder and the Federal Bureau of Investigation as it looks for money laundering, it may be true or false profit because there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1’s.
(iii)
To explain: Whether it recommends further investigation before accusing the company of fraud.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: Our data lead us to reject the null hypothesis, more investigation is merited.
Explanation of Solution
Since, we reject the null hypothesis
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
UNDERSTANDING BASIC STAT LL BUND >A< F
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





