
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater
Answer to Problem C.31P
The structure of
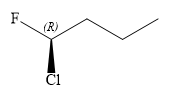
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is butane. The longest continuous carbon chain contains four carbon atoms. A chlorine and a fluorine atom are attached to the C1 carbon atom of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
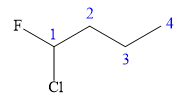
There is one chiral carbon at C1 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is R.
At C1 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
In the given structure, the top-three priority substituents are arranged in a clockwise manner.
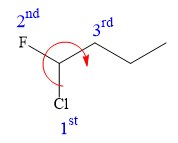
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement at the C1 carbon atom, the fourth priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond and the Cl atom must be attached by a wedge bond. Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has a higher priority. In the case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets the higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.31P
The structure of
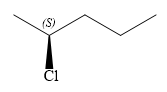
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is pentane. The longest continuous carbon chain should have five carbon atoms. One chlorine atom is attached to the C2 carbon atom of the root.
The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
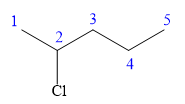
There is one chiral carbon at C2 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is S.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
In the given structure, the top-three priority substituents are arranged in a counterclockwise manner.
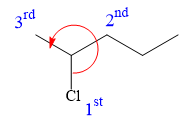
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a wedge bond and the chlorine atom must be attached by a dash bond. Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has a higher priority. In the case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets the higher priority.
When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R.
When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S.
If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S.
If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IPUAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.31P
The structure of
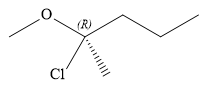
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is pentane. The longest continuous carbon chain should have five carbon atoms. One chlorine atom and a methoxy group are attached to the C2 carbon atom of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
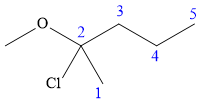
There is one chiral carbon at C2 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is R.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
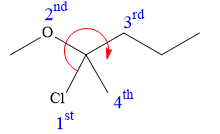
Thus, in order to maintain this clockwise arrangement of substituents at C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond. Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has a higher priority. In the case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets the higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IPUAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.31P
The structure of
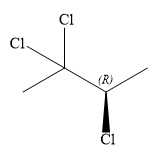
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is butane. The longest continuous carbon chain should have four carbon atoms. Three chlorine atoms are attached to C2, C2 and C3 carbon atoms of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
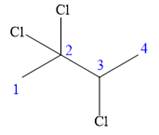
There is one chiral carbon at C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is R.
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
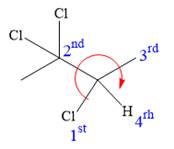
Thus, in order to maintain this clockwise arrangement of substituents at the C3 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond and the chlorine atom must be attached by a wedge bond. Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has a higher priority. In the case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets the higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IPUAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.31P
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is hexane. The longest continuous carbon chain should have six carbon atoms. One methyl group is attached to C3 carbon atoms of the root.
The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
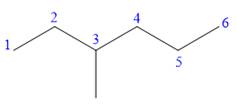
There is one chiral carbon at C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is S.
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the second tiebreaker, the
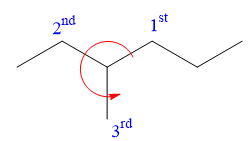
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C3 carbon atom, the third-priority substituent must be attached by a wedge bond. Therefore, the correct structure for
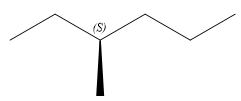
The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(f)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has a higher priority. In the case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets the higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IPUAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.31P
The structure of
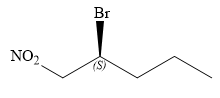
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is pentane. The longest continuous carbon chain has five carbon atoms. A bromine atom and a nitro group are attached to C1 and C2 carbon atoms of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
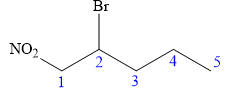
There is only one chiral center at C2 carbon atom in the above molecule.
The required configuration at the chiral center is S.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
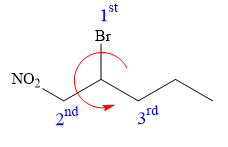
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a wedge bond and the bromine atom must be attached as shown below:

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter C Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY E-BOOK W/SMARTWORK5
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ..... which of these alkenes can be a cis and trans-isomere?arrow_forwardWhat are the following alkenes, E or Z? if neither label as such as with botharrow_forwardProvide structure(s) for the starting material(s), reagent(s) or the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions.arrow_forward
- Complete the following heterocyclic reactions:arrow_forwardCycloheptatrienyl radical (C7H7∙) contains a cyclic, completely conjugated system of π electrons. Is it aromatic? Is it antiaromatic? Explain.arrow_forwardCould someone help me with ranking these with how reactive they would be with an SN2 reaction? Thanks :)arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic product of each reaction. Indicate the stereochemistry at the stereogenic center. Omit byproducts such as salts. If applicable, expand octets to minimize formal charges.arrow_forwardBased on the hydrogenation and the bromination reaction information, how many different alkene structures can you draw that could be Compound X? (If enantiomers are possible, count each pair of enantiomers as one structure.)arrow_forwardName the PRODUCT compound and give it's molecular weight Q. Which is a better nucleophile methoxide or methanol? Suggest a reason why?arrow_forward
- The following SN2 reaction gave J as a major product. Determine the structure of J. Explain your answer.arrow_forwardThe image below shows a permitted cycloaddition reaction.?arrow_forwardUsing the attached molecule and synthesis, please redraw the molecule showing the stereochemistry attained through the synthesis.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


