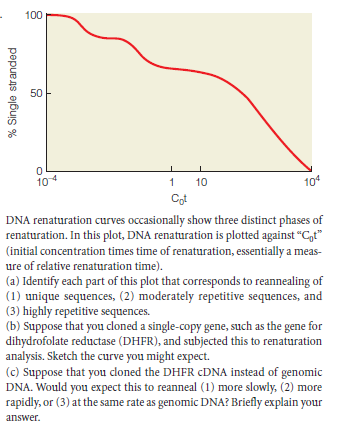
100 50 104 1 10 104 Cot DNA renaturation curves occasionally show three distinct phases of renaturation. In this plot, DNA renaturation is plotted against “C,t" (initial concentration times time of renaturation, essentially a meas- ure of relative renaturation time). (a) Identify each part of this plot that corresponds to reannealing of (1) unique sequences, (2) moderately repetitive sequences, and (3) highly repetitive sequences. (b) Suppose that you cloned a single-copy gene, such as the gene for dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), and subjected this to renaturation analysis. Sketch the curve you might expect. (c) Suppose that you cloned the DHFR CDNA instead of genomic DNA. Would you expect this to reanneal (1) more slowly, (2) more rapidly, or (3) at the same rate as genomic DNA? Briefly explain your answer. % Single stranded
100 50 104 1 10 104 Cot DNA renaturation curves occasionally show three distinct phases of renaturation. In this plot, DNA renaturation is plotted against “C,t" (initial concentration times time of renaturation, essentially a meas- ure of relative renaturation time). (a) Identify each part of this plot that corresponds to reannealing of (1) unique sequences, (2) moderately repetitive sequences, and (3) highly repetitive sequences. (b) Suppose that you cloned a single-copy gene, such as the gene for dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), and subjected this to renaturation analysis. Sketch the curve you might expect. (c) Suppose that you cloned the DHFR CDNA instead of genomic DNA. Would you expect this to reanneal (1) more slowly, (2) more rapidly, or (3) at the same rate as genomic DNA? Briefly explain your answer. % Single stranded
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter28: Dna Metabolism: Replication, Recombination, And Repair
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10P: Homologous Recombination, Heteroduplex DNA, and Mismatch Repair Homologous recombination in E. coli...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:100
50
104
1
10
104
Cot
DNA renaturation curves occasionally show three distinct phases of
renaturation. In this plot, DNA renaturation is plotted against “C,t"
(initial concentration times time of renaturation, essentially a meas-
ure of relative renaturation time).
(a) Identify each part of this plot that corresponds to reannealing of
(1) unique sequences, (2) moderately repetitive sequences, and
(3) highly repetitive sequences.
(b) Suppose that you cloned a single-copy gene, such as the gene for
dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), and subjected this to renaturation
analysis. Sketch the curve you might expect.
(c) Suppose that you cloned the DHFR CDNA instead of genomic
DNA. Would you expect this to reanneal (1) more slowly, (2) more
rapidly, or (3) at the same rate as genomic DNA? Briefly explain your
answer.
% Single stranded
Expert Solution
Step 1
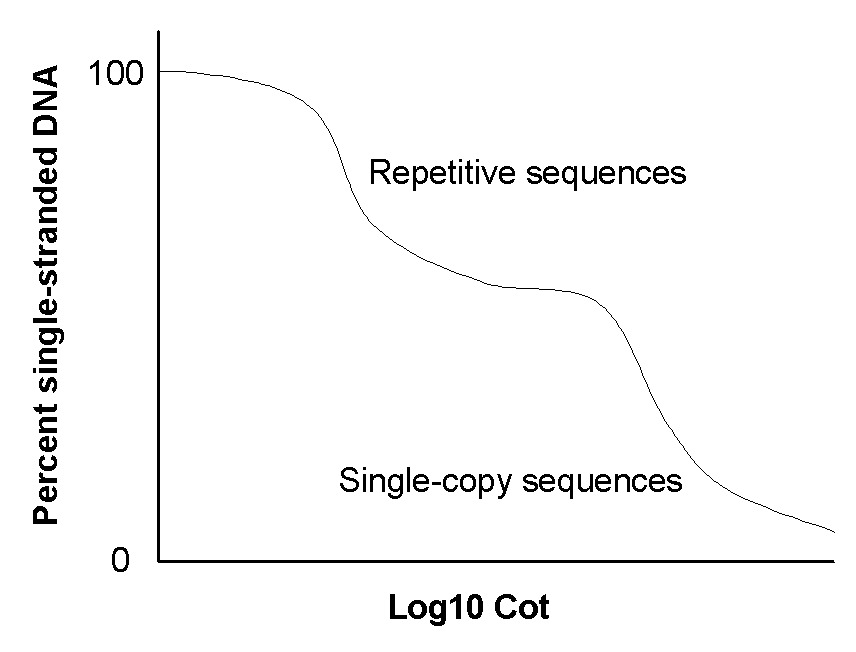
A single stranded DNA binds to its complementary strand to reform double stranded DNA is called renaturation.
Common sequences renature more quickly than rare sequences.
The rate at which a sequence will re-associate is directly proportional to the number of copies of that sequence in the DNA sample.
The amount of renaturation is measured relative to a C0t value. The C0t value is the product of C0 (the initial concentration of DNA), t (time in seconds), and a constant that depends on the concentration of cations in the buffer.
- Repetitive DNA renature at low C0t values, whereas complex and unique DNA sequences renature at high C0t values. The quick renaturation of the repetitive DNA is because of the presence of numerous complementary sequences.
Step 2
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax