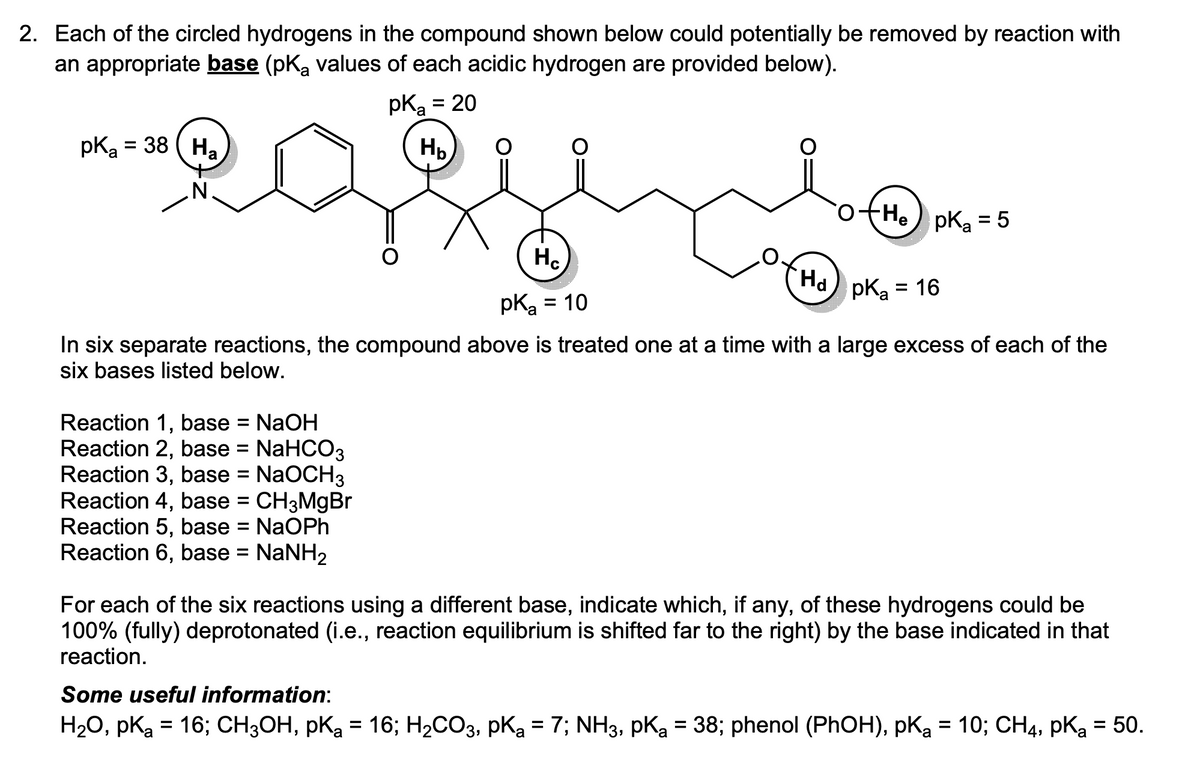
2. Each of the circled hydrogens in the compound shown below could potentially be removed by reaction with an appropriate base (pK₂ values of each acidic hydrogen are provided below). pK₂ = 20 H₂ pKa = 38 (H₂ Hc pka = 10 pka = 16 In six separate reactions, the compound above is treated one at a time with a large excess of each of the six bases listed below. Reaction 1, base = NaOH Reaction 2, base = NaHCO3 Reaction 3, base = NaOCH3 Reaction 4, base = CH3MgBr Reaction 5, base = NaOPh Reaction 6, base = NaNH₂ +He pka = 5 Ha For each of the six reactions using a different base, indicate which, if any, of these hydrogens could be 100% (fully) deprotonated (i.e., reaction equilibrium is shifted far to the right) by the base indicated in that reaction. Some useful information: H₂O, pKa = 16; CH3OH, pKa = 16; H₂CO3, PK₂ = 7; NH3, PK₂ = 38; phenol (PhOH), pK₂ = 10; CH4, pK₂ = 50.
Analyzing Infrared Spectra
The electromagnetic radiation or frequency is classified into radio-waves, micro-waves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays. The infrared spectra emission refers to the portion between the visible and the microwave areas of electromagnetic spectrum. This spectral area is usually divided into three parts, near infrared (14,290 – 4000 cm-1), mid infrared (4000 – 400 cm-1), and far infrared (700 – 200 cm-1), respectively. The number set is the number of the wave (cm-1).
IR Spectrum Of Cyclohexanone
It is the analysis of the structure of cyclohexaone using IR data interpretation.
IR Spectrum Of Anisole
Interpretation of anisole using IR spectrum obtained from IR analysis.
IR Spectroscopy
Infrared (IR) or vibrational spectroscopy is a method used for analyzing the particle's vibratory transformations. This is one of the very popular spectroscopic approaches employed by inorganic as well as organic laboratories because it is helpful in evaluating and distinguishing the frameworks of the molecules. The infra-red spectroscopy process or procedure is carried out using a tool called an infrared spectrometer to obtain an infrared spectral (or spectrophotometer).
q2 - help needed please
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images


