
C++ programming task.
main.cc file:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <
#include "plane.h"
int main() {
std::vector<double> weights{3.2, 4.7, 2.1, 5.5, 9.8, 7.4, 1.6, 9.3};
std::cout << "Printing out all the weights: " << std::endl;
// ======= YOUR CODE HERE ========
// 1. Using an iterator, print out all the elements in
// the weights vector on one line, separated by spaces.
// Hint: see the README for the for loop syntax using
// an iterator, .begin(), and .end()
// ==========================
std::cout << std::endl;
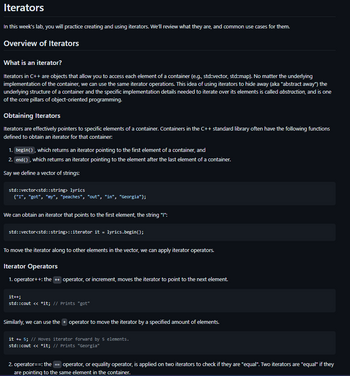
std::map<std::string, std::string> abbrevs{{"AL", "Alabama"},
{"CA", "California"},
{"GA", "Georgia"},
{"TX", "Texas"}};
std::map<std::string, double> populations{
{"CA", 39.2}, {"GA", 10.8}, {"AL", 5.1}, {"TX", 29.5}};
std::cout << "\nPrinting out the state populations: " << std::endl;
// ========= YOUR CODE HERE =========
// 2. Using an iterator, print out each state's population
// on a new line, in the format:
// "Population of Alabama: 5.1 million"
// "Population of California: 39.2 million"
// ... and so on
//
// * abbrevs maps from the state abbreviation to the
// full state name.
// * populations maps from the state abbreviation to
// to the population (in millions)
// Use the abbrevs map to retrieve the full state name
// to print out, while iterating over the populations
// map.
// =======================
std::cout << std::endl;
// 3. Implement the constructors of the Plane class, in
// "plane.h". Refer to the README or the comments in
// "plane.h" for instructions.
// ======= YOUR CODE HERE ========
// 4. Create an empty vector of Plane objects called `fleet`.
// ==========================
// =========== YOUR CODE HERE =======
// 5. Create a Plane `p1` instantiated with the default
// constructor. Add `p1` to the `fleet` vector.
// =========================
// ======= YOUR CODE HERE ====
// 6. Use the constructor overload to create a Plane `p2`
// with 150 seats, 75 passengers, and destination
// "New York City". Add `p2` to the `fleet` vector.
// ==================
// Uncomment these lines of code after completing #3-6.
// Plane p3(220, 220, "Atlanta");
// Plane p4(75, 75, "Guatemala City");
// Plane p5(125, 94, "Medellin");
// ====== YOUR CODE HERE ====
// 7. Add `p3`, `p4`, and `p5` to the `fleet` vector.
// ==========================
// ======= YOUR CODE HERE =======
// 8. Using an iterator, print out all the flights in
// the `fleet` vector, only if the flights are full.
// Hint: see the README for the expected format.
// =========================
plane.cc file
#include "plane.h"
// ============ YOUR CODE HERE ==========
// This implementation file (plane.cc) is where you should implement
// the member functions declared in the header (plane.h), only
// if you didn't implement them inline within plane.h.
//
// Remember to specify the name of the class with :: in this format:
// <return type> MyClassName::MyFunction() {
// ...
// }
// to tell the compiler that each function belongs to the Plane class.
// =============================================
plane.h file
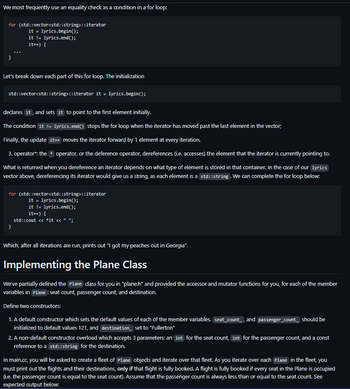
#include <string>
class Plane {
public:
// ========== YOUR CODE HERE ==========
// Define the following constructors using member initializer
// list syntax:
//
// 1. A default constructor, which initializes seat count
// to 121, passenger count to 121, and the flight
// destination to "Fullerton".
// 2. A constructor overload which accepts the seat count,
// passenger count, and flight destination and initializes
// each corresponding member variable appropriately.
// ===========================
int GetPassengerCount() const {
return passenger_count_;
}
void SetPassengerCount(int passengers) {
passenger_count_ = passengers;
}
int GetSeatCount() const {
return seat_count_;
}
void SetSeatCount(int seats) {
seat_count_ = seats;
}
const std::string &GetDestination() const {
return destination_;
}
void SetDestination(const std::string &dest) {
destination_ = dest;
}
private:
int seat_count_;
int passenger_count_;
std::string destination_;
};
Expected Output:
121 passengers flying to Fullerton
220 passengers flying to Atlanta
75 passengers flying to Guatemala City
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

- C++ Program: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; const int AIRPORT_COUNT = 12;string airports[AIRPORT_COUNT] = {"DAL","ABQ","DEN","MSY","HOU","SAT","CRP","MID","OKC","OMA","MDW","LAX"}; int main(){ // define stack (or queue ) here string origin; string dest; string citypair; cout << "Loading the CONTAINER ..." << endl; // LOAD THE STACK ( or queue) HERE // Create all the possible Airport combinations that could exist from the list provided. // i.e DALABQ, DALDEN, ...., ABQDAL, ABQDEN ... // DO NOT Load SameSame - DALDAL, ABQABQ, etc .. cout << "Getting data from the CONTAINER ..." << endl;// Retrieve data from the STACK/QUEUE here } Using the attached program (AirportCombos.cpp), create a list of strings to process and place on a STL STACK container. The provided code is meant to be generic. Using the provided 3 char airport codes, create a 6 character string that is the origin &…arrow_forward#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; class Movie { private: string title = ""; int year = 0; public: void set_title(string title_param); string get_title() const; // "const" safeguards class variable changes within function string get_title_upper() const; void set_year(int year_param); int get_year() const; }; // NOTICE: Class declaration ends with semicolon! void Movie::set_title(string title_param) { title = title_param; } string Movie::get_title() const { return title; } string Movie::get_title_upper() const { string title_upper; for (char c : title) { title_upper.push_back(toupper(c)); } return title_upper; } void Movie::set_year(int year_param) { year = year_param; } int Movie::get_year() const { return year; } int main() { cout << "The Movie List program\n\n"…arrow_forwarduse c++ Programming language Write a program that creates a two dimensional array initialized with test data. Use any data type you wish . The program should have following functions: .getAverage: This function should accept a two dimensional array as its argument and return the average of each row (each student have their average) and each column (class test average) all the values in the array. .getRowTotal: This function should accept a two dimensional array as its first argument and an integer as its second argument. The second argument should be the subscript of a row in the array. The function should return the total of the values in the specified row. .getColumnTotal: This function should accept a two dimensional array as its first argument and an integer as its second argument. The second argument should be the subscript of a column in the array. The function should return the total of the values in the specified column. .getHighestInRow: This function should accept a two…arrow_forward
- #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <string> #include <vector> using namespace std; class Movie { private: string title = ""; int year = 0; public: void set_title(string title_param); string get_title() const; // "const" safeguards class variable changes within function string get_title_upper() const; void set_year(int year_param); int get_year() const; }; // NOTICE: Class declaration ends with semicolon! void Movie::set_title(string title_param) { title = title_param; } string Movie::get_title() const { return title; } string Movie::get_title_upper() const { string title_upper; for (char c : title) { title_upper.push_back(toupper(c)); } return title_upper; } void Movie::set_year(int year_param) { year = year_param; } int Movie::get_year() const { return year; } int main() { cout << "The Movie List program\n\n"…arrow_forwardC++ help with this fixing code .cpp file #include<iostream>#include<string>#include<vector>#include"Food.h"using namespace std; class Nutrition{ private: string name; double Calories double Fat double Sugars double Protein double Sodium Nutrition(string n, double c, double f, double s, double p, double S): name(n), Calories(c), Fat(f),Sugars(s), Protein(p),Sodium(S){} food[Calories]= food[Fat]=food[Sugars]=food[Protein]=food[Sodium]=0; name = "";} Nutrition(string type, double calories, double fat, double sugar,double protein, double sodium){ food[Calories]= calories; food[Fat]=fat; food[Sugars]= sugar; food[Protein]=protein; food[Sodium]=sodium; name= type; } void setName(string type){ name = type; } void setCalories(double calories){ food [Calories]= calories; } void setFat(double fat){ food [Fat]= fat; } void setSugars(double sugar){ food [Sugars]= sugar; } void setProtein(double protein){ food [Protein]= protein; } void…arrow_forward#include <iostream>#include <cstdlib>#include <time.h>#include <chrono> using namespace std::chrono;using namespace std; void randomVector(int vector[], int size){ for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //ToDo: Add Comment vector[i] = rand() % 100; }} int main(){ unsigned long size = 100000000; srand(time(0)); int *v1, *v2, *v3; //ToDo: Add Comment auto start = high_resolution_clock::now(); //ToDo: Add Comment v1 = (int *) malloc(size * sizeof(int *)); v2 = (int *) malloc(size * sizeof(int *)); v3 = (int *) malloc(size * sizeof(int *)); randomVector(v1, size); randomVector(v2, size); //ToDo: Add Comment for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { v3[i] = v1[i] + v2[i]; } auto stop = high_resolution_clock::now(); //ToDo: Add Comment auto duration = duration_cast<microseconds>(stop - start); cout << "Time taken by function: " << duration.count()…arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





