Cytoplasmic segregation In some cases, cells contain mixtures of mutant and normal organelles. These cells are called cytohets, or heteroplasmons. In these mixtures, a type of cytoplasmic segregation can be detected, in which the two types apportion themselves into dif- ferent daughter cells. The process most likely stems from chance partitioning of the multiple organelles in the course of cell divi- sion. Plants provide a good example. Many cases of white leaves are caused by mutations in chloroplast genes that control the production and deposition of the green pigment chlorophyll. Because chlorophyll is necessary for a plant to live, this type of mutation is lethal, and white-leaved plants cannot be obtained for experimental crosses. However, some plants are variegated, bearing both green and white patches, and these plants are via- ble. Thus, variegated plants provide a way of demonstrating cytoplasmic segregation. The four-o'clock plant in Figure 3-21 shows a commonly observed variegated leaf and branch phenotype that demon- strates the inheritance of a mutant allele of a chloroplast gene. Variegated leaves caused by a mutation in cpDNA All-white branch All-green branch FIGURE 3-21 Leaf variegation in Mirabilis jalapa, the four-o'clock plant. Flowers can form on any branch (variegated, green, or white), and these flowers can be used in crosses. Main shoot is variegated
Cytoplasmic segregation In some cases, cells contain mixtures of mutant and normal organelles. These cells are called cytohets, or heteroplasmons. In these mixtures, a type of cytoplasmic segregation can be detected, in which the two types apportion themselves into dif- ferent daughter cells. The process most likely stems from chance partitioning of the multiple organelles in the course of cell divi- sion. Plants provide a good example. Many cases of white leaves are caused by mutations in chloroplast genes that control the production and deposition of the green pigment chlorophyll. Because chlorophyll is necessary for a plant to live, this type of mutation is lethal, and white-leaved plants cannot be obtained for experimental crosses. However, some plants are variegated, bearing both green and white patches, and these plants are via- ble. Thus, variegated plants provide a way of demonstrating cytoplasmic segregation. The four-o'clock plant in Figure 3-21 shows a commonly observed variegated leaf and branch phenotype that demon- strates the inheritance of a mutant allele of a chloroplast gene. Variegated leaves caused by a mutation in cpDNA All-white branch All-green branch FIGURE 3-21 Leaf variegation in Mirabilis jalapa, the four-o'clock plant. Flowers can form on any branch (variegated, green, or white), and these flowers can be used in crosses. Main shoot is variegated
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Chapter31: Completing The Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing, And Degradation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
In Figure 3-21, what would be the leaf types of progeny
of the apical (top) flower?
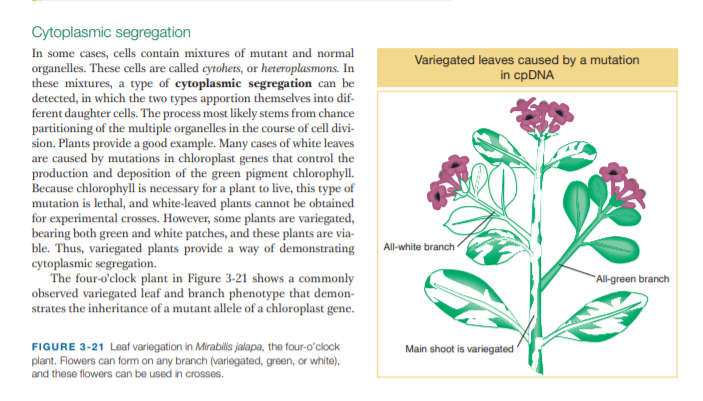
Transcribed Image Text:Cytoplasmic segregation
In some cases, cells contain mixtures of mutant and normal
organelles. These cells are called cytohets, or heteroplasmons. In
these mixtures, a type of cytoplasmic segregation can be
detected, in which the two types apportion themselves into dif-
ferent daughter cells. The process most likely stems from chance
partitioning of the multiple organelles in the course of cell divi-
sion. Plants provide a good example. Many cases of white leaves
are caused by mutations in chloroplast genes that control the
production and deposition of the green pigment chlorophyll.
Because chlorophyll is necessary for a plant to live, this type of
mutation is lethal, and white-leaved plants cannot be obtained
for experimental crosses. However, some plants are variegated,
bearing both green and white patches, and these plants are via-
ble. Thus, variegated plants provide a way of demonstrating
cytoplasmic segregation.
The four-o'clock plant in Figure 3-21 shows a commonly
observed variegated leaf and branch phenotype that demon-
strates the inheritance of a mutant allele of a chloroplast gene.
Variegated leaves caused by a mutation
in cpDNA
All-white branch
All-green branch
FIGURE 3-21 Leaf variegation in Mirabilis jalapa, the four-o'clock
plant. Flowers can form on any branch (variegated, green, or white),
and these flowers can be used in crosses.
Main shoot is variegated
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College